Convert a Row to a Column Header in a Pandas DataFrame
Last updated: Apr 11, 2024
Reading time·6 min

# Convert a Row to a Column Header in a Pandas DataFrame
Set the column property to the result of accessing the iloc indexer at the
given index to convert a row to a column header in a Pandas DataFrame.
The iloc indexer is used for integer, location-based indexing for selection
by position.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'experience': [10, 13, 15], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], }) print(df) df.columns = df.iloc[1] print('-' * 50) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name experience salary 0 Alice 10 175.1 1 Bobby 13 180.2 2 Carl 15 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- 1 Bobby 13 180.2 0 Alice 10 175.1 1 Bobby 13 180.2 2 Carl 15 190.3
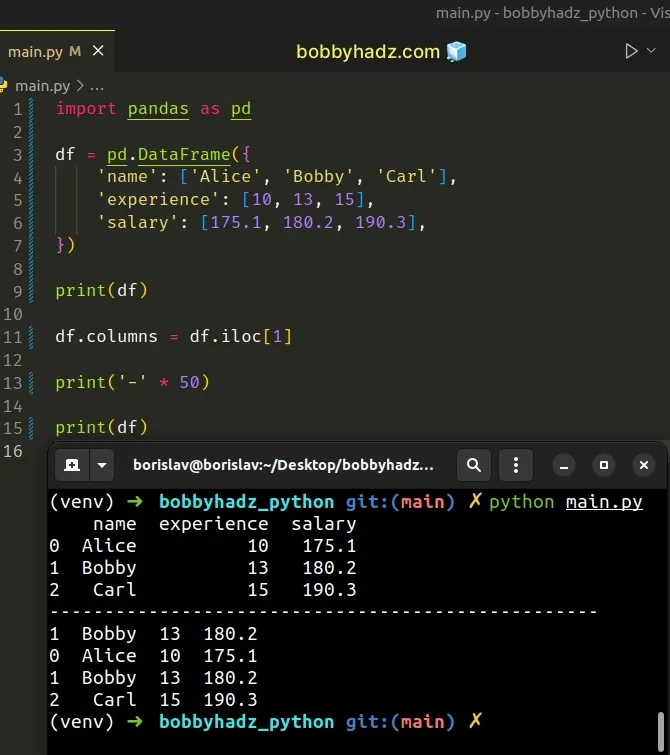
Notice that there is a duplicate row.
You can use the df.drop() method to drop the duplicate.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'experience': [10, 13, 15], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], }) print(df) df.columns = df.iloc[1] print('-' * 50) print(df) df = df.drop(df.index[1]) print('-' * 50) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name experience salary 0 Alice 10 175.1 1 Bobby 13 180.2 2 Carl 15 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- 1 Bobby 13 180.2 0 Alice 10 175.1 1 Bobby 13 180.2 2 Carl 15 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- 1 Bobby 13 180.2 0 Alice 10 175.1 2 Carl 15 190.3
You can also reset the index by using the DataFrame.reset_index() method.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'experience': [10, 13, 15], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], }) print(df) df.columns = df.iloc[1] print('-' * 50) print(df) df = df.drop(df.index[1]) print('-' * 50) print(df) df = df.reset_index(drop=True) print('-' * 50) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name experience salary 0 Alice 10 175.1 1 Bobby 13 180.2 2 Carl 15 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- 1 Bobby 13 180.2 0 Alice 10 175.1 1 Bobby 13 180.2 2 Carl 15 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- 1 Bobby 13 180.2 0 Alice 10 175.1 2 Carl 15 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- 1 Bobby 13 180.2 0 Alice 10 175.1 1 Carl 15 190.3
The df.drop(df.index[1]) method call removes all rows that have the same label
as the second row (index 1).
If the index is not unique, use a RangeIndex object.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'experience': [10, 13, 15], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], }) print(df) df.columns = df.iloc[1] print('-' * 50) print(df) df = df.iloc[pd.RangeIndex(len(df)).drop(1)] print('-' * 50) print(df)
We called the drop() method on the RangeIndex object to delete the row at
index 1.
The DataFrame.iloc indexer returns the row at the given index.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'experience': [10, 13, 15], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], }) print(df.iloc[1]) print('-' * 50) print(df.iloc[2])
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name Bobby experience 13 salary 180.2 Name: 1, dtype: object -------------------------------------------------- name Carl experience 15 salary 190.3 Name: 2, dtype: object
Note that the .iloc indexer raises an IndexError if the supplied index is
out of bounds.
# Using the DataFrame.rename() method to convert a row to a column header
You can also use the DataFrame.rename method to convert a row to a column header in Pandas.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'experience': [10, 13, 15], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], }) print(df) df = df.rename(columns=df.iloc[1]) print('-' * 50) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name experience salary 0 Alice 10 175.1 1 Bobby 13 180.2 2 Carl 15 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- Bobby 13 180.2 0 Alice 10 175.1 1 Bobby 13 180.2 2 Carl 15 190.3
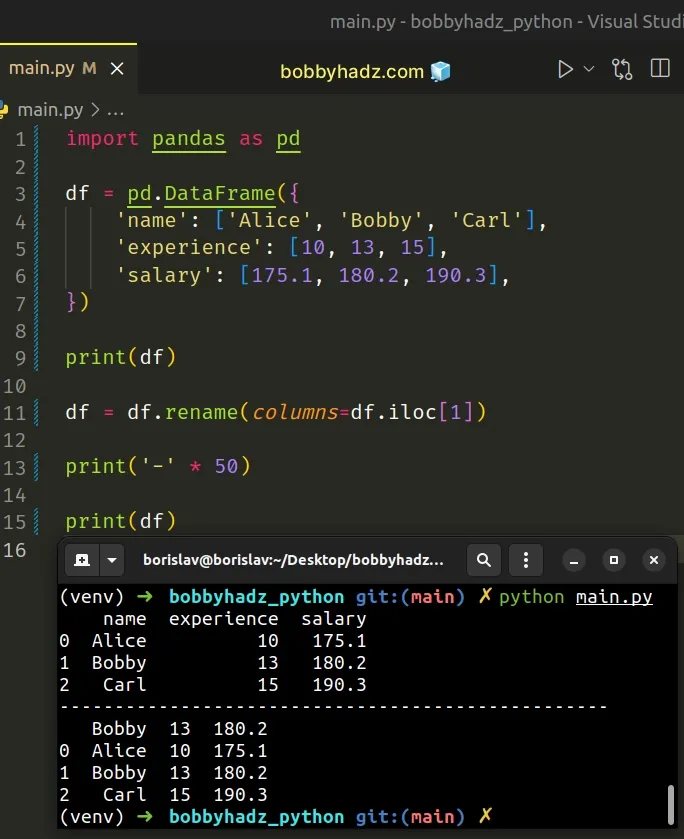
If you want to delete the duplicate row, use the drop() method.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'experience': [10, 13, 15], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], }) print(df) df = df.rename(columns=df.iloc[1]) print('-' * 50) print(df) df = df.drop(df.index[1]) print('-' * 50) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name experience salary 0 Alice 10 175.1 1 Bobby 13 180.2 2 Carl 15 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- Bobby 13 180.2 0 Alice 10 175.1 1 Bobby 13 180.2 2 Carl 15 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- Bobby 13 180.2 0 Alice 10 175.1 2 Carl 15 190.3
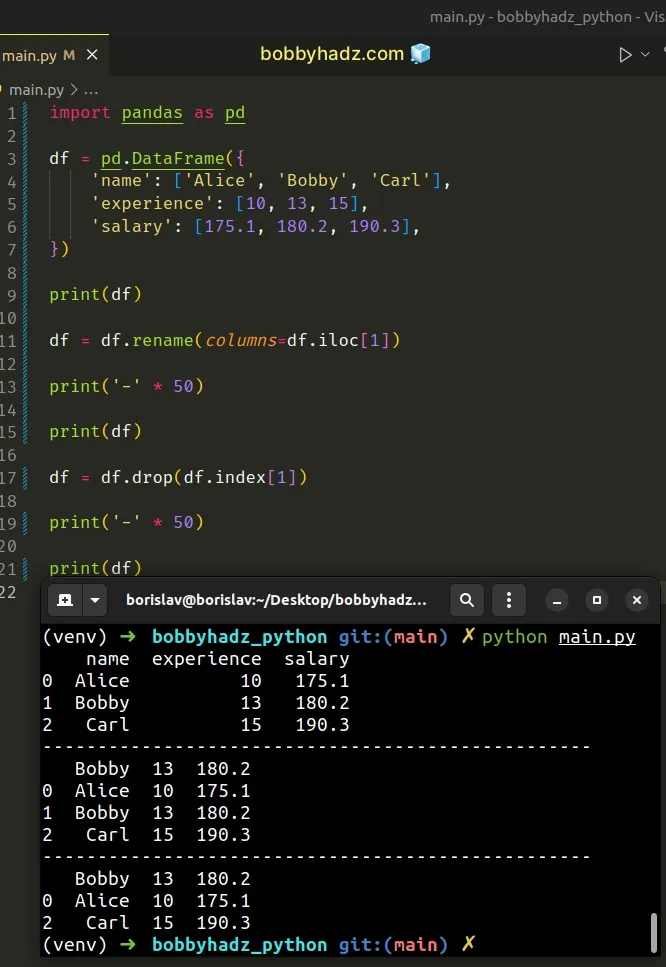
You can also restart the index after removing the duplicate row.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'experience': [10, 13, 15], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], }) print(df) df = df.rename(columns=df.iloc[1]) print('-' * 50) print(df) df = df.drop(df.index[1]) print('-' * 50) print(df) df = df.reset_index(drop=True) print('-' * 50) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name experience salary 0 Alice 10 175.1 1 Bobby 13 180.2 2 Carl 15 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- Bobby 13 180.2 0 Alice 10 175.1 1 Bobby 13 180.2 2 Carl 15 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- Bobby 13 180.2 0 Alice 10 175.1 2 Carl 15 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- Bobby 13 180.2 0 Alice 10 175.1 1 Carl 15 190.3
Notice that the index starts at 0 after calling
DataFrame.reset_index().
If you want to convert a given row to a column header without reassigning the
DataFrame, set the inplace argument to True.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'experience': [10, 13, 15], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], }) print(df) df.rename(columns=df.iloc[1], inplace=True) print('-' * 50) print(df) df.drop(df.index[1], inplace=True) print('-' * 50) print(df) df.reset_index(drop=True, inplace=True) print('-' * 50) print(df)
Running the code sample above produces the following output.
name experience salary 0 Alice 10 175.1 1 Bobby 13 180.2 2 Carl 15 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- Bobby 13 180.2 0 Alice 10 175.1 1 Bobby 13 180.2 2 Carl 15 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- Bobby 13 180.2 0 Alice 10 175.1 2 Carl 15 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- Bobby 13 180.2 0 Alice 10 175.1 1 Carl 15 190.3
# Convert a row to a column header by creating a new DataFrame
You can also convert a row to a column header by creating a new DataFrame.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'experience': [10, 13, 15], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], }) print(df) headers = df.iloc[0] new_df = pd.DataFrame(df.values[1:], columns=headers) print('-' * 50) print(new_df) df.reset_index(drop=True, inplace=True) print('-' * 50) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name experience salary 0 Alice 10 175.1 1 Bobby 13 180.2 2 Carl 15 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- 0 Alice 10 175.1 0 Bobby 13 180.2 1 Carl 15 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- name experience salary 0 Alice 10 175.1 1 Bobby 13 180.2 2 Carl 15 190.3
We created a new DataFrame and set the columns to the first row (index 0) by
supplying the columns
keyword argument.
You can optionally use the reset_index method to reset the index of the
DataFrame and use the default index instead.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- AttributeError module 'pandas' has no attribute 'DataFrame'
- ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'pandas' in Python
- FutureWarning: pandas.Int64Index is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version
- You are trying to merge on int64 and object columns [Fixed]
- Copy a column from one DataFrame to another in Pandas
- ValueError: cannot reindex on an axis with duplicate labels
- ValueError: Length mismatch: Expected axis has X elements, new values have Y elements
- ValueError: cannot reshape array of size X into shape Y
- Object arrays cannot be loaded when allow_pickle=False
- ValueError: Columns must be same length as key [Solved]
- ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called [Fix]
- Convert a Row to a Column Header in a Pandas DataFrame
- Drop Unnamed: 0 columns from a Pandas DataFrame in Python
- IndexError: single positional indexer is out-of-bounds [Fix]
- IndexError: single positional indexer is out-of-bounds [Fix]
- Arrays used as indices must be of integer (or boolean) type
- Boolean index did not match indexed array along dimension 0
- AttributeError: Can only use .dt accessor with datetimelike values
- Count number of non-NaN values in each column of DataFrame
- Add a column with incremental Numbers to a Pandas DataFrame
- Replace whole String if it contains Substring in Pandas
- Usecols do not match columns, columns expected but not found
- Pandas: Create new row for each element in List in DataFrame
- ValueError: Length of values does not match length of index
- How to add a Level to Pandas MultiIndex in Python
- Select all Columns starting with a given String in Pandas
- Pandas: Cannot setitem on a Categorical with a new category
- Pandas: Get a List of Categories or Categorical Columns
- Pandas ValueError: ('Lengths must match to compare')
- Pandas: Drop columns if Name contains a given String
- Pandas: Convert GroupBy results to Dictionary of Lists
- Cannot perform 'rand_' with a dtyped [int64] array and scalar of type [bool]
- How to remove Time from DateTime in Pandas [5 Ways]
- Pandas: Check if a Date is during the Weekend or Weekday
- Pandas: Find the percentage of Missing values in each Column
- Create Date column from Year, Month and Day in Pandas
- ValueError: Grouper for 'X' not 1-dimensional [Solved]
- Cannot subset columns with tuple with more than one element
- Pandas: Select first N or last N columns of DataFrame
- Pandas: Select Rows between two values in DataFrame
- Pandas: How to Filter a DataFrame by value counts
- Pandas: GroupBy columns with NaN (missing) values
- Pandas: Split a Column of Lists into Multiple Columns
- ValueError: Expected object or value with
pd.read_json()

