ValueError: Expected object or value with `pd.read_json()`
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- ValueError: Expected object or value with
pd.read_json() - Make sure your JSON is properly formatted to solve the error
- All JSON string keys and values must be double-quoted
- Make sure you don't have any trailing commas in your JSON
- Make sure to declare a JSON array of objects correctly
- You might have to set the orient argument
- Try setting the lines argument to True
- Try setting the encoding to utf-8-sig when calling read_json
# ValueError: Expected object or value with pd.read_json()
The Pandas "ValueError: Expected object or value" occurs when you pass
malformed JSON to the pandas.read_json() method or other JSON parsing
methods.
To solve the error, make sure your JSON is correctly formatted.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
Suppose we have the following data.json file.
{ 'name': ["Alice", "Bobby", "Carl"], "experience": [10, 13, 15], "salary": [175.1, 180.2, 190.3] }
Notice that the file is incorrectly formatted because the name key is
single-quoted.
All JSON string keys and values must be double-quoted.
If I now try to read the JSON file with pandas.read_json, I would get an error.
import pandas as pd data = pd.read_json('data.json') # ⛔️ ValueError: Expected object or value print(data)
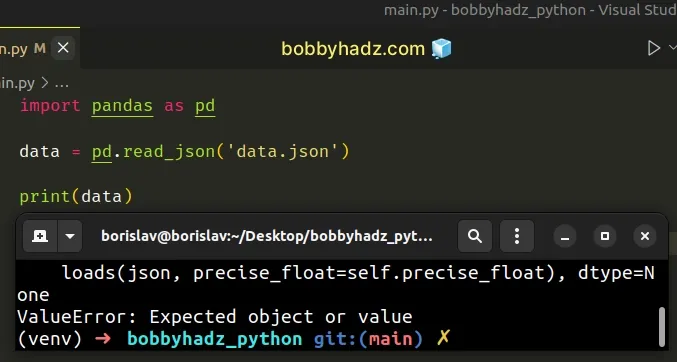
The error occurred because the JSON in the data.json file was not properly
formatted.
In order to solve the error in the example, I have to make sure all keys in the
data.json file are double-quoted.
This would make the contents of the file valid JSON.
{ "name": ["Alice", "Bobby", "Carl"], "experience": [10, 13, 15], "salary": [175.1, 180.2, 190.3] }
I am now able to call the pd.read_json() method without any issues.
import pandas as pd data = pd.read_json('data.json') # name experience salary # 0 Alice 10 175.1 # 1 Bobby 13 180.2 # 2 Carl 15 190.3 print(data)
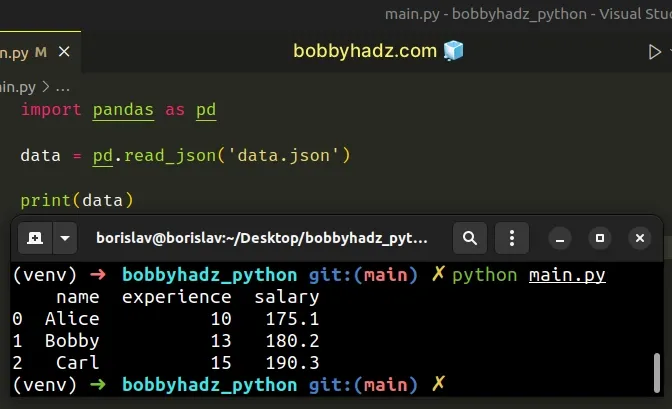
Now that the data.json file stores valid JSON, everything works as expected.
# Make sure your JSON is properly formatted to solve the error
To solve the error, make sure your JSON is properly formatted.
Make sure the file path you passed to pandas.read_json() points to a properly
formatted .json file (and that the file exists).
# All JSON string keys and values must be double-quoted
All JSON string keys and values have to be double-quoted.
For example, the following data.json file does NOT store valid JSON.
// ⛔️ Not valid JSON, `name` key is single-quoted { 'name': ["Alice", "Bobby", "Carl"], "experience": [10, 13, 15], "salary": [175.1, 180.2, 190.3] }
On the other hand, the following file stores valid JSON because all keys and string values are double-quoted.
// ✅ Valid JSON, all keys and string values double-quoted { "name": ["Alice", "Bobby", "Carl"], "experience": [10, 13, 15], "salary": [175.1, 180.2, 190.3] }
# Make sure you don't have any trailing commas in your JSON
Make sure you don't have any trailing commas.
Another common cause of the error is having a trailing comma, which is not allowed in JSON files.
Here is an example.
// ⛔️ Invalid JSON, has trailing comma after `salary` value { "name": ["Alice", "Bobby", "Carl"], "experience": [10, 13, 15], "salary": [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], }
Notice that there is a trailing comma after the salary value.
Remove the trailing comma to make the JSON valid.
// ✅ Valid JSON, has no trailing commas { "name": ["Alice", "Bobby", "Carl"], "experience": [10, 13, 15], "salary": [175.1, 180.2, 190.3] }
# Make sure to declare a JSON array of objects correctly
Don't forget to wrap multiple objects in square brackets.
Another common cause of the error is forgetting to wrap multiple JSON objects in
square [] brackets to make them a list of objects.
Here is an example.
// ⛔️ Invalid JSON, forgot to wrap in [] {"name": "Alice", "salary": 100}, {"name": "Bobby", "salary": 50}, {"name": "Carl", "salary": 75}
To make the JSON valid, wrap the objects in square brackets, to make them a list of objects.
// ✅ Valid JSON - a list of objects [ {"name": "Alice", "salary": 100}, {"name": "Bobby", "salary": 50}, {"name": "Carl", "salary": 75} ]
If I now call the pd.read_json() method with the file, everything works as
expected.
import pandas as pd data = pd.read_json('data.json') # name salary # 0 Alice 100 # 1 Bobby 50 # 2 Carl 75 print(data)
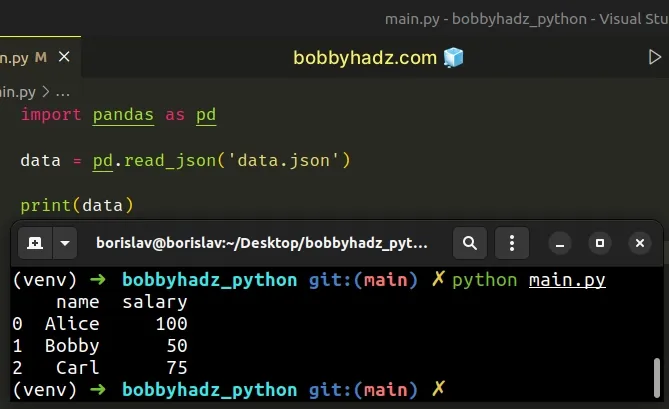
# You might have to set the orient argument
Depending on how your JSON file is structured, you might have to set the
orient argument when calling pd.read_json().
Suppose we have the following data.json file.
{ "columns":["COL1", "COL2"], "index":["row 1", "row 2"], "data":[["a","b"], ["c","d"]] }
You would have to set the orient argument to split to read the JSON file
correctly into a Pandas object.
import pandas as pd data = pd.read_json('data.json', orient='split') # COL1 COL2 # row 1 a b # row 2 c d print(data)
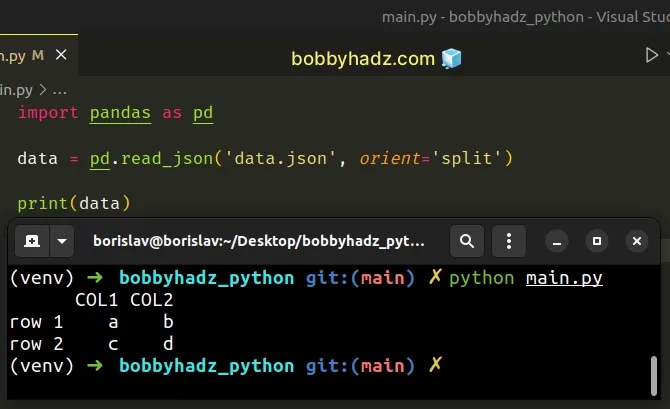
As shown in
this section
of the docs, the orient argument indicates the expected JSON string format.
When set to split, the expected data format is
{index -> [index], columns -> [columns], data -> [values]}.
And if your data.json file is structured as follows.
[ {"COL1":"a","COL2":"b"}, {"COL1":"c","COL2":"d"} ]
Try setting the orient argument to "records".
import pandas as pd data = pd.read_json('data.json', orient='records') # COL1 COL2 # 0 a b # 1 c d print(data)
You can view all available values of the orient argument in
this section of the docs.
# Try setting the lines argument to True
Depending on how your JSON data is structured, you might have to set the lines
argument to True when calling pd.read_json().
Suppose you have the following data.json file.
{"name": "Alice", "salary": 100, "experience": 5}
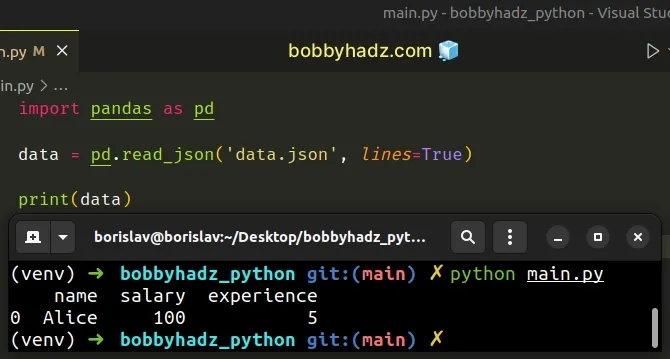
Try setting the lines argument to True.
import pandas as pd data = pd.read_json('data.json', lines=True) # name salary experience # 0 Alice 100 5 print(data)
When the lines argument is set to True, the file is read as a JSON object
per line.
The argument defaults to False.
# Try setting the encoding to utf-8-sig when calling read_json
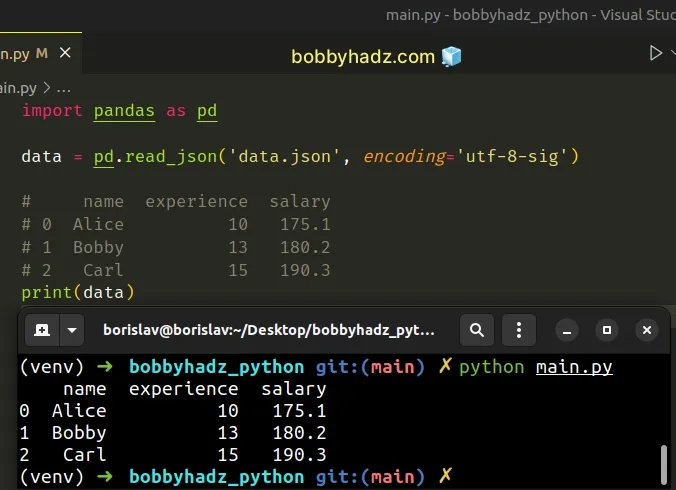
If none of the suggestions helped, try to set the encoding argument to
utf-8-sig in the call to pd.read_json.
Suppose we have the following data.json file.
{ "name": ["Alice", "Bobby", "Carl"], "experience": [10, 13, 15], "salary": [175.1, 180.2, 190.3] }
Here is the related Python script.
import pandas as pd data = pd.read_json('data.json', encoding='utf-8-sig') # name experience salary # 0 Alice 10 175.1 # 1 Bobby 13 180.2 # 2 Carl 15 190.3 print(data)
By default, the encoding argument is set to utf-8.
The default encoding is not suitable if the JSON file was encoding using
UTF-8-BOM.
Setting the encoding to utf-8-sig often helps.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

