Select all Columns starting with a given String in Pandas
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- Select all Columns starting with a given String in Pandas
- Select all Columns starting with a given String by creating a Series
- Select all Columns starting with a given String using DataFrame.loc
- Select all Columns starting with a given String using DataFrame.filter()
# Select all Columns starting with a given String in Pandas
To select all columns starting with a given string in a Pandas DataFrame:
- Use a list comprehension to iterate over the
DataFrame. - Use the
str.startswith()method to check if each column name starts with the given string. - Optionally use bracket notation to select the matching columns.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'Employee_ID': [1, 2, 3, 4], 'Employee_Name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'Age': [29, 30, 31, 32], 'Employee_Salary': [1500, 1000, 2000, 3000], }) column_names = [column for column in df if column.startswith('Employee')] # 👇️ ['Employee_ID', 'Employee_Name', 'Employee_Salary'] print(column_names) print('-' * 50) # Employee_ID Employee_Name Employee_Salary # 0 1 Alice 1500 # 1 2 Bobby 1000 # 2 3 Carl 2000 # 3 4 Dan 3000 print(df[column_names])
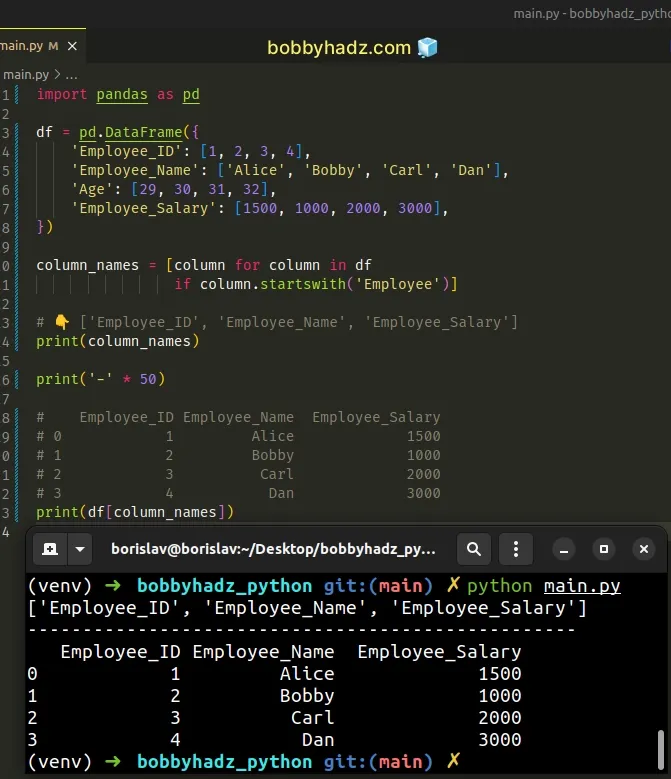
We used a
list comprehension to
iterate over the DataFrame.
On each iteration, we use the str.startswith method to check if the current column name starts with a given string and return the result.
You can then use bracket notation if you only want to select the matching
columns from the DataFrame.
Note that the str.startswith() method is case-sensitive.
If you need to select all columns starting with a given string in a case-insensitive manner, convert the column name and the substring to lowercase.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'Employee_ID': [1, 2, 3, 4], 'Employee_Name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'Age': [29, 30, 31, 32], 'Employee_Salary': [1500, 1000, 2000, 3000], }) column_names = [column for column in df if column.lower().startswith('EMPLOYEE'.lower())] # 👇️ ['Employee_ID', 'Employee_Name', 'Employee_Salary'] print(column_names) print('-' * 50) # Employee_ID Employee_Name Employee_Salary # 0 1 Alice 1500 # 1 2 Bobby 1000 # 2 3 Carl 2000 # 3 4 Dan 3000 print(df[column_names])
By converting each column name and the substring we are checking for to lowercase, we are able to perform a case-insensitive string comparison.
# Select all Columns starting with a given String by creating a Series
You can also create a Series and use str.startswith to select all columns
that start with a given string.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'Employee_ID': [1, 2, 3, 4], 'Employee_Name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'Age': [29, 30, 31, 32], 'Employee_Salary': [1500, 1000, 2000, 3000], }) column_names = df.columns[ pd.Series(df.columns).str.startswith('Employee') ] # 👇️ Index(['Employee_ID', 'Employee_Name', 'Employee_Salary'], dtype='object') print(column_names) print('-' * 50) # Employee_ID Employee_Name Employee_Salary # 0 1 Alice 1500 # 1 2 Bobby 1000 # 2 3 Carl 2000 # 3 4 Dan 3000 print(df[column_names])
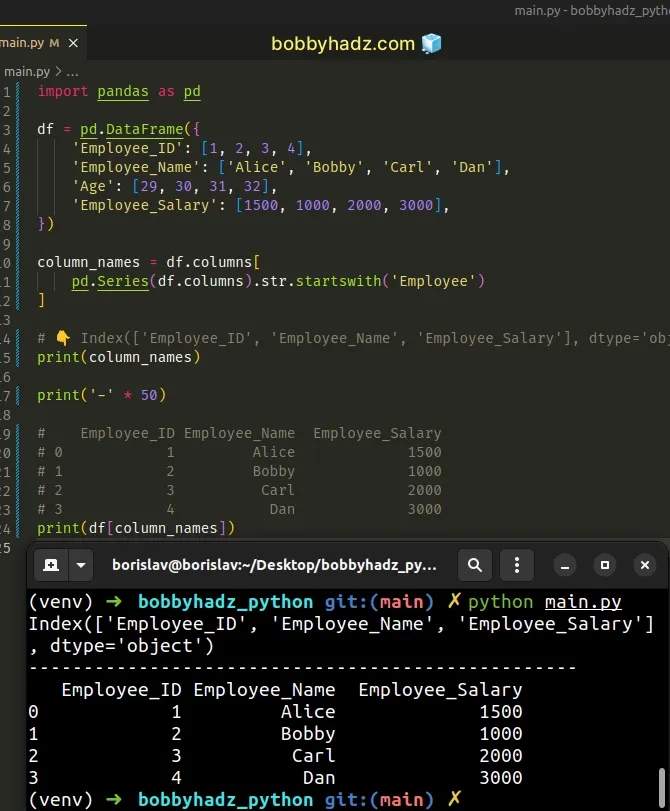
We used the
pandas.Series()
method to create a Series from the columns of the DataFrame.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'Employee_ID': [1, 2, 3, 4], 'Employee_Name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'Age': [29, 30, 31, 32], 'Employee_Salary': [1500, 1000, 2000, 3000], }) # 0 Employee_ID # 1 Employee_Name # 2 Age # 3 Employee_Salary # dtype: object print(pd.Series(df.columns))
We are then able to use the Series.str.startswith() method to check if the start of each string element matches a pattern.
You can use bracket notation to select the matching columns from the
DataFrame.
# Employee_ID Employee_Name Employee_Salary # 0 1 Alice 1500 # 1 2 Bobby 1000 # 2 3 Carl 2000 # 3 4 Dan 3000 print(df[column_names])
# Select all Columns starting with a given String using DataFrame.loc
You can also use the DataFrame.loc indexer to select all columns starting with a given string.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'Employee_ID': [1, 2, 3, 4], 'Employee_Name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'Age': [29, 30, 31, 32], 'Employee_Salary': [1500, 1000, 2000, 3000], }) df2 = df.loc[:, df.columns.str.startswith('Employee')] # Employee_ID Employee_Name Employee_Salary # 0 1 Alice 1500 # 1 2 Bobby 1000 # 2 3 Carl 2000 # 3 4 Dan 3000 print(df2)
The DataFrame.loc indexer is primarily label-based but can also be used with a
boolean array.
We used the DataFrame.columns.str.startswith() method to get a boolean array
with True values for the matching column names.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'Employee_ID': [1, 2, 3, 4], 'Employee_Name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'Age': [29, 30, 31, 32], 'Employee_Salary': [1500, 1000, 2000, 3000], }) # 👇️ [ True True False True] print(df.columns.str.startswith('Employee'))
The df2 variable only stores the matching columns.
df2 = df.loc[:, df.columns.str.startswith('Employee')] # Employee_ID Employee_Name Employee_Salary # 0 1 Alice 1500 # 1 2 Bobby 1000 # 2 3 Carl 2000 # 3 4 Dan 3000 print(df2)
# Select all Columns starting with a given String using DataFrame.filter()
You can also use the DataFrame.filter() method to select all columns starting with a given string.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'Employee_ID': [1, 2, 3, 4], 'Employee_Name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'Age': [29, 30, 31, 32], 'Employee_Salary': [1500, 1000, 2000, 3000], }) # Employee_ID Employee_Name Employee_Salary # 0 1 Alice 1500 # 1 2 Bobby 1000 # 2 3 Carl 2000 # 3 4 Dan 3000 print(df.filter(regex=r'^Employee'))
The DataFrame.filter() method returns a subset of the DataFrame rows or
columns according to the specified index labels.
The regex argument can be set to a regular expression to only keep the labels
from the specified axis for which re.search(regex, label) == True.
The caret ^ matches the beginning of the input, so the regex matches column
names starting with "Employee".
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Usecols do not match columns, columns expected but not found
- Pandas: Create new row for each element in List in DataFrame
- ValueError: Cannot merge a Series without a name [Solved]
- Index(...) must be called with a collection of some kind
- ValueError: Shape of passed values is X, indices imply Y
- Reindexing only valid with uniquely valued Index objects
- How to add a Level to Pandas MultiIndex in Python
- Converting a Nested Dictionary to a Pandas DataFrame
- Replace negative Numbers in a Pandas DataFrame with Zero
- Pandas ValueError: cannot insert X, already exists [Solved]
- How to swap two DataFrame columns in Pandas
- Reading specific columns from an Excel File in Pandas
- Pandas: Cannot setitem on a Categorical with a new category
- Only valid with DatetimeIndex, TimedeltaIndex or PeriodIndex, but got an instance of X
- Pandas ValueError: ('Lengths must match to compare')
- Pandas SpecificationError: nested renamer is not supported
- Cannot perform 'rand_' with a dtyped [int64] array and scalar of type [bool]
- Pandas: Select the Rows where two Columns are Equal
- Pandas: Find first and last non-NaN values in a DataFrame
- How to shuffle two NumPy Arrays together (in Unison)

