Pandas: Split a Column of Lists into Multiple Columns
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- Pandas: Split a Column of Lists into Multiple Columns
- Pandas: Split a Column of Lists into Multiple Columns using apply()
- Pandas: Split a Column of Lists with different lengths into Multiple Columns
# Pandas: Split a Column of Lists into Multiple Columns
To split a column of lists (or tuples) into multiple columns in Pandas:
- Use the
DataFrame.tolist()to convert the column values to a list. - Use the
pandas.DataFrame()constructor to create a newDataFrame. - Set the
indexargument to the index of the existingDataFrame.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'B': [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]], }) print(df) print('-' * 50) df[['B1', 'B2']] = pd.DataFrame( df['B'].tolist(), index=df.index ) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
A B 0 Alice [1, 2] 1 Bobby [3, 4] 2 Carl [5, 6] -------------------------------------------------- A B B1 B2 0 Alice [1, 2] 1 2 1 Bobby [3, 4] 3 4 2 Carl [5, 6] 5 6
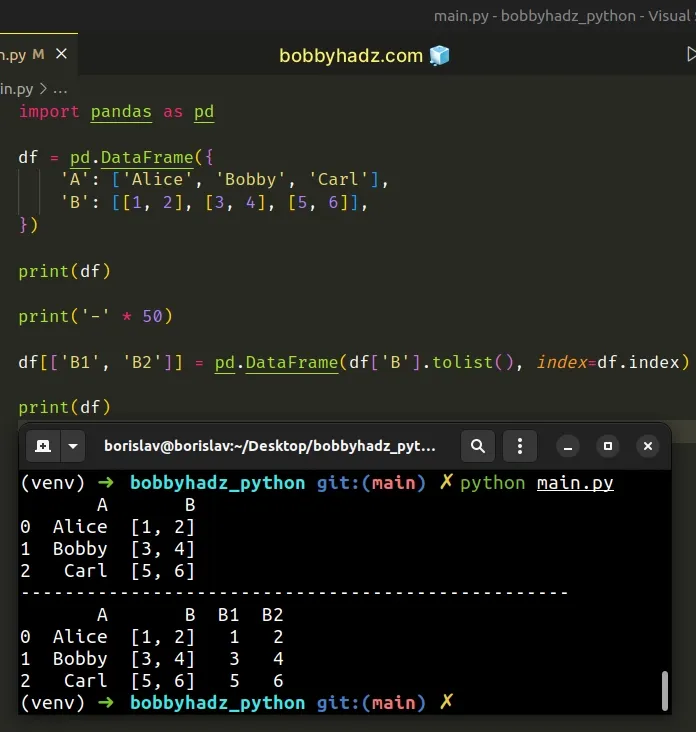
The code sample splits the B column into B1 and B2 columns.
You could use the same approach to split the B column into 3 columns if the
lists contained 3 values.
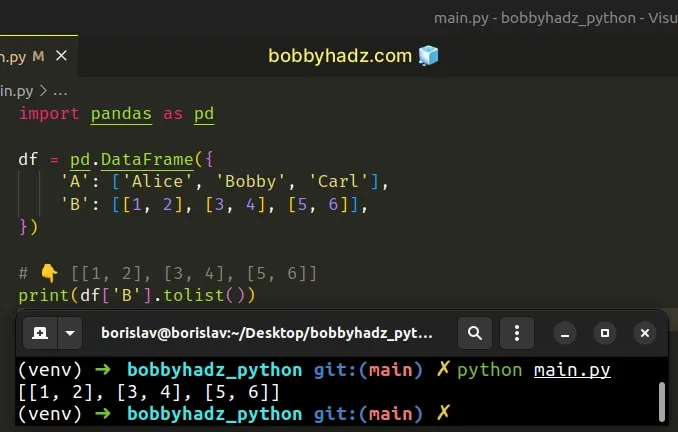
We used the
tolist()
method to convert the Series to a list of lists.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'B': [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]], }) # 👇️ [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]] print(df['B'].tolist())
# A B B1 B2 # 0 Alice [1, 2] 1 2 # 1 Bobby [3, 4] 3 4 # 2 Carl [5, 6] 5 6 df[['B1', 'B2']] = pd.DataFrame( df['B'].tolist(), index=df.index )
We passed the list of lists and the DataFrame index to the
pandas.DataFrame
constructor to create a new DataFrame that contains the split columns.
The row values for the new B1 and B2 columns come from each sublist.
If you want to store the results of splitting the column into a new DataFrame,
declare a new variable.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'B': [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]], }) new_df = pd.DataFrame(df['B'].to_list(), columns=['B1', 'B2']) # B1 B2 # 0 1 2 # 1 3 4 # 2 5 6 print(new_df)
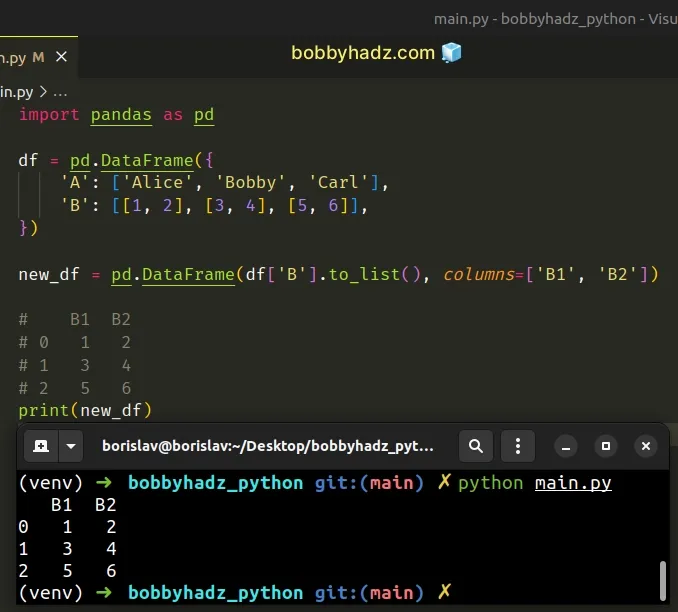
The new_df variable stores only the results of splitting the B column into
B1 and B2.
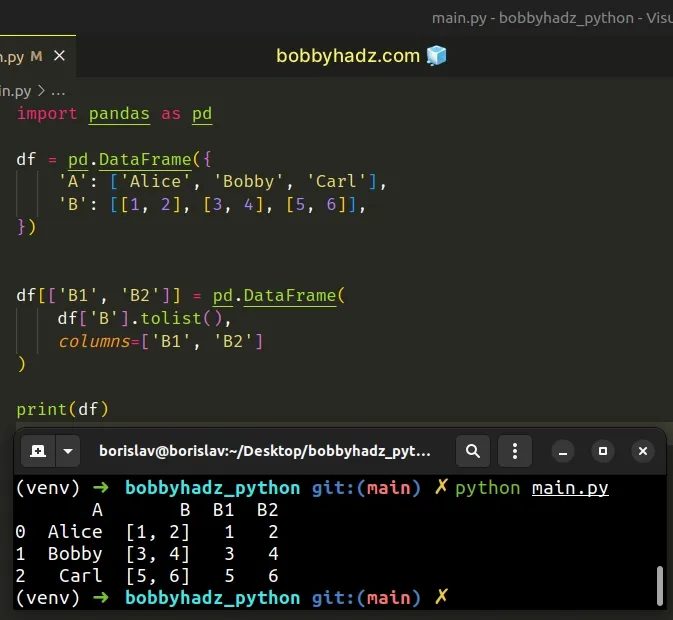
The same approach can be used to add the split columns to the existing
DataFrame.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'B': [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]], }) df[['B1', 'B2']] = pd.DataFrame( df['B'].tolist(), columns=['B1', 'B2'] ) # A B B1 B2 # 0 Alice [1, 2] 1 2 # 1 Bobby [3, 4] 3 4 # 2 Carl [5, 6] 5 6 print(df)
# Pandas: Split a Column of Lists into Multiple Columns using apply()
You can also use the DataFrame.apply() method to split a column of lists (or tuples) into multiple columns.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'B': [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]], }) print(df) print('-' * 50) df[['B1', 'B2']] = pd.DataFrame( df['B'].apply(pd.Series), index=df.index ) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
A B 0 Alice [1, 2] 1 Bobby [3, 4] 2 Carl [5, 6] -------------------------------------------------- A B B1 B2 0 Alice [1, 2] 1 2 1 Bobby [3, 4] 3 4 2 Carl [5, 6] 5 6
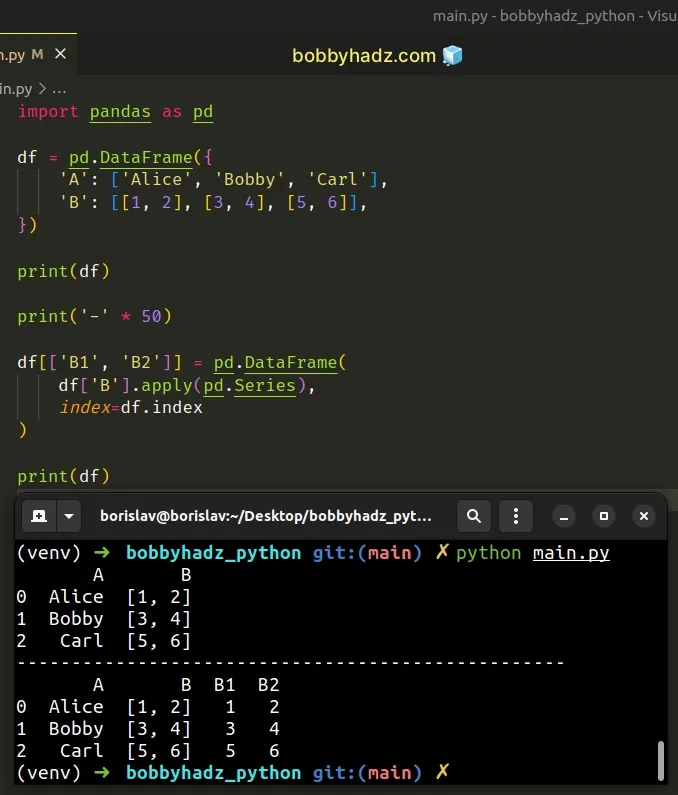
We used the DataFrame.apply() method to apply the
pd.Series
class to each column.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'B': [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]], }) # 0 1 # 0 1 2 # 1 3 4 # 2 5 6 print(df['B'].apply(pd.Series))
The last step is to use the pandas.DataFrame({}) constructor to add the B1
and B2 columns to the existing DataFrame.
# A B B1 B2 # 0 Alice [1, 2] 1 2 # 1 Bobby [3, 4] 3 4 # 2 Carl [5, 6] 5 6 df[['B1', 'B2']] = pd.DataFrame( df['B'].apply(pd.Series), index=df.index )
You can use the same approach to add the split columns to a new DataFrame.
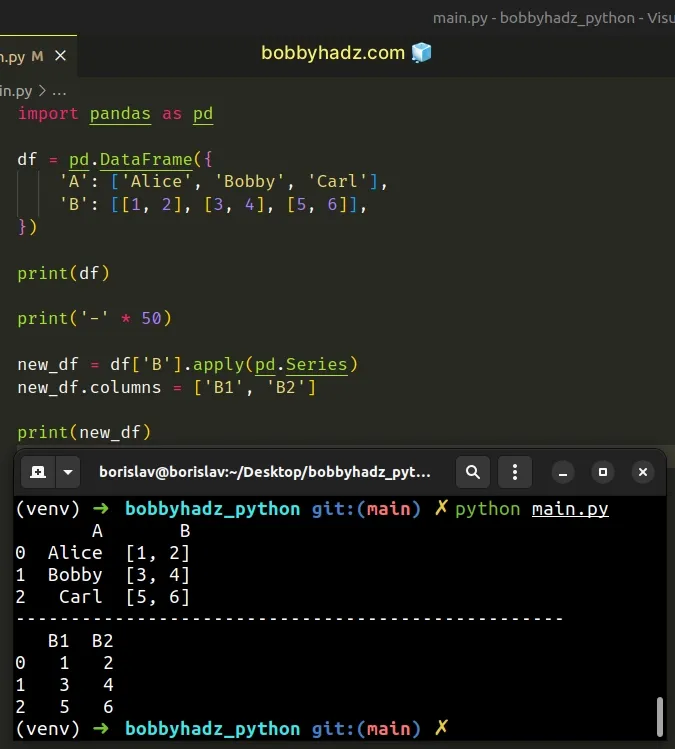
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'B': [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]], }) print(df) print('-' * 50) new_df = df['B'].apply(pd.Series) new_df.columns = ['B1', 'B2'] print(new_df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
A B 0 Alice [1, 2] 1 Bobby [3, 4] 2 Carl [5, 6] -------------------------------------------------- B1 B2 0 1 2 1 3 4 2 5 6
# Pandas: Split a Column of Lists with different lengths into Multiple Columns
You can also use the tolist() method if you need to split a column of lists
with different lengths into multiple columns.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'B': [[1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9]], }) new_df = pd.DataFrame(df['B'].tolist()) new_df.columns = ['B1', 'B2', 'B3', 'B4'] # B1 B2 B3 B4 # 0 1 2 NaN NaN # 1 3 4 5.0 NaN # 2 6 7 8.0 9.0 print(new_df)
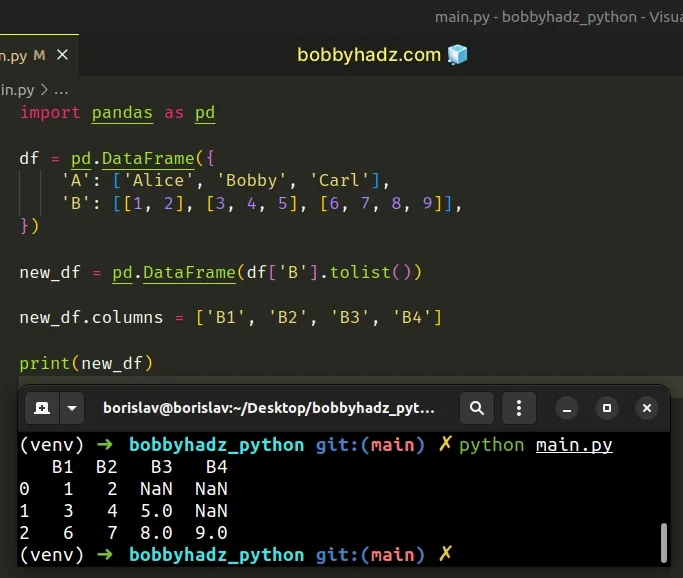
The longest sublist in the example has a length of 4.
This is why we supplied 4 column names.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'B': [[1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9]], }) # 👇️ [[1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9]] print(df['B'].tolist())
Since not all sublists contain 4 values, some of the rows contain NaN.
new_df = pd.DataFrame(df['B'].tolist()) new_df.columns = ['B1', 'B2', 'B3', 'B4'] # B1 B2 B3 B4 # 0 1 2 NaN NaN # 1 3 4 5.0 NaN # 2 6 7 8.0 9.0 print(new_df)
You can use the same approach if you want to add the split columns to the
existing DataFrame.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'B': [[1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9]], }) print(df) print('-' * 50) df[['B1', 'B2', 'B3', 'B4']] = pd.DataFrame(df['B'].tolist()) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
A B 0 Alice [1, 2] 1 Bobby [3, 4, 5] 2 Carl [6, 7, 8, 9] -------------------------------------------------- A B B1 B2 B3 B4 0 Alice [1, 2] 1 2 NaN NaN 1 Bobby [3, 4, 5] 3 4 5.0 NaN 2 Carl [6, 7, 8, 9] 6 7 8.0 9.0
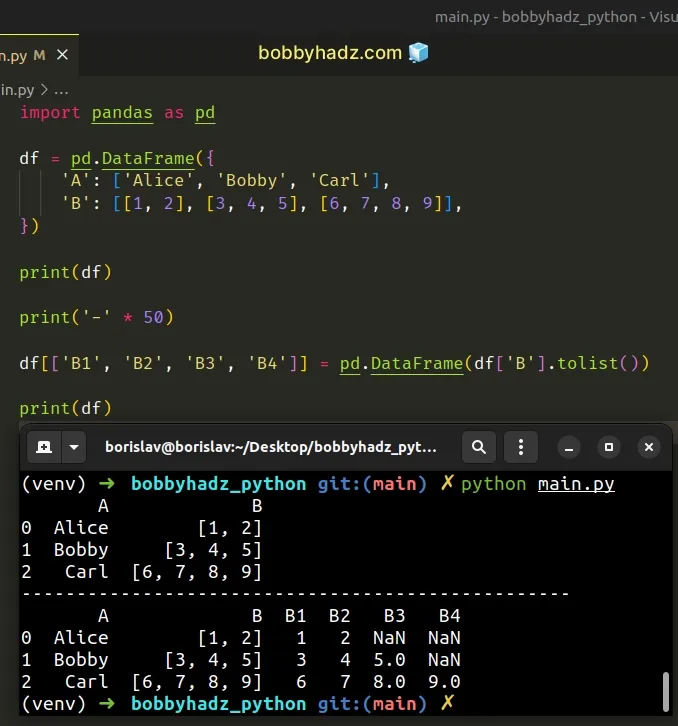
We specified 4 column names because the longest sublist has 4 values.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to shuffle two NumPy Arrays together (in Unison)
- Filter rows in a Pandas DataFrame using Regex
- Pandas: Convert a DataFrame to a List of Dictionaries
- Pandas: GroupBy columns with NaN (missing) values
- Panda: Using fillna() with specific columns in a DataFrame
- Pandas: How to Convert a Pivot Table to a DataFrame
- Pandas: Count the unique combinations of two Columns

