ValueError: cannot reindex on an axis with duplicate labels
Last updated: Apr 11, 2024
Reading time·6 min

# Table of Contents
- ValueError: cannot reindex on an axis with duplicate labels
- Resetting the index to solve the error
- Solving the error when concatenating DataFrames
- Removing duplicate columns to solve the error
- Solving the error when adding a column to a DataFrame
# ValueError: cannot reindex on an axis with duplicate labels
The Pandas "ValueError: cannot reindex on an axis with duplicate labels" occurs when you join or assign to a column when the index (row or column names) has duplicate values.
To solve the error, remove the rows with duplicate indexes.
Here is an example of how the error occurs when calling DataFrame.reindex()
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'id': [112, 113, 114, 115], 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'salary': [1500, 2500, 3500, 4500], }, index=[0, 1, 1, 2]) # 👈️ non-unique indexes # ⛔️ ValueError: cannot reindex on an axis with duplicate labels df.reindex([0, 1, 2, 3])
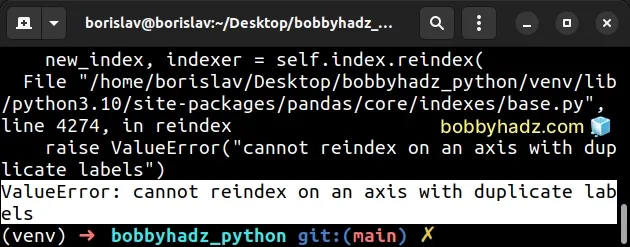
Notice that the original index contains duplicate values.
You can print the duplicates with df[df.index.duplicated()].
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'id': [112, 113, 114, 115], 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'salary': [1500, 2500, 3500, 4500], }, index=[0, 1, 1, 2]) # 👈️ non-unique indexes # id name salary # 1 114 Carl 3500 print(df[df.index.duplicated()])
Use the duplicated() method to remove the rows with duplicate indexes before
reindexing.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'id': [112, 113, 114, 115], 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'salary': [1500, 2500, 3500, 4500], }, index=[0, 1, 1, 2]) # 👈️ non-unique indexes # id name salary # 1 114 Carl 3500 print(df[df.index.duplicated()]) df = df[~df.index.duplicated()] # Empty DataFrame # Columns: [id, name, salary] # Index: [] print(df[df.index.duplicated()])
The pandas.index.duplicated method indicates the duplicate index values.
After removing the rows with duplicate indexes, the duplicated() method
returns an empty DataFrame.
You can now safely call the reindex() method.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'id': [112, 113, 114, 115], 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'salary': [1500, 2500, 3500, 4500], }, index=[0, 1, 1, 2]) # 👈️ non-unique indexes df = df[~df.index.duplicated()] df.reindex([0, 1, 2, 3]) # id name salary # 0 112 Alice 1500 # 1 113 Bobby 2500 # 2 115 Dan 4500 print(df)
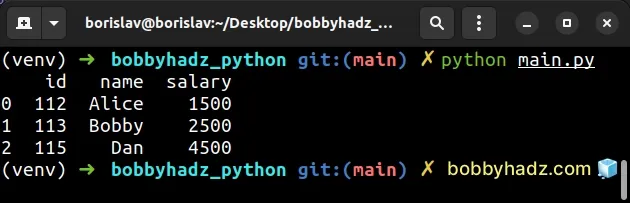
Notice that the DataFrame doesn't contain the row with the duplicate index.
The DataFrame.reindex() method
conforms the DataFrame to the new index.
# Resetting the index to solve the error
You can also solve the error by resetting the index.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'id': [112, 113, 114, 115], 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'salary': [1500, 2500, 3500, 4500], }, index=[0, 1, 1, 2]) # 👈️ non-unique indexes df = df.reset_index(drop=True) # id name salary # 0 112 Alice 1500 # 1 113 Bobby 2500 # 2 114 Carl 3500 # 3 115 Dan 4500 print(df)
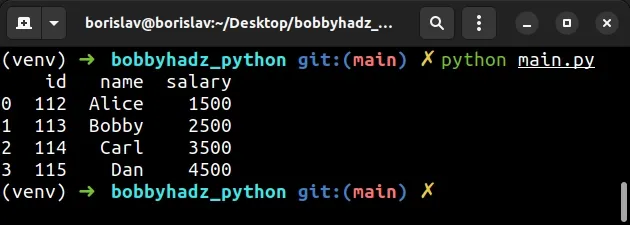
The DataFrame.reset_index()
method resets the index of the DataFrame.
The DataFrame now uses the default index.
We also set the drop keyword argument to True to reset the index to the
default integer index.
# Solving the error when concatenating DataFrames
You might also get indexes with duplicate values when you create a DataFrame
by concatenating other DataFrames.
If you don't need to preserve the values of your index, and simply want them to
be unique, set the ignore_index keyword argument to True when calling
pandas.concat.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.DataFrame({'a': 1, 'b': 2}, index=[3]) df2 = pd.DataFrame({'c': 3, 'd': 4}, index=[10]) df3 = pd.concat([df1, df2], ignore_index=True) # a b c d # 0 1.0 2.0 NaN NaN # 1 NaN NaN 3.0 4.0 print(df3)
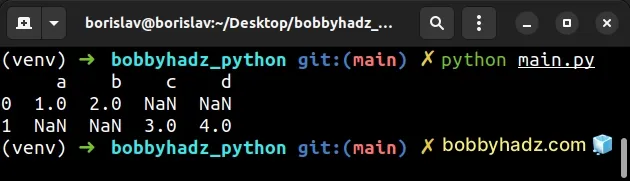
The pandas.concat() method concatenates pandas objects along a particular
axis.
When the ignore_index argument is set to True, the index values along the
concatenation axis are not used.
The resulting axis is labeled 0, ..., n - 1.
Setting the ignore_index argument to True is useful when concatenating
objects where the concatenation axis doesn't have meaningful indexing
information.
Alternatively, you can overwrite the current indexes with
df.index = new_index.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.DataFrame({'a': 1, 'b': 2}, index=[3]) df2 = pd.DataFrame({'c': 3, 'd': 4}, index=[10]) # 👇️ overwrite the indexes df1.index = [0] df2.index = [1] df3 = pd.concat([df1, df2]) # a b c d # 0 1.0 2.0 NaN NaN # 1 NaN NaN 3.0 4.0 print(df3)
# Removing duplicate columns to solve the error
The error also commonly occurs if you have a DataFrame where multiple columns
have the same name.
You can use the df.loc indexer to remove the duplicate columns.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'id': [112, 113, 114, 115], # 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'salary': [1500, 2500, 3500, 4500], 'nums': [1500, 2500, 3500, 4500], }, index=[0, 1, 2, 3]) df.columns = ['id', 'salary', 'salary'] # id salary salary # 0 112 1500 1500 # 1 113 2500 2500 # 2 114 3500 3500 # 3 115 4500 4500 print(df) print('-' * 50) # ✅ Remove duplicate column df = df.loc[:, ~df.columns.duplicated()] # id salary # 0 112 1500 # 1 113 2500 # 2 114 3500 # 3 115 4500 print(df)
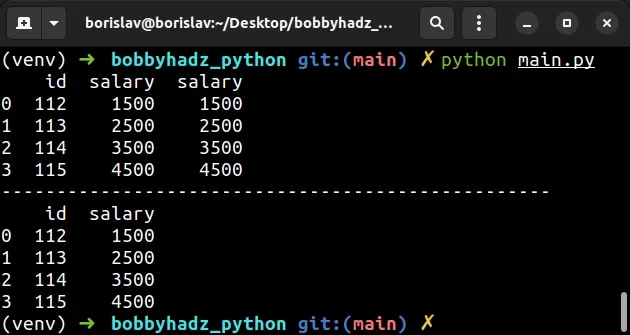
Notice that the DataFrame has 2 columns named salary.
The following line removes the duplicate columns.
# ✅ Remove duplicate column df = df.loc[:, ~df.columns.duplicated()]
You can also specify which column you want to keep.
When the keep argument is set to first, the first occurrence is kept.
df = df.loc[:, ~df.columns.duplicated(keep='first')]
When the argument is set to false, the last occurrence is kept.
df = df.loc[:, ~df.columns.duplicated(keep='last')]
When the argument is set to False, none of the duplicate columns is kept.
df = df.loc[:, ~df.columns.duplicated(keep=False)]
# Solving the error when adding a column to a DataFrame
You might also get the error when adding a column to a DataFrame if your
DataFrame has duplicate indexes.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.DataFrame({ 'id': [112, 113, 114, 115], 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'salary': [1500, 2500, 3500, 4500], }, index=[0, 1, 2, 3]) df2 = pd.DataFrame({ 'age': [25, 26, 27, 28] }, index=[1, 1, 2, 3]) # 👈️ has duplicate index df1['age'] = df2['age'] # ⛔️ ValueError: cannot reindex on an axis with duplicate labels print(df1)
Notice that df2 has a duplicate index.
You can use the DataFrame.values property to solve the error.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.DataFrame({ 'id': [112, 113, 114, 115], 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'salary': [1500, 2500, 3500, 4500], }, index=[0, 1, 2, 3]) df2 = pd.DataFrame({ 'age': [25, 26, 27, 28] }, index=[1, 1, 2, 3]) # 👈️ has duplicate index # ✅ access .values df1['age'] = df2['age'].values # id name salary age # 0 112 Alice 1500 25 # 1 113 Bobby 2500 26 # 2 114 Carl 3500 27 # 3 115 Dan 4500 28 print(df1)
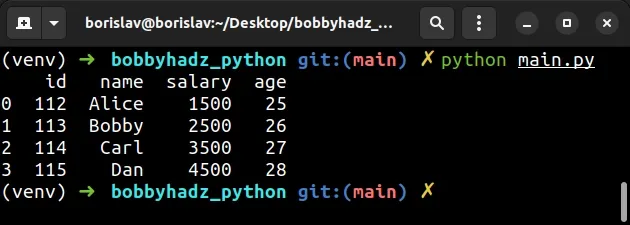
We used the values property to solve the error.
# ✅ access .values df1['age'] = df2['age'].values
The
DataFrame.values
property returns a NumPy ndarray containing the values of the DataFrame.
You can also use the to_numpy() method to solve the error.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.DataFrame({ 'id': [112, 113, 114, 115], 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'salary': [1500, 2500, 3500, 4500], }, index=[0, 1, 2, 3]) df2 = pd.DataFrame({ 'age': [25, 26, 27, 28] }, index=[1, 1, 2, 3]) # 👈️ has duplicate index # ✅ Using to_numpy() method df1['age'] = df2['age'].to_numpy() # id name salary age # 0 112 Alice 1500 25 # 1 113 Bobby 2500 26 # 2 114 Carl 3500 27 # 3 115 Dan 4500 28 print(df1)
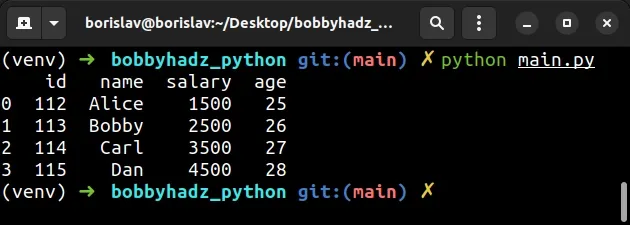
The DataFrame.to_numpy() method converts the DataFrame to a NumPy array.
I've written a detailed guide on how to copy a column from one DataFrame to another in Pandas.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- AttributeError module 'pandas' has no attribute 'DataFrame'
- ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'pandas' in Python
- FutureWarning: pandas.Int64Index is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version
- TypeError Invalid comparison between datetime64[ns] and date
- How to change the Port and Host in a Flask application
- How to replace None with NaN in Pandas DataFrame
- You are trying to merge on int64 and object columns [Fixed]
- Reindexing only valid with uniquely valued Index objects
- Cannot concatenate object of type 'X'; only Series and DataFrame objs are valid
- ValueError: No axis named X for object type DataFrame
- How to add a Level to Pandas MultiIndex in Python
- Select all Columns starting with a given String in Pandas

