Add a column with incremental Numbers to a Pandas DataFrame
Last updated: Apr 11, 2024
Reading time·6 min

# Table of Contents
- Add a column with incremental Numbers to a Pandas DataFrame
- Adding a column with incremental numbers to a DataFrame by using rename()
- Add a column with incremental numbers to a DataFrame using assign()
# Add a column with incremental Numbers to a Pandas DataFrame
To add a column with incremental numbers to a Pandas DataFrame:
- Use the
DataFrame.insert()method to insert a column into theDataFrameat a specific index. - Specify the name of the column as the second parameter.
- Use the
range()class to add a column with incremental numbers.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', None, None], 'experience': [None, 5, None, None], 'salary': [None, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) # name experience salary # 0 Alice NaN NaN # 1 Bobby 5.0 180.2 # 2 None NaN 190.3 # 3 None NaN 205.4 print(df) df.insert(0, 'ID', range(0, 0 + len(df))) # ID name experience salary # 0 0 Alice NaN NaN # 1 1 Bobby 5.0 180.2 # 2 2 None NaN 190.3 # 3 3 None NaN 205.4 print(df)
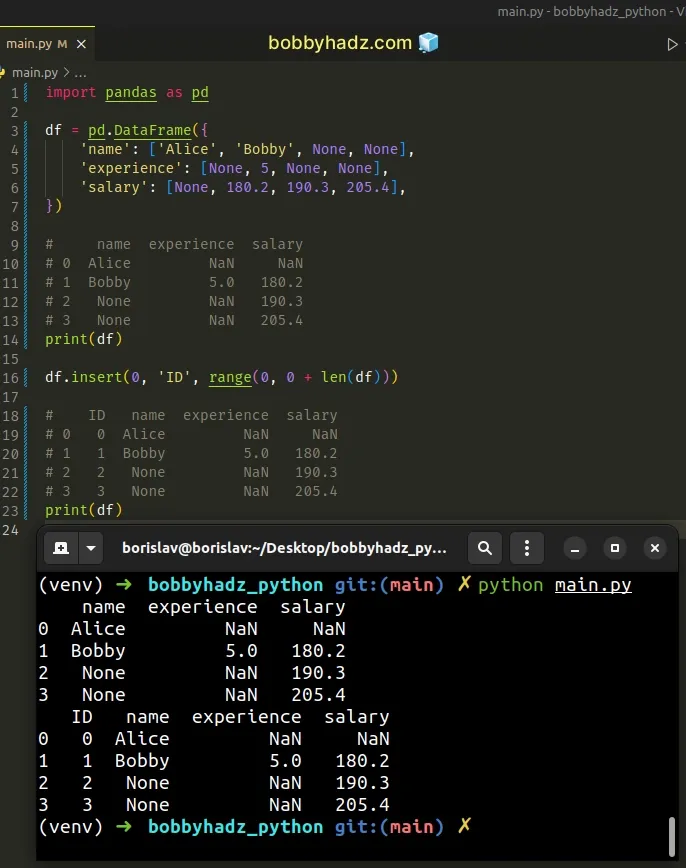
The
DataFrame.insert()
method inserts a column into a DataFrame at a specified location.
ValueError if a column with the specified name is already contained in the DataFrame unless the allow_duplicates parameter is set to `True`.We passed the following 3 parameters to the DataFrame.insert() method:
- The insertion index. Indices are zero-based, so an index of
0inserts theIDcolumn as the first in theDataFrame.
Note that the insertion index has to be greater than or equal to 0 and less
than or equal to len(df).
- The label of the inserted column (
IDin the example). - The
valuesthe column should contain. Can be scalar,Seriesor array-like.
df.insert(0, 'ID', range(0, 0 + len(df))) # ID name experience salary # 0 0 Alice NaN NaN # 1 1 Bobby 5.0 180.2 # 2 2 None NaN 190.3 # 3 3 None NaN 205.4 print(df)
We used the range() class to get an object that contains the values of the
column.
The incremental numbers in the example start from 0, however, you can specify
any other starting value.
Here is an example that uses the number 5 as the starting value of the
incremental column.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', None, None], 'experience': [None, 5, None, None], 'salary': [None, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) # name experience salary # 0 Alice NaN NaN # 1 Bobby 5.0 180.2 # 2 None NaN 190.3 # 3 None NaN 205.4 print(df) df.insert(0, 'ID', range(5, 5 + len(df))) # ID name experience salary # 0 5 Alice NaN NaN # 1 6 Bobby 5.0 180.2 # 2 7 None NaN 190.3 # 3 8 None NaN 205.4 print(df)
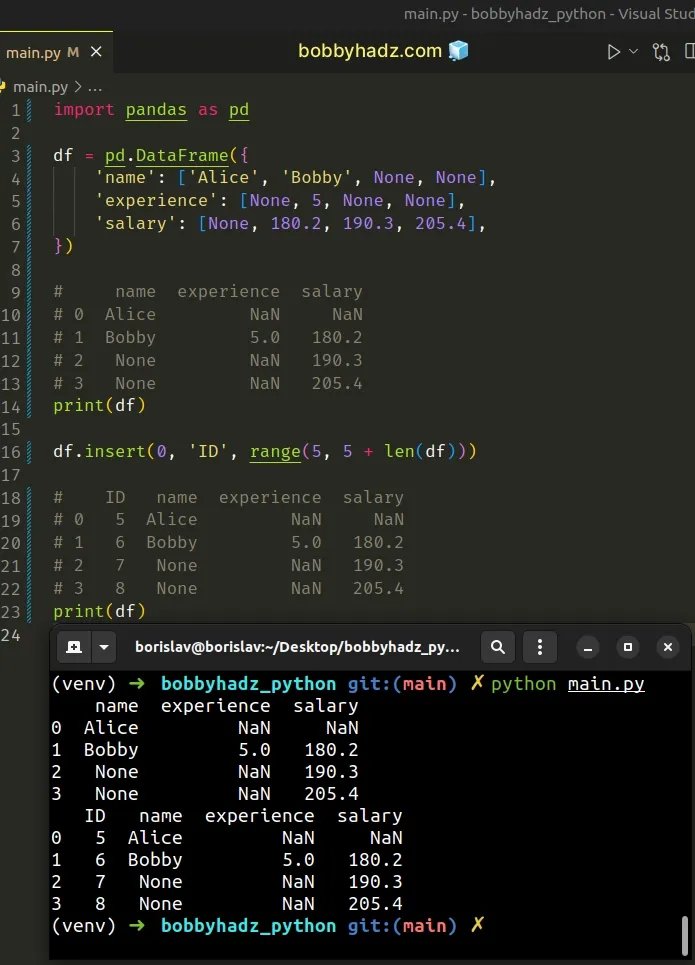
The range() class is commonly used for looping
a specific number of times in for loops and takes the following arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
start | An integer representing the start of the range (defaults to 0) |
stop | Go up to, but not including the provided integer |
step | Range will consist of every N numbers from start to stop (defaults to 1) |
The first argument you pass to the range() class is going to be the number you
want to start incrementing from.
The second argument is the stop value (exclusive) and is determined by adding
the start value to the length of the DataFrame.
Note that the DataFrame.insert() method modifies the DataFrame in place
and returns None.
If you don't need to add the new column at a specific index, you can shorten this a bit.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', None, None], 'experience': [None, 5, None, None], 'salary': [None, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) # name experience salary # 0 Alice NaN NaN # 1 Bobby 5.0 180.2 # 2 None NaN 190.3 # 3 None NaN 205.4 print(df) df['ID'] = range(5, 5 + len(df)) print('-' * 50) # name experience salary ID # 0 Alice NaN NaN 5 # 1 Bobby 5.0 180.2 6 # 2 None NaN 190.3 7 # 3 None NaN 205.4 8 print(df)
We directly added a column with incremental numbers to the DataFrame without
using insert().
However, notice that the column is added at the end of the DataFrame.
# Adding a column with incremental numbers to a DataFrame by using rename()
You can also use the
DataFrame.rename() method
to add a column with incremental numbers to a DataFrame.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', None, None], 'experience': [None, 5, None, None], 'salary': [None, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) # name experience salary # 0 Alice NaN NaN # 1 Bobby 5.0 180.2 # 2 None NaN 190.3 # 3 None NaN 205.4 print(df) df = df.reset_index() df = df.rename(columns={'index': 'ID'}) df['ID'] = df.index + 5 print('-' * 50) # ID name experience salary # 0 5 Alice NaN NaN # 1 6 Bobby 5.0 180.2 # 2 7 None NaN 190.3 # 3 8 None NaN 205.4 print(df)
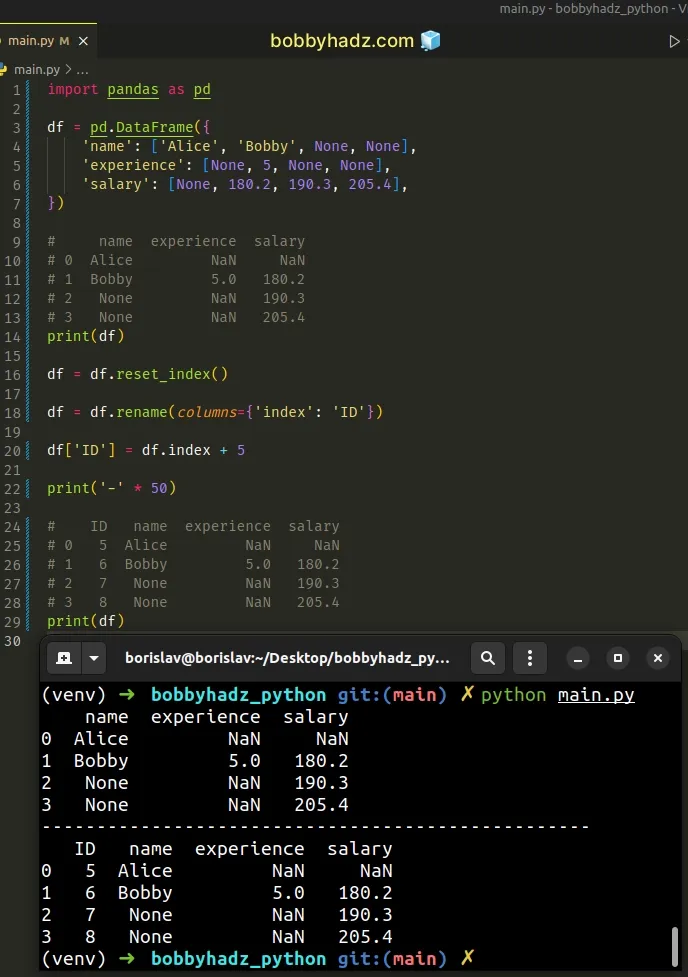
We used the
DataFrame.reset_index() method
to reset the index of the DataFrame.
The next step is to use the
DataFrame.rename()
method to rename the index column to ID (or any other name).
Lastly, we set the starting value of the ID column to 5.
This can be any other value you want to start incrementing from.
The ID column is an index column, so it automatically increments the value
with each row.
# Add a column with incremental numbers to a DataFrame using assign()
You can also use the
pandas.assign()
method to add a column with incremental numbers to a DataFrame.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', None, None], 'experience': [None, 5, None, None], 'salary': [None, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) # name experience salary # 0 Alice NaN NaN # 1 Bobby 5.0 180.2 # 2 None NaN 190.3 # 3 None NaN 205.4 print(df) df = df.assign(ID=lambda x: range(5, 5 + len(x))) print('-' * 50) # name experience salary ID # 0 Alice NaN NaN 5 # 1 Bobby 5.0 180.2 6 # 2 None NaN 190.3 7 # 3 None NaN 205.4 8 print(df)
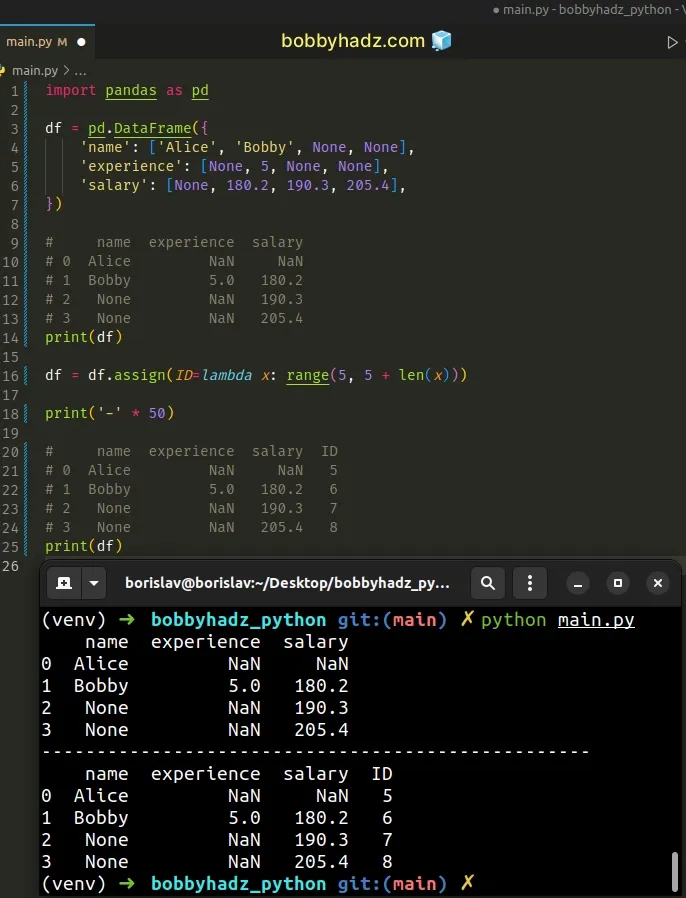
The
DataFrame.assign()
method assigns a new column to a DataFrame.
The method returns a new object with all the existing DataFrame columns and
the new columns.
Columns whose names already exist in the DataFrame, get overwritten.
We start incrementing from 5 in the example, however, you could use any other
value.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- ValueError: Columns must be same length as key [Solved]
- ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called [Fix]
- TypeError: Field elements must be 2- or 3-tuples, got 1
- ValueError: Expected 2D array, got 1D array instead [Fixed]
- TypeError: ufunc 'isnan' not supported for the input types
- ValueError: columns overlap but no suffix specified [Solved]
- Columns have mixed types. Specify dtype option on import
- Convert a Row to a Column Header in a Pandas DataFrame
- Drop Unnamed: 0 columns from a Pandas DataFrame in Python
- IndexError: single positional indexer is out-of-bounds [Fix]
- AttributeError: Can only use .dt accessor with datetimelike values
- Count number of non-NaN values in each column of DataFrame
- Replace whole String if it contains Substring in Pandas
- Using pandas.read_csv() with multiple delimiters in Python
- Pandas: Create new row for each element in List in DataFrame
- ValueError: Cannot merge a Series without a name [Solved]
- ValueError: Length of values does not match length of index
- Reindexing only valid with uniquely valued Index objects
- Cannot concatenate object of type 'X'; only Series and DataFrame objs are valid
- Pandas: Sum the values in a Column that match a Condition
- Pandas: Find length of longest String in DataFrame column
- How to add a Count Column to a Pandas DataFrame
- Pandas: Make new Column from string Slice of another Column
- Pandas: Out of bounds nanosecond timestamp [Solved]
- How to get a Quarter from a Date in Pandas [4 Ways]
- How to remove Time from DateTime in Pandas [5 Ways]
- Pandas: Check if a Date is during the Weekend or Weekday
- Pandas: Find the percentage of Missing values in each Column
- Create Date column from Year, Month and Day in Pandas

