Pandas: Merge only specific DataFrame columns [4 Ways]
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·6 min

# Table of Contents
- Pandas: Merge only specific DataFrame columns
- Specifying which columns to include in the merge from both DataFrames
- Pandas: Merge only specific DataFrame columns using DataFrame.drop()
- Pandas: Merge only specific DataFrame columns using DataFrame.loc
# Pandas: Merge only specific DataFrame columns
To merge only specific DataFrame columns in Pandas:
- Call the
merge()method on the firstDataFrame. - Select the columns you want to include in the result
DataFramefrom the secondDataFrame.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'profit': [1500, 2500, 3500, 4500], }) df2 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'employees': [10, 15, 20, 25], 'CEO': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'], 'CFO': ['Q', 'W', 'E', 'R'] }) df3 = df1.merge( df2[['year', 'employees']], on='year', how='left' ) # year profit employees # 0 2020 1500 10 # 1 2021 2500 15 # 2 2022 3500 20 # 3 2023 4500 25 print(df3)
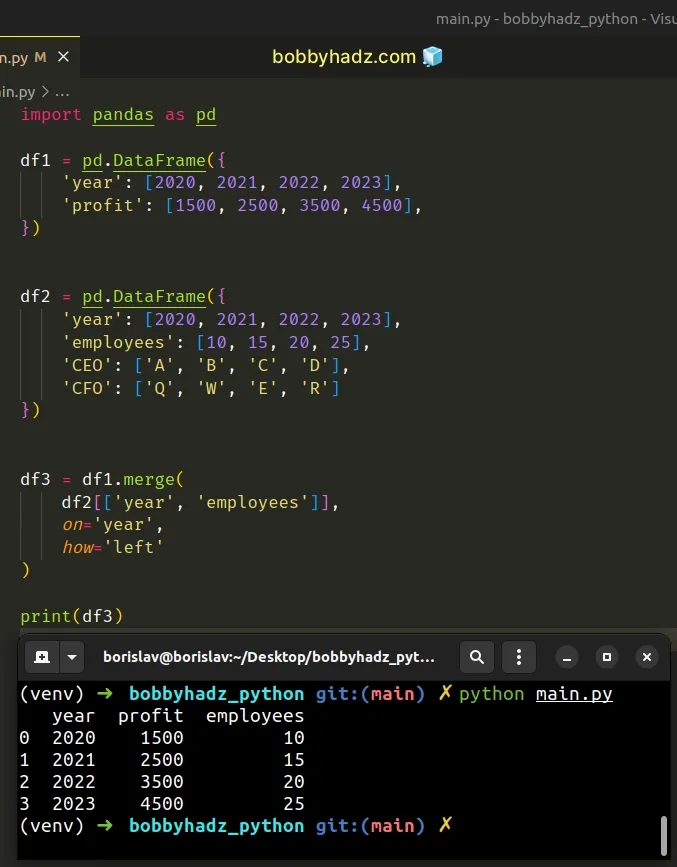
The DataFrame.merge() method merges DataFrames with a database-style join.
Notice that we used two sets of square brackets [[]] to select the columns
from df2 that we want to include in the resulting DataFrame.
df3 = df1.merge( df2[['year', 'employees']], on='year', how='left' ) # year profit employees # 0 2020 1500 10 # 1 2021 2500 15 # 2 2022 3500 20 # 3 2023 4500 25 print(df3)
The new DataFrame only has the year, profit and employees columns.
You can select as many columns from df2 as necessary by specifying the column
names between the two sets of square brackets.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'profit': [1500, 2500, 3500, 4500], }) df2 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'employees': [10, 15, 20, 25], 'CEO': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'], 'CFO': ['Q', 'W', 'E', 'R'] }) df3 = df1.merge( df2[['year', 'employees', 'CEO']], on='year', how='left' ) # year profit employees CEO # 0 2020 1500 10 A # 1 2021 2500 15 B # 2 2022 3500 20 C # 3 2023 4500 25 D print(df3)
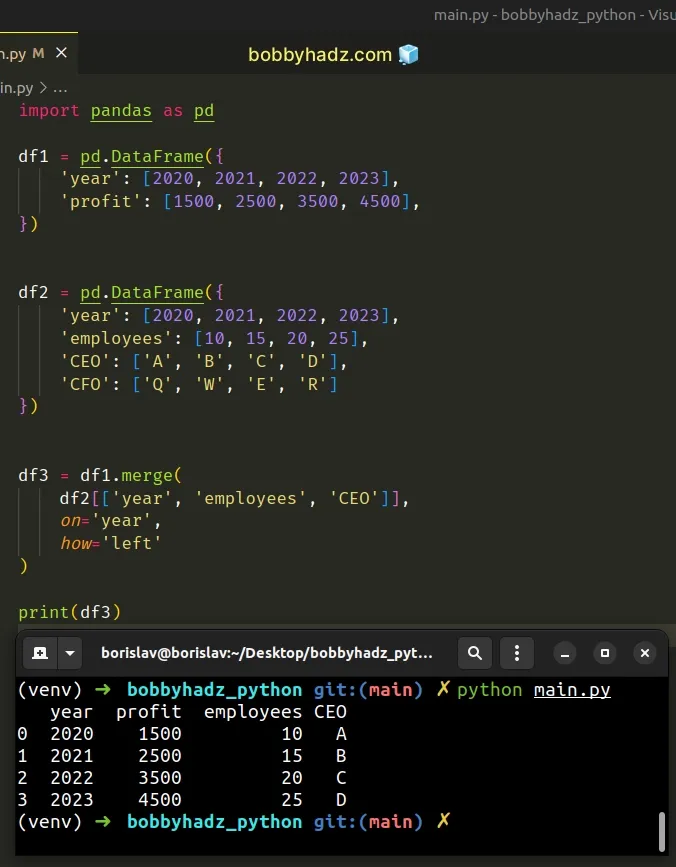
The resulting DataFrame now has the year, profit, employees and CEO
columns.
In other words, we include all columns from df1 and only the specified columns
from d2 in the resulting DataFrame.
# Specifying which columns to include in the merge from both DataFrames
If you want to specify which columns to include in the merge operation from
both DataFrames, use two sets of square brackets.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'profit': [1500, 2500, 3500, 4500], 'CFO': ['Q', 'W', 'E', 'R'] }) df2 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'employees': [10, 15, 20, 25], 'CEO': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'], }) df3 = df1[['year', 'profit']].merge( df2[['year', 'employees']], on='year', how='left' ) # year profit employees # 0 2020 1500 10 # 1 2021 2500 15 # 2 2022 3500 20 # 3 2023 4500 25 print(df3)
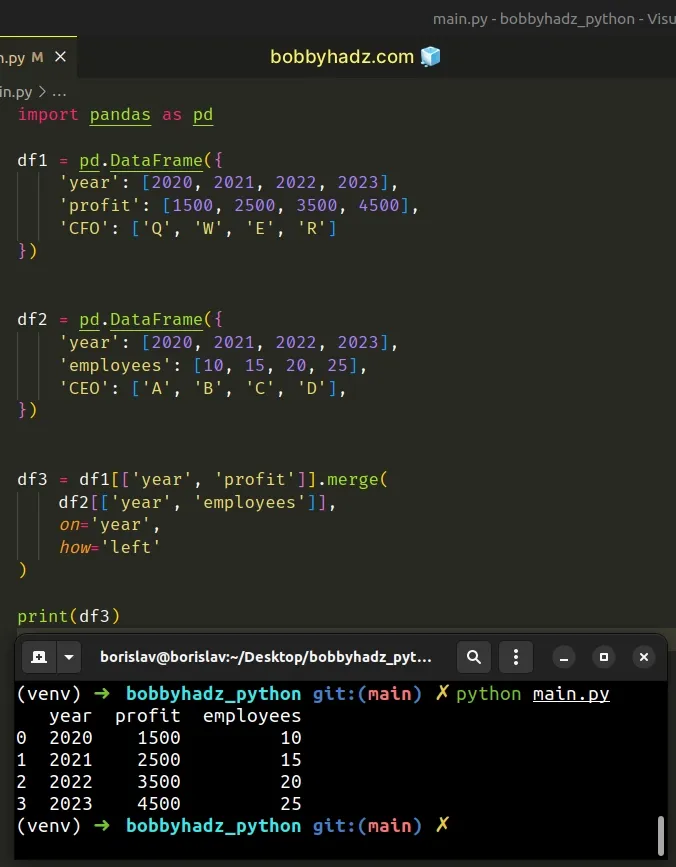
We first used two sets of square brackets [[]] to select the columns from
df1 we want to include in the merge operation and then used two sets of square
brackets to select the specific columns from df2.
# Pandas: Merge only specific DataFrame columns using DataFrame.drop()
In some cases, you might need the columns for the merge operation but might
want to remove the columns from the resulting DataFrame.
If that's the case, include the columns in the merge() call and use the
DataFrame.drop() method to remove
them after merging.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'profit': [1500, 2500, 3500, 4500], }) df2 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'employees': [10, 15, 20, 25], 'CEO': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'], 'CFO': ['Q', 'W', 'E', 'R'] }) df3 = df1.merge( df2[['year', 'employees', 'CEO']], on='year', how='left' ).drop(columns=['CEO']) # year profit employees # 0 2020 1500 10 # 1 2021 2500 15 # 2 2022 3500 20 # 3 2023 4500 25 print(df3)
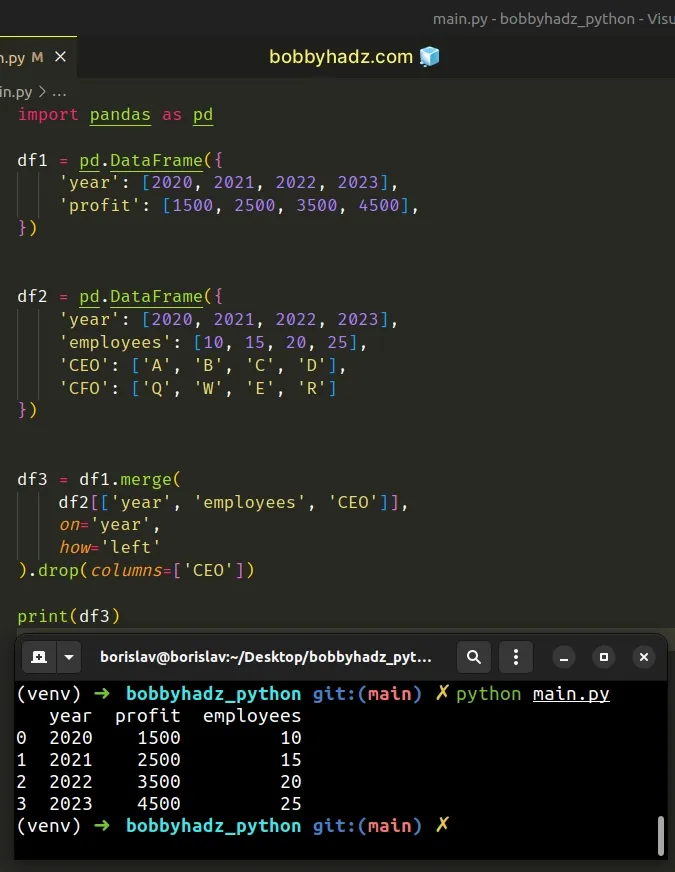
We included the CEO column in the merge() call but wanted to exclude it from
the result, so we used the drop() method.
The DataFrame.drop() method drops the
specified columns from the DataFrame.
DataFrame without the specified columns.This approach should only be used when you want to remove columns that you need
for the join operation after merging.
# Pandas: Merge only specific DataFrame columns using DataFrame.loc
You can also use the
DataFrame.loc label-based
indexer to select the columns you want to include in the merge operation.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'profit': [1500, 2500, 3500, 4500], }) df2 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'employees': [10, 15, 20, 25], 'CEO': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'], 'CFO': ['Q', 'W', 'E', 'R'] }) df3 = df1.merge( df2.loc[:, ['year', 'employees']], on='year', how='left' ) # year profit employees # 0 2020 1500 10 # 1 2021 2500 15 # 2 2022 3500 20 # 3 2023 4500 25 print(df3)
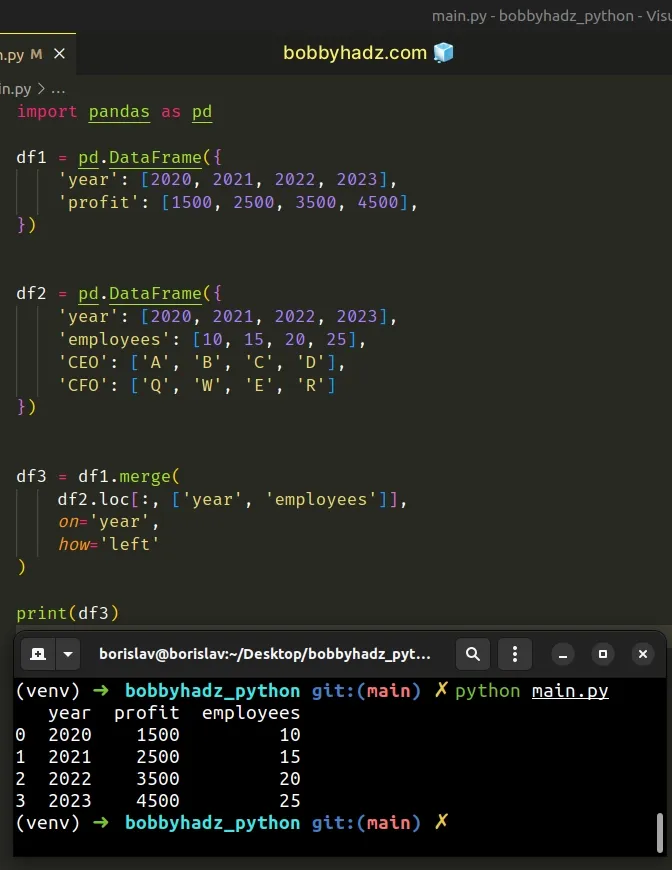
Make sure to specify the names of the columns you want to include in the
resulting DataFrame in the list after the comma.
df3 = df1.merge( df2.loc[:, ['year', 'employees']], on='year', how='left' )
You can also use the loc indexer to select the specific columns from df1 in
case you don't want to include all columns from df1 in the resulting
DataFrame.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'profit': [1500, 2500, 3500, 4500], 'CFO': ['Q', 'W', 'E', 'R'] }) df2 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'employees': [10, 15, 20, 25], 'CEO': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'], }) df3 = df1.loc[:, ['year', 'profit']].merge( df2.loc[:, ['year', 'employees']], on='year', how='left' ) # year profit employees # 0 2020 1500 10 # 1 2021 2500 15 # 2 2022 3500 20 # 3 2023 4500 25 print(df3)
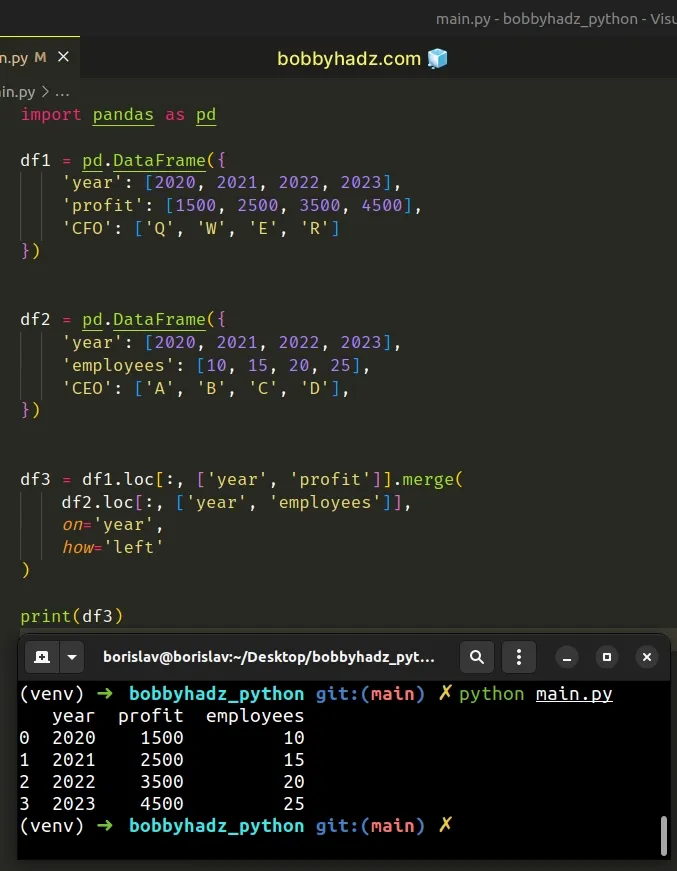
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Pandas: Select first N or last N columns of DataFrame
- Pandas: Convert entire DataFrame to numeric (int or float)
- Pandas: Find common Rows (intersection) between 2 DataFrames
- Pandas: How to Filter a DataFrame by value counts
- Pandas: Get the Rows that are NOT in another DataFrame
- How to modify a Subset of Rows in a Pandas DataFrame
- How to Start the Index of a Pandas DataFrame at 1
- Pandas: DataFrame.reset_index() not working [Solved]
- How to Add Axis Labels to a Plot in Pandas [5 Ways]
- How to Create a Set from a Series in Pandas
- ValueError: If using all scalar values, you must pass index
- First argument must be an iterable of pandas objects [Fix]
- Pandas: Setting column names when reading a CSV file
- Export a Pandas DataFrame to Excel without the Index
- Pandas: How to Convert a Pivot Table to a DataFrame
- Pandas: Count the unique combinations of two Columns
- Pandas: How to Query a Column name with Spaces
- Pandas: Find the closest value to a Number in a Column
- Annotate Bars in Barplot with Pandas and Matplotlib
- Pandas: Create a Tuple from two DataFrame Columns
- Cannot mask with non-boolean array containing NA / NaN values
- Disable the TOKENIZERS_PARALLELISM=(true | false) warning
- RuntimeError: Expected scalar type Float but found Double
- Pandas: Convert timezone-aware DateTimeIndex to naive timestamp
- RuntimeError: Input type (torch.FloatTensor) and weight type (torch.cuda.FloatTensor) should be the same
- ValueError: Failed to convert a NumPy array to a Tensor (Unsupported object type float)
- Mixing dicts with non-Series may lead to ambiguous ordering
- ValueError: NaTType does not support strftime [Solved]
- Pandas: How to efficiently Read a Large CSV File
- TypeError: '(slice(None, None, None), 0)' is an invalid key
- ERROR: YouTube said: Unable to extract video data [Solved]
- OSError: [E050] Can't find model 'en_core_web_sm'
- Pandas: Apply a Function to each Cell of a DataFrame

