How to modify a Subset of Rows in a Pandas DataFrame
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- How to modify a Subset of Rows in a Pandas DataFrame
- Modify a Subset of Rows in a Pandas DataFrame using numpy.where()
- Modify a Subset of Rows in multiple columns in a Pandas DataFrame
- Modify a Subset of Rows in a Pandas DataFrame using apply()
# How to modify a Subset of Rows in a Pandas DataFrame
To modify a subset of rows in a Pandas DataFrame:
- Use the
DataFrame.loclabel-based indexer to select the rows you'd like to modify. - Set the values in the selected rows to the replacement value.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'experience': [1, 3, 1, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) print(df) df.loc[df.experience == 1, 'salary'] = 150 print('-' * 50) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name experience salary 0 Alice 1 175.1 1 Bobby 3 180.2 2 Carl 1 190.3 3 Dan 7 205.4 -------------------------------------------------- name experience salary 0 Alice 1 150.0 1 Bobby 3 180.2 2 Carl 1 150.0 3 Dan 7 205.4
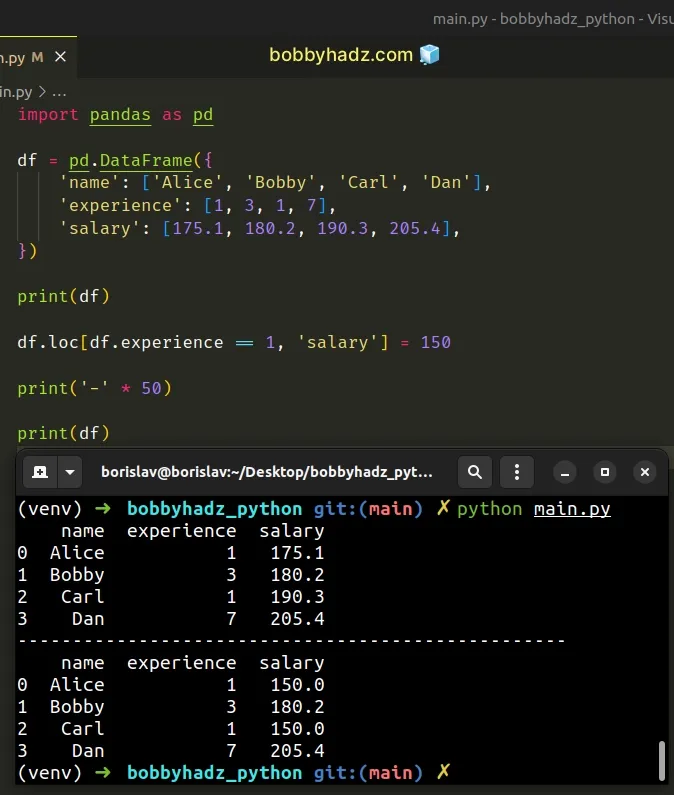
We used the
DataFrame.loc
label-based indexer to access specific rows of the DataFrame by a boolean
Series.
The df.experience == 1 expression returns a boolean Series containing True
values for the rows that match the condition and False for those that don't.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'experience': [1, 3, 1, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) # 0 True # 1 False # 2 True # 3 False # Name: experience, dtype: bool print(df.experience == 1)
Notice that we specified the name of the column we want to update after the comma.
df.loc[df.experience == 1, 'salary'] = 150
We basically select the rows in which the "experience" column values are equal
to 1 and update the corresponding "salary" values to 150.
You can also calculate the value on the right-hand side using the df.loc
indexer.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'experience': [1, 3, 1, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) print(df) df.loc[df.experience == 1, 'salary'] = df.loc[ df.experience == 1, 'salary'] - 100 print('-' * 50) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name experience salary 0 Alice 1 175.1 1 Bobby 3 180.2 2 Carl 1 190.3 3 Dan 7 205.4 -------------------------------------------------- name experience salary 0 Alice 1 75.1 1 Bobby 3 180.2 2 Carl 1 90.3 3 Dan 7 205.4
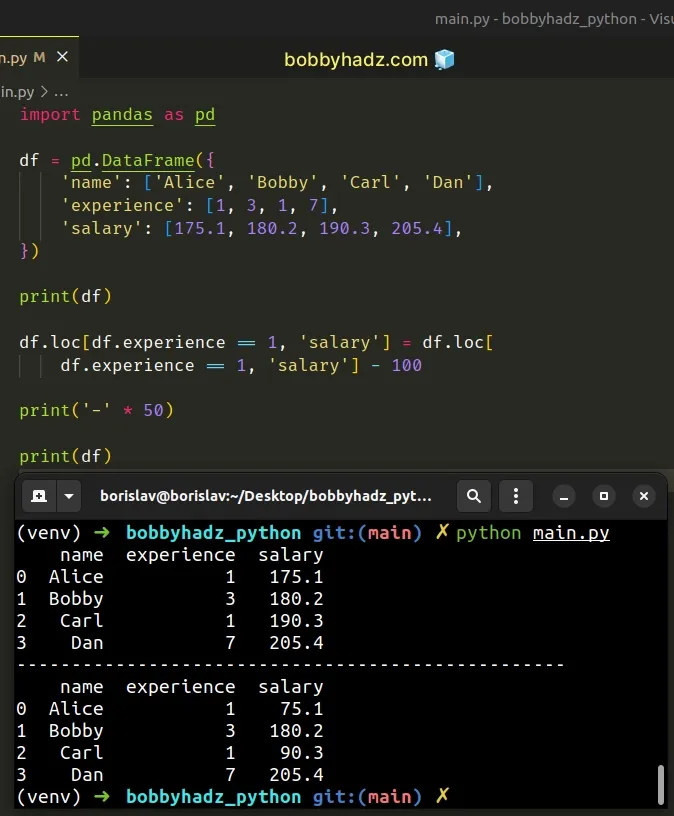
The code sample updates the salary values of the rows in which the
experience value is equal to 1.
df.loc[df.experience == 1, 'salary'] = df.loc[ df.experience == 1, 'salary'] - 100
The salary value of the matching rows is set to the current value minus 100.
In other words, the syntax is:
df.loc[selection criteria, columns to update] = value
DataFrame.loc indexer is primarily label-based, but it can also be used with a boolean array (or Series).The boolean array (or Series) tells Pandas which rows we want to select.
The column name after the comma instructs Pandas about the rows in which column we want to update.
# Modify a Subset of Rows in a Pandas DataFrame using numpy.where()
You can also use the numpy.where() method to modify a subset of rows in a Pandas DataFrame.
First, make sure you
have the numpy module installed.
pip install numpy # or with pip3 pip3 install numpy
Now, import the numpy module and use the numpy.where() method.
import pandas as pd import numpy as np df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'experience': [1, 3, 1, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) print(df) replacement_value = 150 df['salary'] = np.where( df.experience.values == 1, replacement_value, df.salary.values ) print('-' * 50) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name experience salary 0 Alice 1 175.1 1 Bobby 3 180.2 2 Carl 1 190.3 3 Dan 7 205.4 -------------------------------------------------- name experience salary 0 Alice 1 150.0 1 Bobby 3 180.2 2 Carl 1 150.0 3 Dan 7 205.4
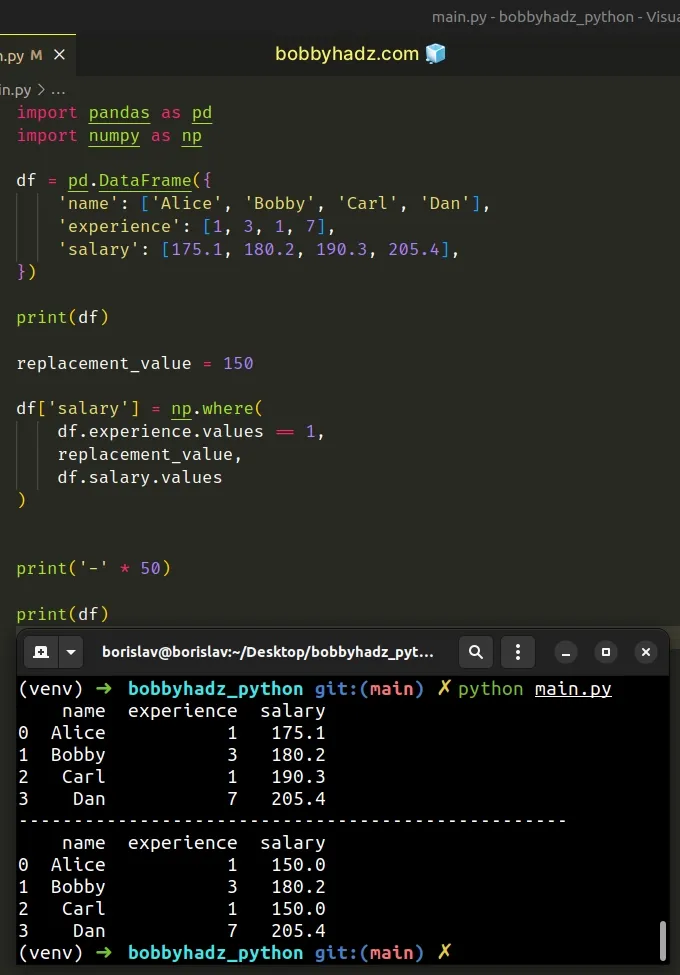
The numpy.where() method returns the elements chosen from x or y depending
on the supplied condition.
df['salary'] = np.where( df.experience.values == 1, replacement_value, df.salary.values )
The first argument the method takes is the condition and the second and third
arguments are x and y.
import pandas as pd import numpy as np df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'experience': [1, 3, 1, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) replacement_value = 150 # [150. 180.2 150. 205.4] print(np.where( df.experience.values == 1, replacement_value, df.salary.values ))
The where() method returns an array with the elements from x where the
condition is True and the elements from y elsewhere.
# Modify a Subset of Rows in multiple columns in a Pandas DataFrame
If you need to modify a subset of rows in multiple columns in a DataFrame, use
the
DataFrame.values
attribute.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Bobby', 'Dan'], 'experience': [1, 3, 1, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) print(df) print('-' * 50) df.loc[df.name == 'Bobby', ['experience', 'salary'] ] = df.loc[ df.name == 'Bobby', ['experience', 'salary'] ].values / 2 print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name experience salary 0 Alice 1 175.1 1 Bobby 3 180.2 2 Bobby 1 190.3 3 Dan 7 205.4 -------------------------------------------------- name experience salary 0 Alice 1.0 175.10 1 Bobby 1.5 90.10 2 Bobby 0.5 95.15 3 Dan 7.0 205.40
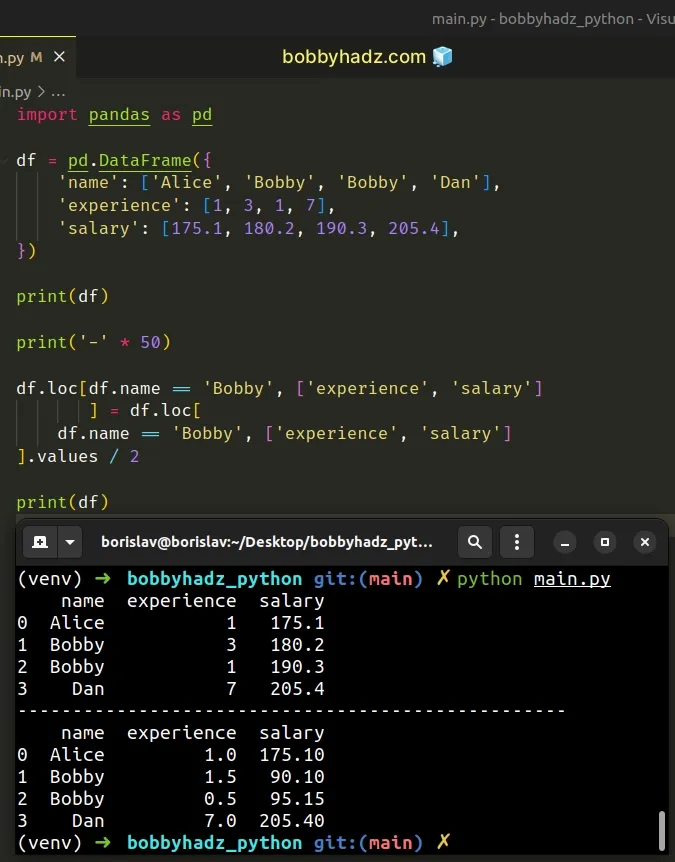
The code sample updates the values in the experience and salary columns
where the name column has a value of "Bobby".
df.loc[df.name == 'Bobby', ['experience', 'salary'] ] = df.loc[ df.name == 'Bobby', ['experience', 'salary'] ].values / 2
The corresponding values in the experience and salary columns are set to
their current value divided by 2.
# Modify a Subset of Rows in a Pandas DataFrame using apply()
You can also use the
DataFrame.apply
method to modify a subset of rows in a Pandas DataFrame.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Bobby', 'Dan'], 'experience': [1, 3, 1, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) print(df) print('-' * 50) replacement_value = 150 df['salary'] = df.apply( lambda x: replacement_value if x['experience'] == 1 else x['salary'], axis=1 ) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name experience salary 0 Alice 1 175.1 1 Bobby 3 180.2 2 Bobby 1 190.3 3 Dan 7 205.4 -------------------------------------------------- name experience salary 0 Alice 1 150.0 1 Bobby 3 180.2 2 Bobby 1 150.0 3 Dan 7 205.4
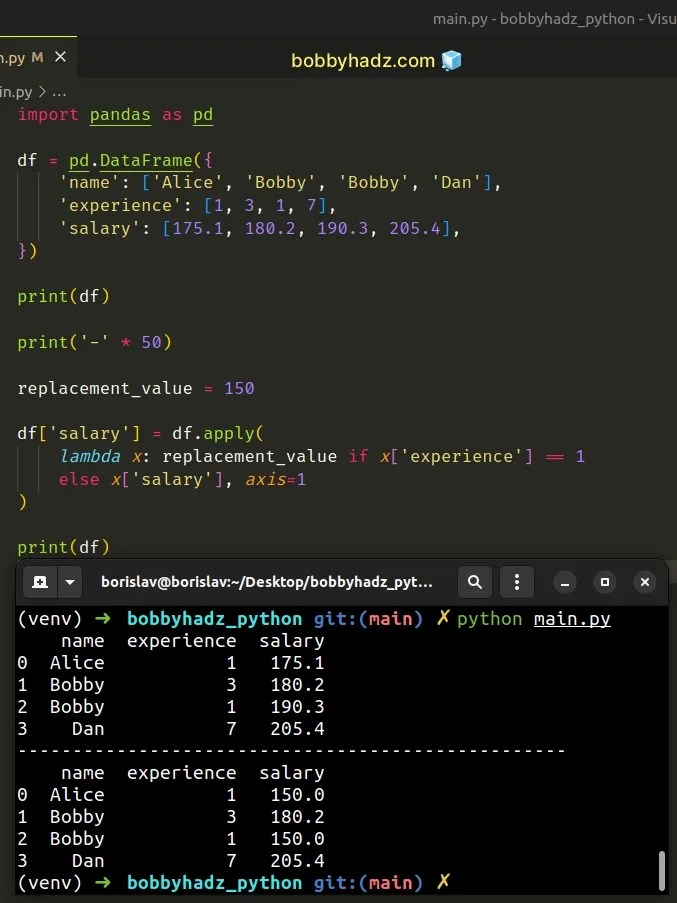
The DataFrame.apply() method applies a function along an axis of the
DataFrame.
df['salary'] = df.apply( lambda x: replacement_value if x['experience'] == 1 else x['salary'], axis=1 )
The axis parameter defines the axis along which the function is applied.
axis parameter is set to 0 which means that the function is applied to each column.However, we want to apply the function to the matching rows, so we set the
axis argument to 1.
The code sample updates the rows in the salary column where the value in the
experience column is equal to 1.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Reading specific columns from an Excel File in Pandas
- Pandas: Changing the column type to Categorical
- Pandas: Get a List of Categories or Categorical Columns
- Calculate the Average for each Row in a Pandas DataFrame
- Pandas: Drop columns if Name contains a given String
- How to convert a Pandas DataFrame to a Markdown Table
- Must have equal len keys and value when setting with iterable

