Mixing dicts with non-Series may lead to ambiguous ordering
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Mixing dicts with non-Series may lead to ambiguous ordering
- Access the key that stores the data you want to construct the DataFrame from
- Using the pandas.json_normalize() method to solve the error
- If you also want to add the other properties as columns
# Mixing dicts with non-Series may lead to ambiguous ordering
The "ValueError: Mixing dicts with non-Series may lead to ambiguous ordering"
occurs when you try to convert a JSON object of an incorrect shape to a Pandas
DataFrame.
To solve the error, access the dictionary key that points to the data from
which you want to construct the DataFrame.
For example, suppose that we have the following example.json file.
{ "status": { "code": 200, "message": "OK" }, "body": [ {"name": "Alice", "salary": 100}, {"name": "Bobby", "salary": 50}, {"name": "Carl", "salary": 75} ] }
And here is the related Python script that causes the error.
import json import pandas as pd data = json.load(open('example.json')) df = pd.DataFrame(data) # ⛔️ ValueError: Mixing dicts with non-Series may lead to ambiguous ordering. print(df)
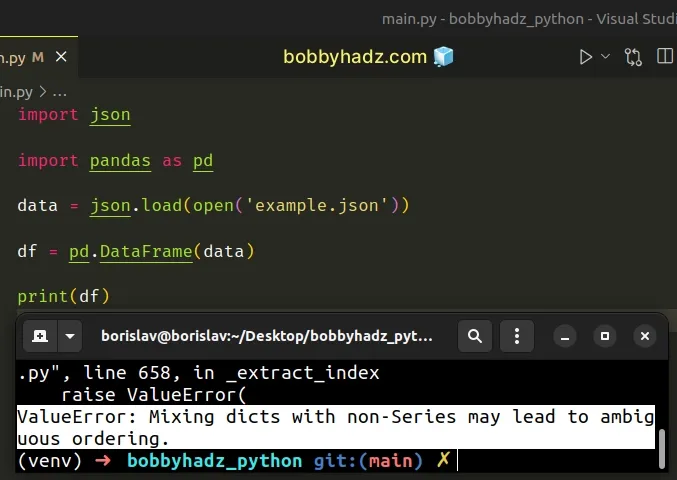
The error is caused because the shape of the JSON data in the example.json
file cannot be directly passed to the
pandas.DataFrame()
constructor.
# Access the key that stores the data you want to construct the DataFrame from
To solve the error, we have to access the dictionary key that stores the data we
want to construct the DataFrame from.
Assuming you have the following example.json file.
{ "status": { "code": 200, "message": "OK" }, "body": [ {"name": "Alice", "salary": 100}, {"name": "Bobby", "salary": 50}, {"name": "Carl", "salary": 75} ] }
You would have to access the body key when calling pd.DataFrame().
import json import pandas as pd data = json.load(open('example.json')) df = pd.DataFrame(data['body']) # name salary # 0 Alice 100 # 1 Bobby 50 # 2 Carl 75 print(df)
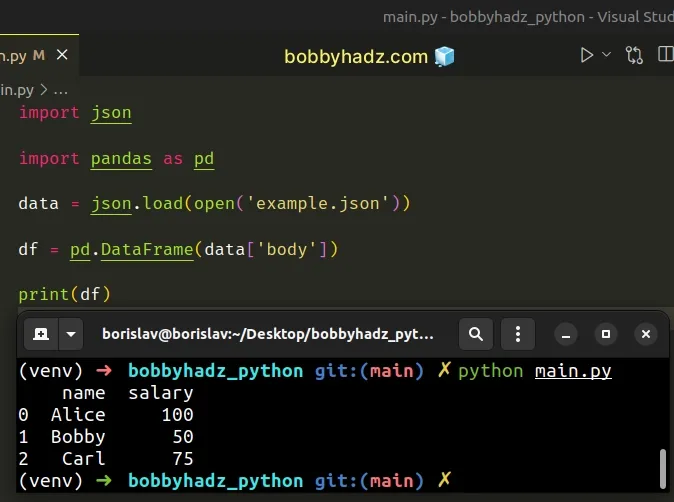
Accessing the body key resolved the issue.
You can print the loaded data to see which key you need to access in your case.
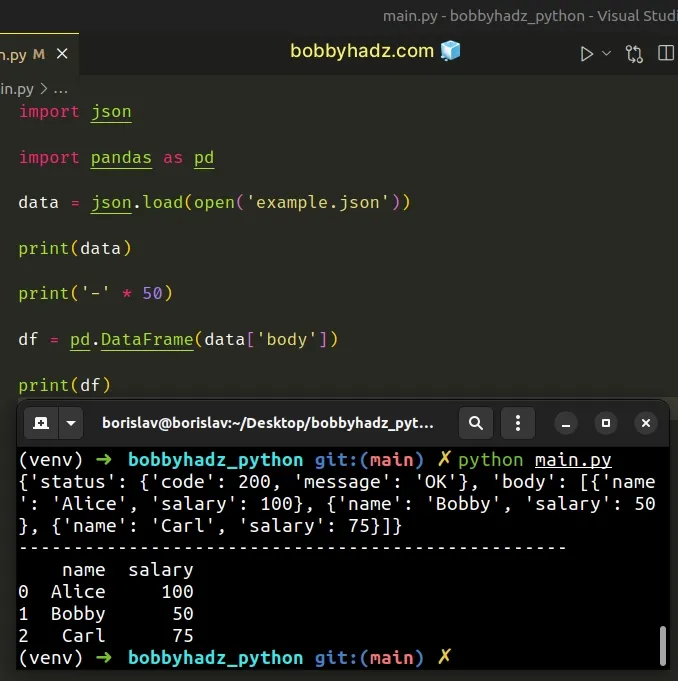
import json import pandas as pd data = json.load(open('example.json')) print(data) print('-' * 50) df = pd.DataFrame(data['body']) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
{'status': {'code': 200, 'message': 'OK'}, 'body': [{'name': 'Alice', 'salary': 100}, {'name': 'Bobby', 'salary': 50}, {'name': 'Carl', 'salary': 75}]} -------------------------------------------------- name salary 0 Alice 100 1 Bobby 50 2 Carl 75
We could've also used the with open() statement when opening the JSON file.
import json import pandas as pd with open('example.json') as json_file: data = json.load(json_file) df = pd.DataFrame(data['body']) # name salary # 0 Alice 100 # 1 Bobby 50 # 2 Carl 75 print(df)
The with open() statement takes care of automatically closing the file for us
(even if an exception occurs).
The json.load method is used to deserialize a file to a Python object.
Not to be confused with json.loads which deserializes a JSON string to a Python object.
# Using the pandas.json_normalize() method to solve the error
You can also use the pandas.json_normalize method to solve the error.
Suppose you have the following example.json file.
{ "status": { "code": 200, "message": "OK" }, "body": [ {"name": "Alice", "salary": 100}, {"name": "Bobby", "salary": 50}, {"name": "Carl", "salary": 75} ] }
Here is the related Python script.
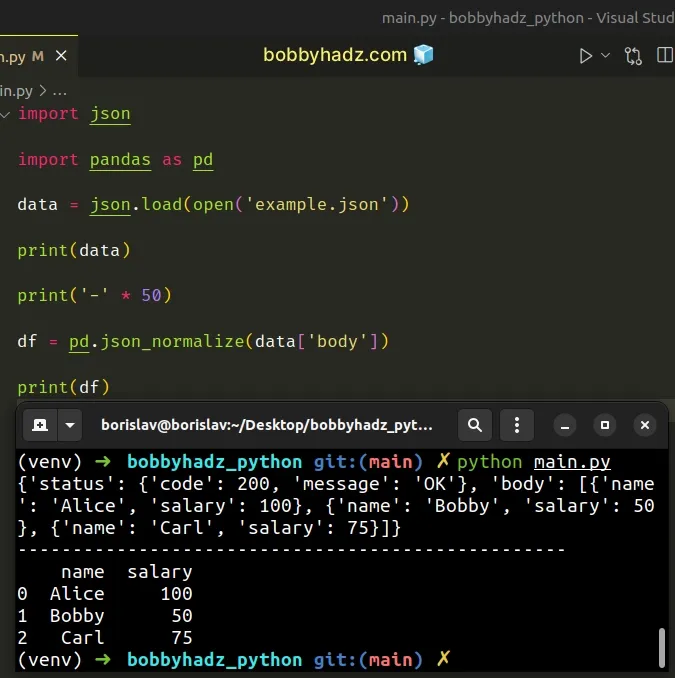
import json import pandas as pd data = json.load(open('example.json')) print(data) print('-' * 50) df = pd.json_normalize(data['body']) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
{'status': {'code': 200, 'message': 'OK'}, 'body': [{'name': 'Alice', 'salary': 100}, {'name': 'Bobby', 'salary': 50}, {'name': 'Carl', 'salary': 75}]} -------------------------------------------------- name salary 0 Alice 100 1 Bobby 50 2 Carl 75
The pandas.json_normalize() method normalizes semi-structured JSON data into a
flat table.
The first argument the method takes is the data - a dict or a list of dicts containing the unserialized JSON objects.
df = pd.json_normalize(data['body'])
We could've also passed 2 arguments to the pandas.json_normalize() method -
the data and the record path.
The following code sample achieves the same result.
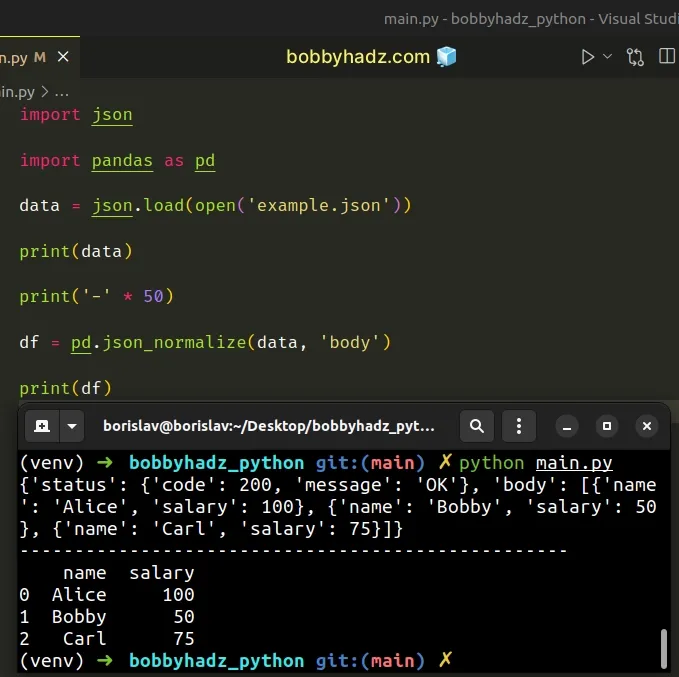
import json import pandas as pd data = json.load(open('example.json')) print(data) print('-' * 50) df = pd.json_normalize(data, 'body') print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
{'status': {'code': 200, 'message': 'OK'}, 'body': [{'name': 'Alice', 'salary': 100}, {'name': 'Bobby', 'salary': 50}, {'name': 'Carl', 'salary': 75}]} -------------------------------------------------- name salary 0 Alice 100 1 Bobby 50 2 Carl 75
# If you also want to add the other properties as columns
If you also want to add the rest of the properties as columns in the
DataFrame, use the
DataFrame.assign
method.
Suppose we have the same example.json file.
{ "status": { "code": 200, "message": "OK" }, "body": [ {"name": "Alice", "salary": 100}, {"name": "Bobby", "salary": 50}, {"name": "Carl", "salary": 75} ] }
Here is the related Python code.
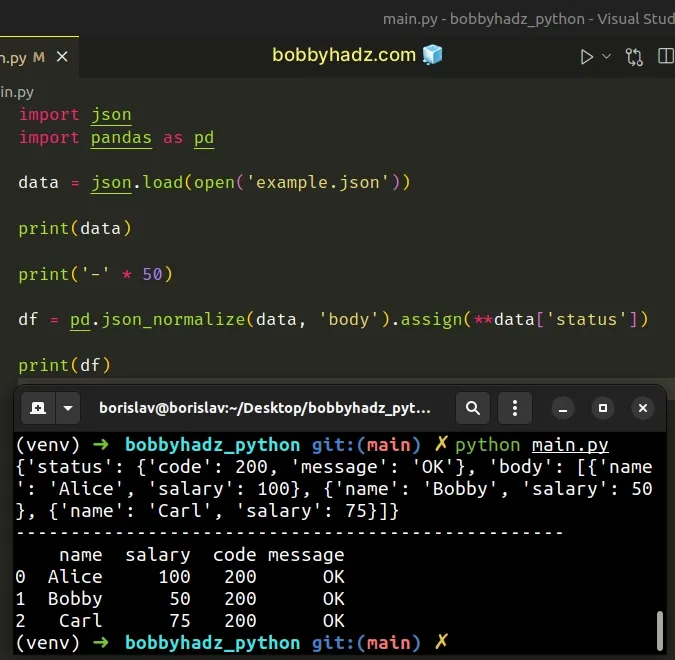
import json import pandas as pd data = json.load(open('example.json')) print(data) print('-' * 50) df = pd.json_normalize(data, 'body').assign(**data['status']) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
{'status': {'code': 200, 'message': 'OK'}, 'body': [{'name': 'Alice', 'salary': 100}, {'name': 'Bobby', 'salary': 50}, {'name': 'Carl', 'salary': 75}]} -------------------------------------------------- name salary code message 0 Alice 100 200 OK 1 Bobby 50 200 OK 2 Carl 75 200 OK
The
DataFrame.assign
method assigns a new column to a DataFrame.
df = pd.json_normalize(data, 'body').assign(**data['status'])
We used the dictionary unpacking ** operator to unpack the key-value pairs of
the status dictionary and added the code and message keys aws columns in
the DataFrame.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

