RuntimeError: Expected scalar type Float but found Double
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# RuntimeError: Expected scalar type Float but found Double
The PyTorch "RuntimeError: Expected scalar type Float but found Double"
occurs when you pass an object of Double type when a Float tensor is
expected.
To solve the error, use the float() method in the call to model().
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import numpy as np import torch import torch.nn as nn from torch.autograd import Variable kernel = torch.from_numpy(np.random.random_sample((1, 3))).double() input_ = torch.from_numpy(np.random.random_sample((1, 1, 1, 6))).double() print(kernel) print(input_) model = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(1, 1, (1, 3), stride=1, padding=0, bias=False) ) model[0].weight.data.copy_(kernel) A = Variable(input_) # ⛔️ RuntimeError: expected scalar type Double but found Float # ⛔️ RuntimeError: expected scalar type Float but found Double out = model(A) print(out.data)
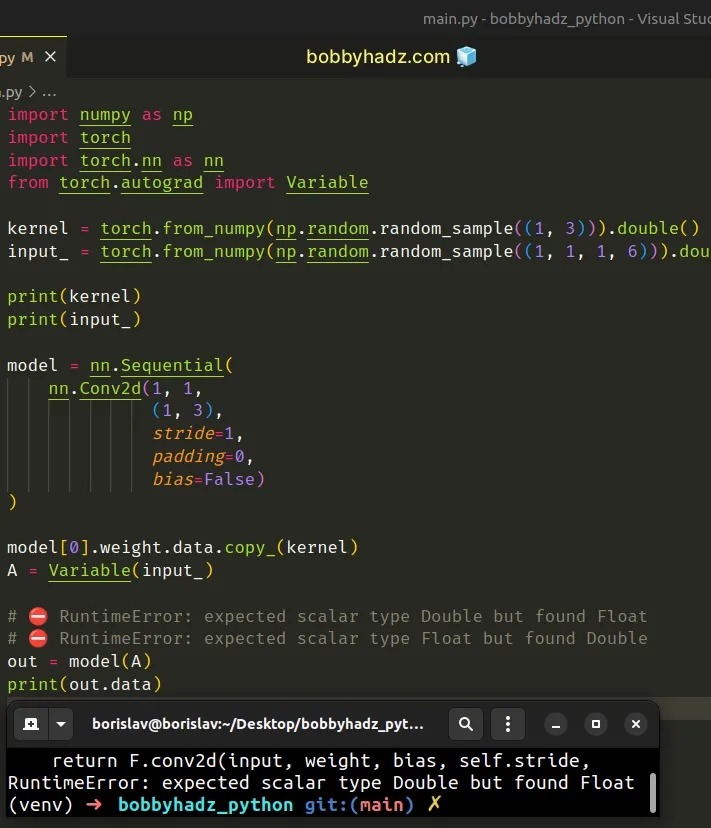
The model() function expects to get called with a floating-point value but
gets called with a double value.
# Convert the tensor to a float when calling model()
One way to solve the error is to convert the tensor to a float when calling the
model() object.
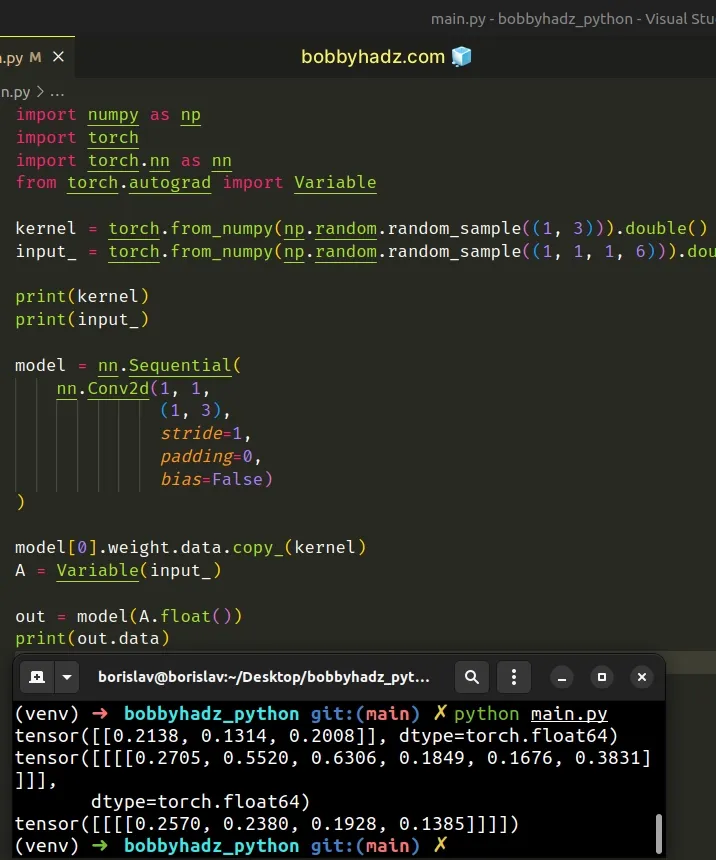
import numpy as np import torch import torch.nn as nn from torch.autograd import Variable kernel = torch.from_numpy(np.random.random_sample((1, 3))).double() input_ = torch.from_numpy(np.random.random_sample((1, 1, 1, 6))).double() print(kernel) print(input_) model = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(1, 1, (1, 3), stride=1, padding=0, bias=False) ) model[0].weight.data.copy_(kernel) A = Variable(input_) # ✅ Call float() method in call to model() out = model(A.float()) # 👈️ print(out.data)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
tensor([[0.2995, 0.2112, 0.1614]], dtype=torch.float64) tensor([[[[0.2408, 0.1265, 0.3745, 0.3934, 0.8293, 0.0694]]]], dtype=torch.float64) tensor([[[[0.1593, 0.1805, 0.3291, 0.3042]]]])
The
Tensor.float()
method is equivalent to self.to(torch.float32).
Therefore, the following code sample is equivalent.
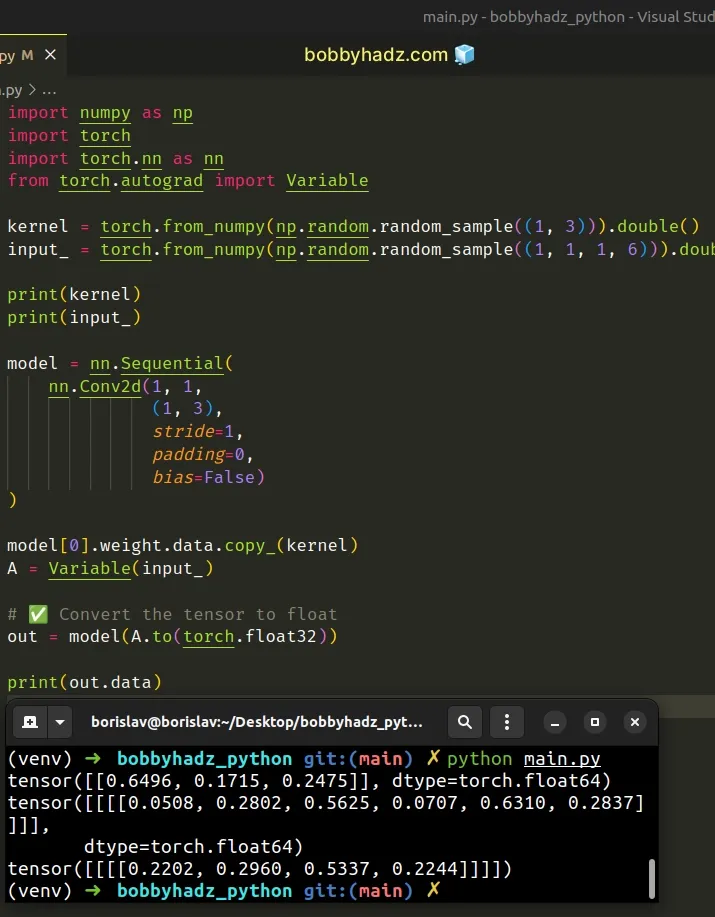
import numpy as np import torch import torch.nn as nn from torch.autograd import Variable kernel = torch.from_numpy(np.random.random_sample((1, 3))).double() input_ = torch.from_numpy(np.random.random_sample((1, 1, 1, 6))).double() print(kernel) print(input_) model = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(1, 1, (1, 3), stride=1, padding=0, bias=False) ) model[0].weight.data.copy_(kernel) A = Variable(input_) # ✅ Convert the tensor to float out = model(A.to(torch.float32)) # 👈️ print(out.data)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
tensor([[0.8885, 0.5696, 0.5680]], dtype=torch.float64) tensor([[[[0.7581, 0.0192, 0.6453, 0.4124, 0.6039, 0.8607]]]], dtype=torch.float64) tensor([[[[1.0510, 0.6189, 1.1513, 1.1993]]]])
Note that torch.float32 is Float and torch.float64 is Double.
# Call the double() method on the model
Your error message will contain the type that you need to convert your tensor or model to.
For example:
- RuntimeError: expected scalar type Double but found Float
- Means that you need to convert the model to Double by calling the
double(). function.
- Means that you need to convert the model to Double by calling the
- RuntimeError: Expected scalar type Float but found Double
- Means that you need to convert the model to Float by calling the
float()function.
- Means that you need to convert the model to Float by calling the
Here is an example of getting the first error.
import numpy as np import torch import torch.nn as nn from torch.autograd import Variable kernel = torch.from_numpy(np.random.random_sample((1, 3))).double() input_ = torch.from_numpy(np.random.random_sample((1, 1, 1, 6))).double() print(kernel) print(input_) model = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(1, 1, (1, 3), stride=1, padding=0, bias=False) ) model[0].weight.data.copy_(kernel) A = Variable(input_) # ⛔️ RuntimeError: expected scalar type Double but found Float out = model(A) print(out.data)
Notice that the error message states: "expected scalar type Double", therefore,
we have to call the double() method on the model.
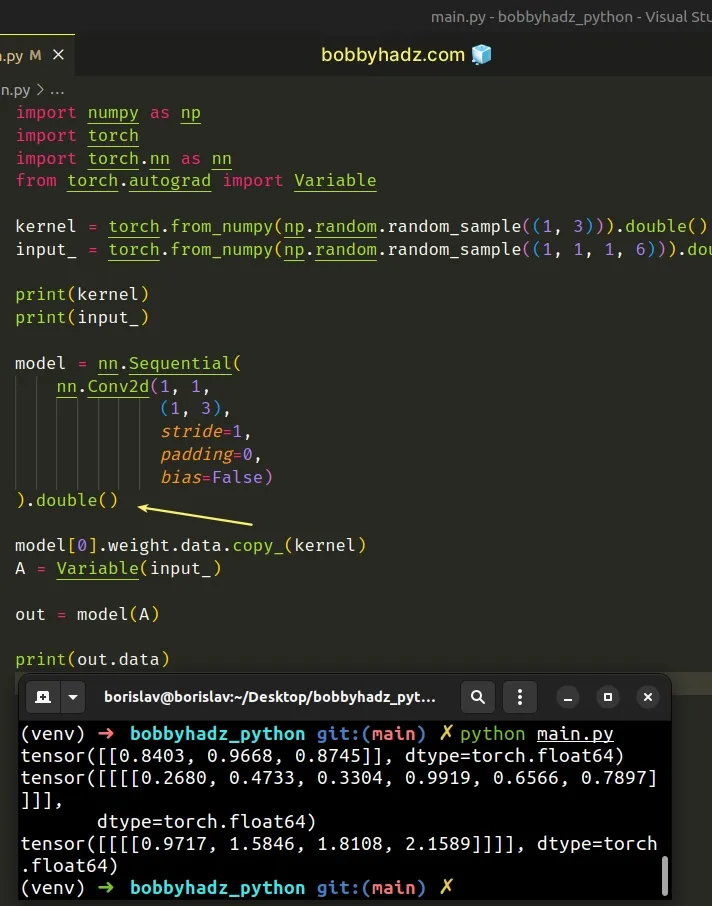
import numpy as np import torch import torch.nn as nn from torch.autograd import Variable kernel = torch.from_numpy(np.random.random_sample((1, 3))).double() input_ = torch.from_numpy(np.random.random_sample((1, 1, 1, 6))).double() print(kernel) print(input_) model = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(1, 1, (1, 3), stride=1, padding=0, bias=False) ).double() # 👈️ call double() function here model[0].weight.data.copy_(kernel) A = Variable(input_) out = model(A) print(out.data)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
tensor([[0.8403, 0.9668, 0.8745]], dtype=torch.float64) tensor([[[[0.2680, 0.4733, 0.3304, 0.9919, 0.6566, 0.7897]]]], dtype=torch.float64) tensor([[[[0.9717, 1.5846, 1.8108, 2.1589]]]], dtype=torch.float64)
Depending on your error message, you might also have to call the float() or
long() methods on the model.
# Calling float() directly on the input
You can also solve the error by calling float() directly on the input.
import numpy as np import torch import torch.nn as nn from torch.autograd import Variable kernel = torch.from_numpy(np.random.random_sample((1, 3))).double() # 👇️ Call float() directly on the input input_ = torch.from_numpy( np.random.random_sample((1, 1, 1, 6)) ).float() print(kernel) print(input_) model = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(1, 1, (1, 3), stride=1, padding=0, bias=False) ) model[0].weight.data.copy_(kernel) A = Variable(input_) out = model(A) print(out.data)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
tensor([[0.1354, 0.4203, 0.9403]], dtype=torch.float64) tensor([[[[0.3909, 0.9533, 0.5753, 0.9366, 0.6232, 0.6240]]]]) tensor([[[[0.9945, 1.2515, 1.0575, 0.9755]]]])
# Calling the float() method after instantiating the Variable() class
You can also solve the error by calling the float() method after instantiating
the Variable() class.
import numpy as np import torch import torch.nn as nn from torch.autograd import Variable kernel = torch.from_numpy(np.random.random_sample((1, 3))).double() input_ = torch.from_numpy(np.random.random_sample((1, 1, 1, 6))).double() print(kernel) print(input_) model = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(1, 1, (1, 3), stride=1, padding=0, bias=False) ) model[0].weight.data.copy_(kernel) # 👇️ Calling float() method here A = Variable(input_).float() out = model(A) print(out.data)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
tensor([[0.3257, 0.1915, 0.0070]], dtype=torch.float64) tensor([[[[0.3627, 0.7398, 0.4000, 0.6038, 0.8281, 0.2235]]]], dtype=torch.float64) tensor([[[[0.2626, 0.3218, 0.2517, 0.3568]]]])
# Using torch.set_default_dtype() to solve the error
You can also use the torch.set_default_dtype() method to solve the error.
Here is an example.
import numpy as np import torch import torch.nn as nn from torch.autograd import Variable # ✅ Set default dtype here torch.set_default_dtype(torch.float64) kernel = torch.from_numpy(np.random.random_sample((1, 3))).double() input_ = torch.from_numpy(np.random.random_sample((1, 1, 1, 6))).double() print(kernel) print(input_) model = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(1, 1, (1, 3), stride=1, padding=0, bias=False) ) model[0].weight.data.copy_(kernel) A = Variable(input_) out = model(A) print(out.data)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
tensor([[0.1479, 0.4833, 0.8837]]) tensor([[[[0.7442, 0.2410, 0.6052, 0.1779, 0.0842, 0.3530]]]]) tensor([[[[0.7614, 0.4853, 0.2499, 0.3789]]]])
Note that torch.float32 is Float and torch.float64 is Double.
So if you get an error, such as:
- RuntimeError: expected scalar type Double but found Float
You would have to pass torch.float64 to the torch.set_default_dtype method
And if you get an error such as:
- "RuntimeError: Expected scalar type Float but found Double"
You would have to pass torch.float32 to the method.
The
torch.set_default_dtype()
method sets the default floating-point dtype to the supplied type.
The method supports torch.float32 and torch.float64 as inputs.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

