Pandas: Create a Tuple from two DataFrame Columns
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- Pandas: Create a Tuple from two DataFrame Columns
- Pandas: Create a Tuple from two DataFrame Columns using apply()
- Pandas: Create a Tuple from two DataFrame Columns using itertuples()
- Pandas: Create a List from two DataFrame Columns
- Pandas: Create a List from two DataFrame Columns using values.tolist()
# Pandas: Create a Tuple from two DataFrame Columns
To create a tuple from two DataFrame columns in Pandas:
- Use the
zip()function to get azipobject of tuples with the values of the two columns. - Convert the
zipobject to a list. - Add the result as a
DataFramecolumn.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'first_name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], 'experience': [10, 15, 20] }) df['stats'] = list(zip(df['salary'], df['experience'])) # first_name salary experience stats # 0 Alice 175.1 10 (175.1, 10) # 1 Bobby 180.2 15 (180.2, 15) # 2 Carl 190.3 20 (190.3, 20) print(df)
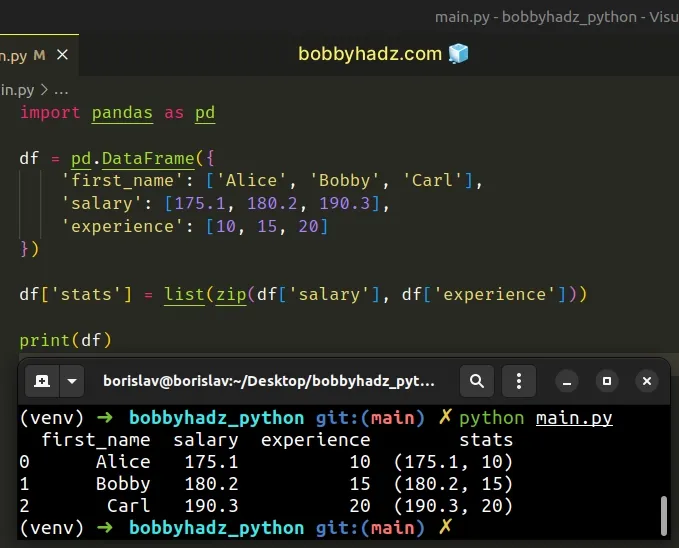
The zip() function iterates over several iterables in parallel and produces tuples with an item from each iterable.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'first_name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], 'experience': [10, 15, 20] }) # [(175.1, 10), (180.2, 15), (190.3, 20)] print(list(zip(df['salary'], df['experience'])))
The first item in each tuple is the salary value and the second is the
experience value.
Once we've created the list of tuples, we can add it as a column to the
DataFrame using bracket notation.
df['stats'] = list(zip(df['salary'], df['experience'])) # first_name salary experience stats # 0 Alice 175.1 10 (175.1, 10) # 1 Bobby 180.2 15 (180.2, 15) # 2 Carl 190.3 20 (190.3, 20) print(df)
The zip() function returns a zip object, so make sure to convert the result
to a list by using the list class.
# Pandas: Create a Tuple from two DataFrame Columns using apply()
You can also use the
DataFrame.apply()
method to create a tuple from two DataFrame columns.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'first_name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], 'experience': [10, 15, 20] }) df['stats'] = df[['salary', 'experience']].apply(tuple, axis=1) # first_name salary experience stats # 0 Alice 175.1 10 (175.1, 10.0) # 1 Bobby 180.2 15 (180.2, 15.0) # 2 Carl 190.3 20 (190.3, 20.0) print(df)
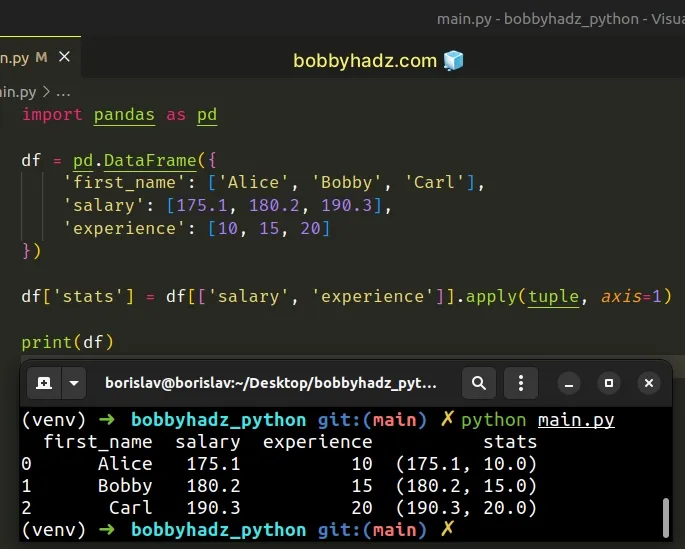
The DataFrame.apply() method applies a function along an axis of the
DataFrame.
We set the axis to 1, so the given function is applied to each row.
df['stats'] = df[['salary', 'experience']].apply(tuple, axis=1)
We passed the tuple class as the first argument to apply(), so the values of
the salary and experience columns get converted to a tuple.
Notice that we used two sets of square brackets when accessing the values of the two columns.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'first_name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], 'experience': [10, 15, 20] }) # salary experience # 0 175.1 10 # 1 180.2 15 # 2 190.3 20 print(df[['salary', 'experience']])
# Pandas: Create a Tuple from two DataFrame Columns using itertuples()
You can also use the
DataFrame.itertuples()
method to create a tuple from two DataFrame columns.
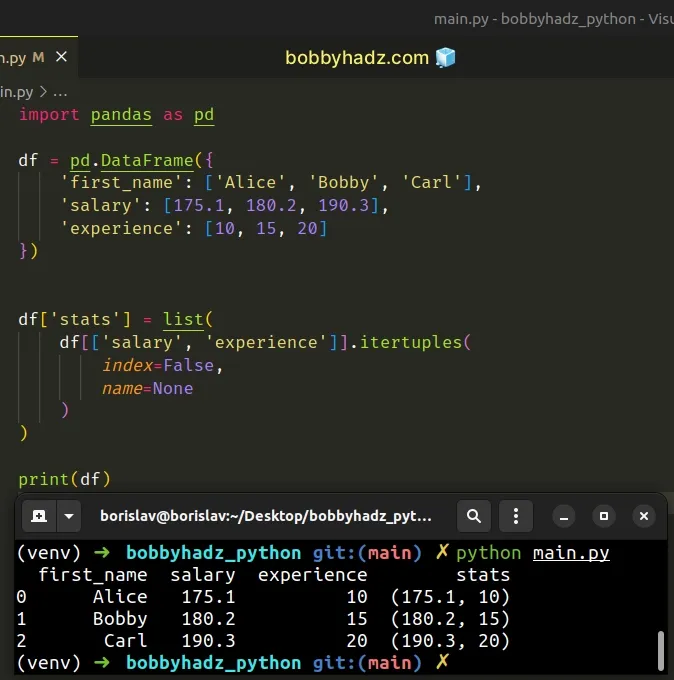
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'first_name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], 'experience': [10, 15, 20] }) df['stats'] = list( df[['salary', 'experience']].itertuples( index=False, name=None ) ) # first_name salary experience stats # 0 Alice 175.1 10 (175.1, 10) # 1 Bobby 180.2 15 (180.2, 15) # 2 Carl 190.3 20 (190.3, 20) print(df)
The method iterates over the rows of the DataFrame as named tuples.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'first_name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], 'experience': [10, 15, 20] }) # [(175.1, 10), (180.2, 15), (190.3, 20)] print( list(df[['salary', 'experience']].itertuples( index=False, name=None )) )
Notice that we set the name argument to None.
This is necessary because, by default, the tuples are named.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'first_name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], 'experience': [10, 15, 20] }) # [Pandas(salary=175.1, experience=10), Pandas(salary=180.2, experience=15), Pandas(salary=190.3, experience=20)] print( list(df[['salary', 'experience']].itertuples( index=False, )) )
We also had to set the index argument to False.
If you don't, the index is the first element of each tuple.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'first_name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], 'experience': [10, 15, 20] }) # [(0, 175.1, 10), (1, 180.2, 15), (2, 190.3, 20)] print( list(df[['salary', 'experience']].itertuples( name=None )) )
# Pandas: Create a List from two DataFrame Columns
If you need to create a list from two DataFrame columns (instead of a tuple),
you can also use the
DataFrame.to_records()
method.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'first_name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], 'experience': [10, 15, 20] }) df['stats'] = list( df[['salary', 'experience']].to_records(index=False) ) # first_name salary experience stats # 0 Alice 175.1 10 [175.1, 10] # 1 Bobby 180.2 15 [180.2, 15] # 2 Carl 190.3 20 [190.3, 20] print(df)
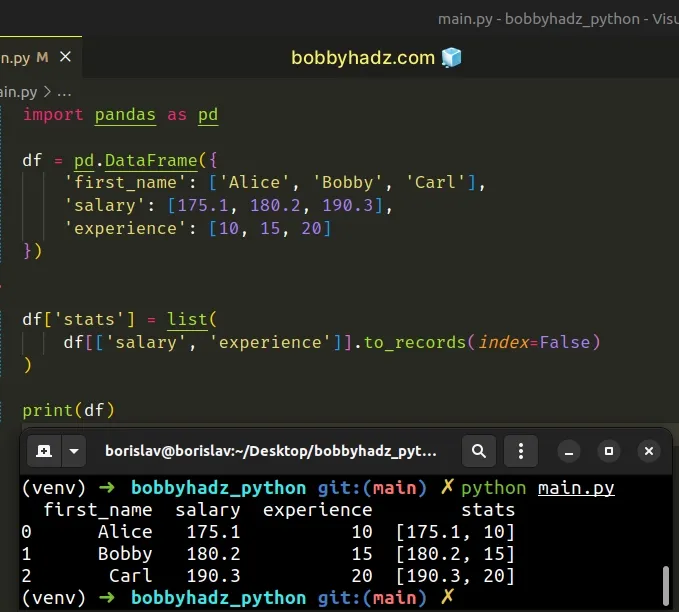
The DataFrame.to_records() method converts the DataFrame to a NumPy record
array.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'first_name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], 'experience': [10, 15, 20] }) # [(175.1, 10), (180.2, 15), (190.3, 20)] print( list( df[['salary', 'experience']].to_records(index=False) ) )
Notice that we had to set the index argument to False.
The argument defaults to True which means that the index is the first element
of each
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'first_name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], 'experience': [10, 15, 20] }) # [(0, 175.1, 10), (1, 180.2, 15), (2, 190.3, 20)] print( list( df[['salary', 'experience']].to_records(index=True) ) )
# Pandas: Create a List from two DataFrame Columns using values.tolist()
You can also use the DataFrame.values.tolist() method to achieve the same
result.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'first_name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], 'experience': [10, 15, 20] }) df['stats'] = df[['salary', 'experience']].values.tolist() # first_name salary experience stats # 0 Alice 175.1 10 [175.1, 10.0] # 1 Bobby 180.2 15 [180.2, 15.0] # 2 Carl 190.3 20 [190.3, 20.0] print(df)
The
DataFrame.values()
method returns a NumPy representation of the DataFrame.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'first_name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], 'experience': [10, 15, 20] }) # [[175.1 10. ] # [180.2 15. ] # [190.3 20. ]] print(df[['salary', 'experience']].values)
The last step is to use the
tolist
method to convert the values ndarray to a list.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

