How to drop all Rows in a Pandas DataFrame in Python
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- How to drop all Rows in a Pandas DataFrame in Python
- Drop all Rows in a DataFrame using DataFrame.iloc
- Drop all rows in a DataFrame by instantiating a new DataFrame with the same columns
# How to drop all Rows in a Pandas DataFrame in Python
To drop all rows in a Pandas DataFrame:
- Call the
drop()method on theDataFrame - Pass the DataFrame's index as the first parameter.
- Set the
inplaceparameter toTrue.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], }) print(df) print('-' * 50) df.drop(df.index, inplace=True) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name salary 0 Alice 175.1 1 Bobby 180.2 2 Carl 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- Empty DataFrame Columns: [name, salary] Index: []
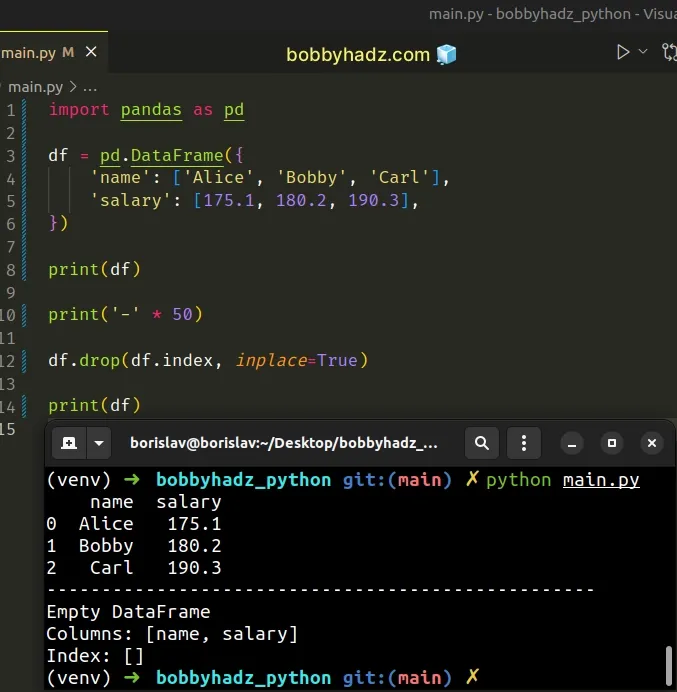
We used the
DataFrame.drop
method to drop all rows from a DataFrame.
The first argument the method takes is the column labels that you want to drop.
The method can be called with a single label or a list-like object of column labels.
We set the argument to
DataFrame.index in order to drop all
rows from the DataFrame.
The DataFrame.index method returns the index (row labels) of the DataFrame.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], }) print(df) print('-' * 50) # 👇️ [0, 1, 2] print(df.index.tolist())
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name salary 0 Alice 175.1 1 Bobby 180.2 2 Carl 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- [0, 1, 2]
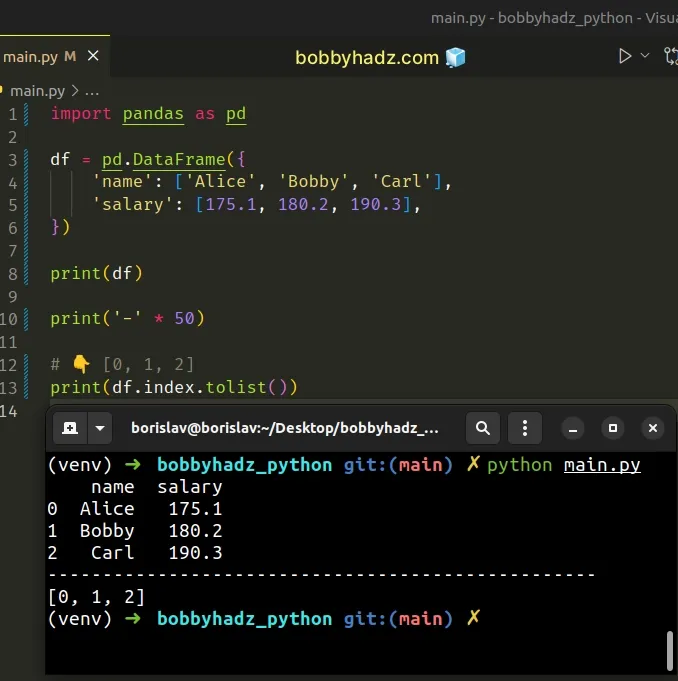
Notice that we also set the inplace argument to True when calling
DataFrame.drop().
df.drop(df.index, inplace=True)
When the inplace argument is set to True, the DataFrame rows are dropped
in place and None is returned.
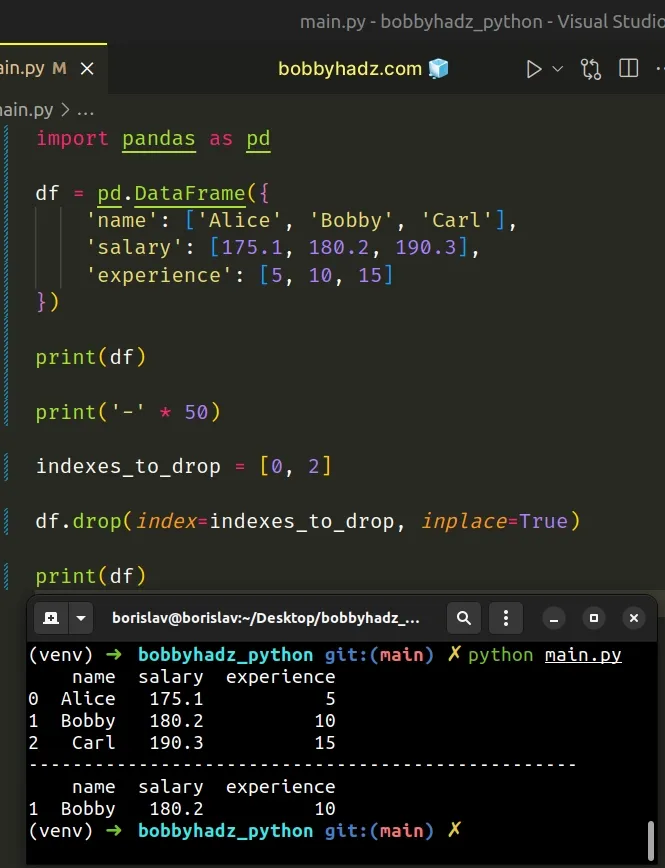
If you only want to drop specific rows from the DataFrame, set the index
argument to a list containing the index labels you want to drop.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], 'experience': [5, 10, 15] }) print(df) print('-' * 50) indexes_to_drop = [0, 2] df.drop(index=indexes_to_drop, inplace=True) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name salary experience 0 Alice 175.1 5 1 Bobby 180.2 10 2 Carl 190.3 15 -------------------------------------------------- name salary experience 1 Bobby 180.2 10
# Drop all Rows in a DataFrame using DataFrame.iloc
You can also use the iloc
position-based indexer to drop all rows in a DataFrame.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], }) print(df) print('-' * 50) df = df.iloc[0:0] print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name salary 0 Alice 175.1 1 Bobby 180.2 2 Carl 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- Empty DataFrame Columns: [name, salary] Index: []
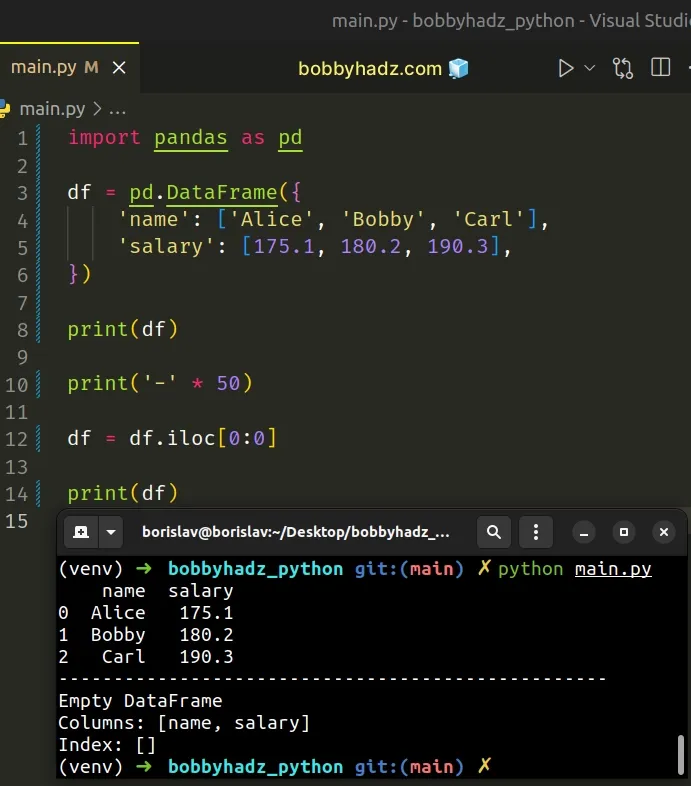
We used the df.iloc position-based indexer to select an empty slice of the
rows.
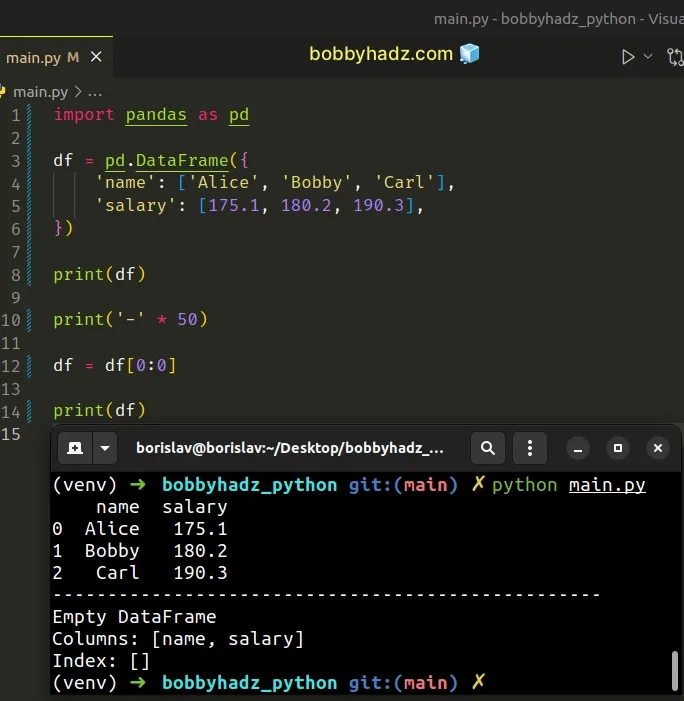
df = df.iloc[0:0]
You can also shorten this a little.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], }) print(df) print('-' * 50) df = df[0:0] print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name salary 0 Alice 175.1 1 Bobby 180.2 2 Carl 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- Empty DataFrame Columns: [name, salary] Index: []
# Drop all rows in a DataFrame by instantiating a new DataFrame with the same columns
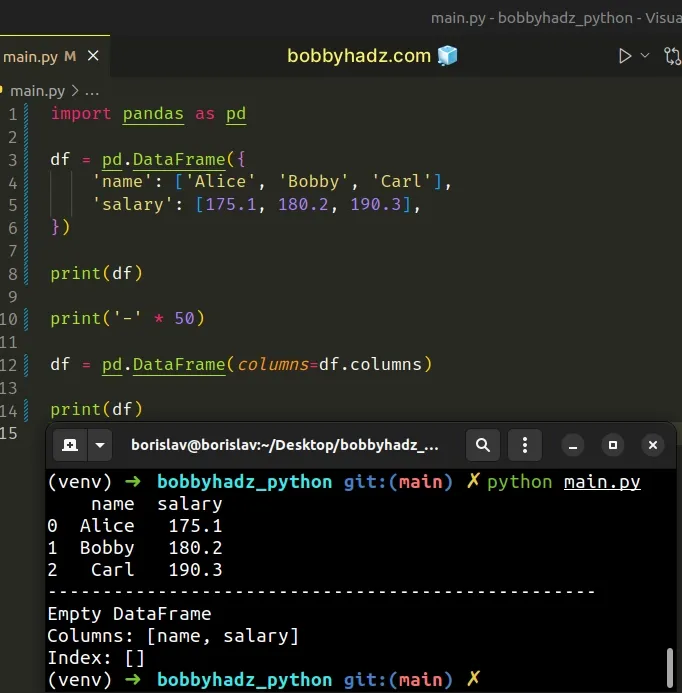
You can also drop all rows in a DataFrame by using the pandas.DataFrame
constructor to instantiate a new DataFrame with the same columns.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], }) print(df) print('-' * 50) df = pd.DataFrame(columns=df.columns) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name salary 0 Alice 175.1 1 Bobby 180.2 2 Carl 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- Empty DataFrame Columns: [name, salary] Index: []
The pandas.DataFrame constructor takes a columns argument.
We set the argument to the columns of the existing DataFrame to create a new
DataFrame with the same columns, without any rows.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], }) # 👇️ Index(['name', 'salary'], dtype='object') print(df.columns)
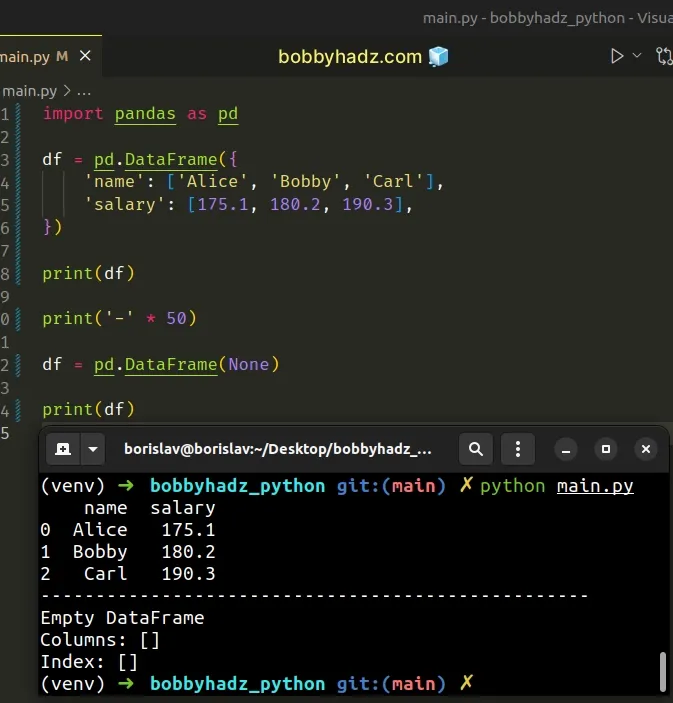
If you don't want to keep the columns around, pass None to the
pandas.DataFrame() constructor.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl'], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3], }) print(df) print('-' * 50) df = pd.DataFrame(None) print(df)
name salary 0 Alice 175.1 1 Bobby 180.2 2 Carl 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- Empty DataFrame Columns: [] Index: []
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Replace whole String if it contains Substring in Pandas
- Pandas: Create new row for each element in List in DataFrame
- ValueError: Length of values does not match length of index
- Get the first Row of each Group in a Pandas DataFrame
- Convert Epoch to Datetime in a Pandas DataFrame
- Calculate the Average for each Row in a Pandas DataFrame
- Pandas: Drop columns if Name contains a given String
- How to repeat Rows N times in a Pandas DataFrame
- How to remove Time from DateTime in Pandas [5 Ways]
- Create Date column from Year, Month and Day in Pandas
- Pandas ValueError: Cannot index with multidimensional key
- ValueError: Grouper for 'X' not 1-dimensional [Solved]
- Check if all values in a Column are Equal in Pandas
- Pandas: Get Nth row or every Nth row in a DataFrame
- Pandas: Select first N or last N columns of DataFrame
- Pandas: Describe not showing all columns in DataFrame [Fix]
- Pandas: Select Rows between two values in DataFrame
- Pandas: How to Filter a DataFrame by value counts
- NumPy: Get the indices of the N largest values in an Array
- Pandas: Merge only specific DataFrame columns
- How to modify a Subset of Rows in a Pandas DataFrame
- How to Start the Index of a Pandas DataFrame at 1
- Pandas: DataFrame.reset_index() not working [Solved]
- How to Add Axis Labels to a Plot in Pandas [5 Ways]
- How to Create a Set from a Series in Pandas
- Matplotlib: No artists with labels found to put in legend

