Pandas: Find common Rows (intersection) between 2 DataFrames
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·4 min
# Table of Contents
- Pandas: Find common Rows (intersection) between 2 DataFrames
- Specifying multiple columns in the call to merge()
# Pandas: Find common Rows (intersection) between 2 DataFrames
Use the pandas.merge() method to find the common rows (intersection) between
2 DataFrames.
The method can be passed an on argument that stores a list of column names
to join on.
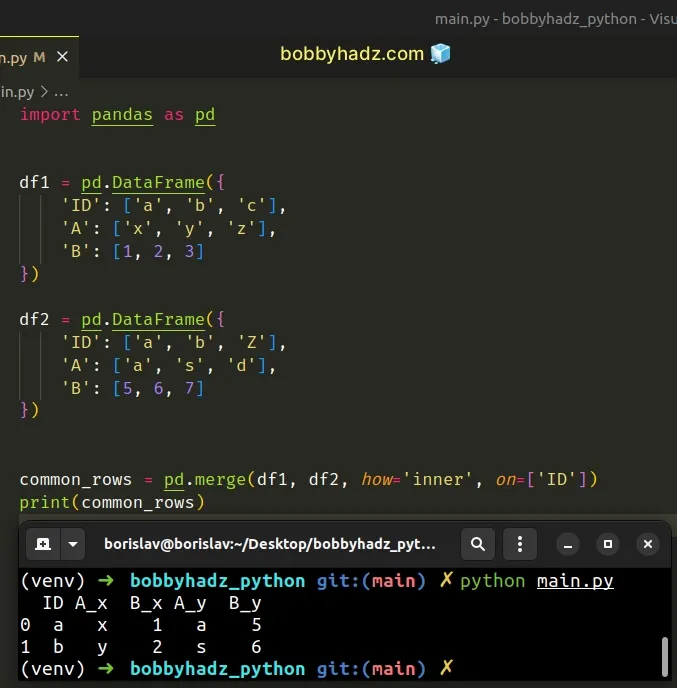
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.DataFrame({ 'ID': ['a', 'b', 'c'], 'A': ['x', 'y', 'z'], 'B': [1, 2, 3] }) df2 = pd.DataFrame({ 'ID': ['a', 'b', 'Z'], 'A': ['a', 's', 'd'], 'B': [5, 6, 7] }) common_rows = pd.merge(df1, df2, how='inner', on=['ID']) # ID A_x B_x A_y B_y # 0 a x 1 a 5 # 1 b y 2 s 6 print(common_rows)
Note: if you need to drop the NA values (if any) after finding the common rows,
use the DataFrame.dropna() method.
common_rows = pd.merge(df1, df2, how='inner', on=['ID']) common_rows.dropna(inplace=True)
The code sample finds the common rows between the two DataFrames based on the
ID column.
In other words, if the ID value in df1 matches the ID value in df2, the
corresponding row is returned.
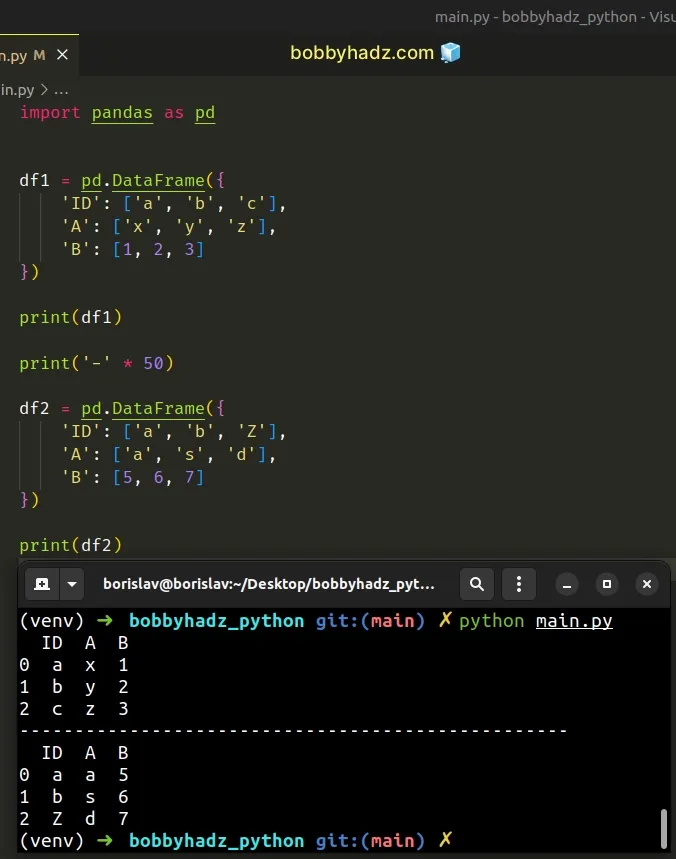
Here are the two DataFrames from the example.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.DataFrame({ 'ID': ['a', 'b', 'c'], 'A': ['x', 'y', 'z'], 'B': [1, 2, 3] }) # ID A B # 0 a x 1 # 1 b y 2 # 2 c z 3 print(df1) print('-' * 50) df2 = pd.DataFrame({ 'ID': ['a', 'b', 'Z'], 'A': ['a', 's', 'd'], 'B': [5, 6, 7] }) # ID A B # 0 a a 5 # 1 b s 6 # 2 Z d 7 print(df2)
We passed the following arguments to the DataFrame.merge() method:
- The first
DataFrame. - The second
DataFrame - The type of merge to be performed. The
innervalue means "use an intersection of keys from both frames, similar to a SQL inner join and preserve the order of the left keys". - The
onargument is a list of column names to join on. These column names must be contained in both DataFrames.
common_rows = pd.merge(df1, df2, how='inner', on=['ID']) # ID A_x B_x A_y B_y # 0 a x 1 a 5 # 1 b y 2 s 6 print(common_rows)
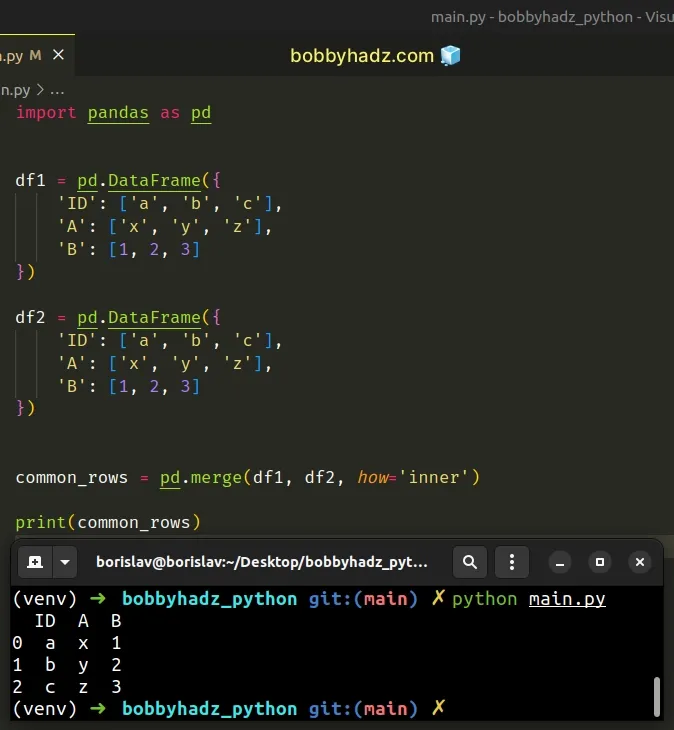
If the on argument is None or not provided, then the method defaults to the
intersection of the columns in both DataFrames.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.DataFrame({ 'ID': ['a', 'b', 'c'], 'A': ['x', 'y', 'z'], 'B': [1, 2, 3] }) df2 = pd.DataFrame({ 'ID': ['a', 'b', 'c'], 'A': ['x', 'y', 'z'], 'B': [1, 2, 3] }) common_rows = pd.merge(df1, df2, how='inner') # ID A B # 0 a x 1 # 1 b y 2 # 2 c z 3 print(common_rows)
# Specifying multiple columns in the call to merge()
You can specify multiple columns in the on list when calling pandas.merge().
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.DataFrame({ 'ID': ['a', 'b', 'c'], 'A': ['x', 'y', 'z'], 'B': [1, 2, 3] }) print(df1) print('-' * 50) df2 = pd.DataFrame({ 'ID': ['a', 'b', 'Z'], 'A': ['x', 'y', 'z'], 'B': [5, 6, 7] }) print(df2) print('-' * 50) common_rows = pd.merge(df1, df2, how='inner', on=['ID', 'A']) # 👇️ Optionally drop NA values common_rows.dropna(inplace=True) # ID A B_x B_y # 0 a x 1 5 # 1 b y 2 6 print(common_rows)
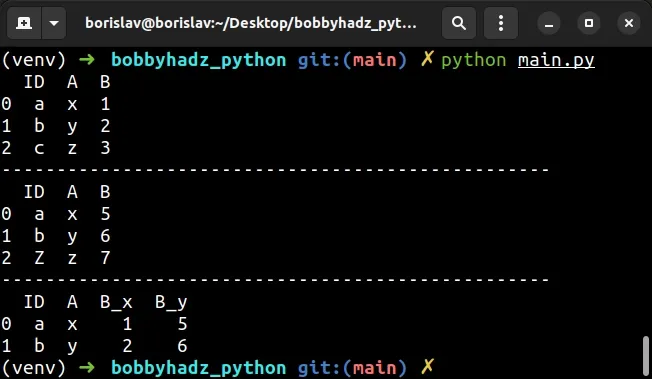
The code sample selects the rows where the ID and A columns in both
DataFrames have matching values.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Usecols do not match columns, columns expected but not found
- ValueError: Shape of passed values is X, indices imply Y
- ValueError: Length of values does not match length of index
- How to get the Memory size of a DataFrame in Pandas
- Pandas: Select distinct across multiple DataFrame columns
- Filter rows in a Pandas DataFrame using Regex
- Pandas: Get the Rows that are NOT in another DataFrame
- How to Transpose a Pandas DataFrame without index
- Pandas: How to keep the Index when merging DataFrames
- Pandas: Merge only specific DataFrame columns
- How to modify a Subset of Rows in a Pandas DataFrame
- How to Start the Index of a Pandas DataFrame at 1
- Pandas: DataFrame.reset_index() not working [Solved]
- How to Add Axis Labels to a Plot in Pandas [5 Ways]
- How to Create a Set from a Series in Pandas
- Pandas: Remove non-numeric rows in a DataFrame column
- NumPy: Apply a Mask from one Array to another Array
- Pandas: Select rows based on a List of Indices
- Pandas: Find an element's Index in Series [7 Ways]

