Pandas: Convert timezone-aware DateTimeIndex to naive timestamp
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Pandas: Convert timezone-aware DateTimeIndex to naive timestamp
- Using the tz_localize() method to get a naive local time
- Using the tz_convert() method to get a naive UTC time
- Pandas: Convert timezone-aware DateTimeIndex to naive timestamp using replace()
- Use apply() if you have a Series with multiple timezones
- The same approach can be used for a Pandas Timestamp
# Pandas: Convert timezone-aware DateTimeIndex to naive timestamp
To convert a timezone-aware DateTimeIndex to a naive timestamp, in a certain
timezone:
- Use the
tz_localize()method to remove the timezone information and get a naive local time. - Or use the
tz_convert()method to remove the timezone information and get the result in naive UTC time.
# Using the tz_localize() method to get a naive local time
The first example uses the tz_localize() method to convert a timezone-aware
DateTimeIndex to a naive local time.
import pandas as pd dt_index = pd.date_range( start='2023-04-11 13:30:00', periods=2, freq='H', tz='US/Pacific', ) # DatetimeIndex(['2023-04-11 13:30:00-07:00', '2023-04-11 14:30:00-07:00'], dtype='datetime64[ns, US/Pacific]', freq='H') print(dt_index) dt_index = dt_index.tz_localize(None) # DatetimeIndex(['2023-04-11 13:30:00', '2023-04-11 14:30:00'], dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq=None) print(dt_index)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
DatetimeIndex(['2023-04-11 13:30:00-07:00', '2023-04-11 14:30:00-07:00'], dtype='datetime64[ns, US/Pacific]', freq='H') DatetimeIndex(['2023-04-11 13:30:00', '2023-04-11 14:30:00'], dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq=None)
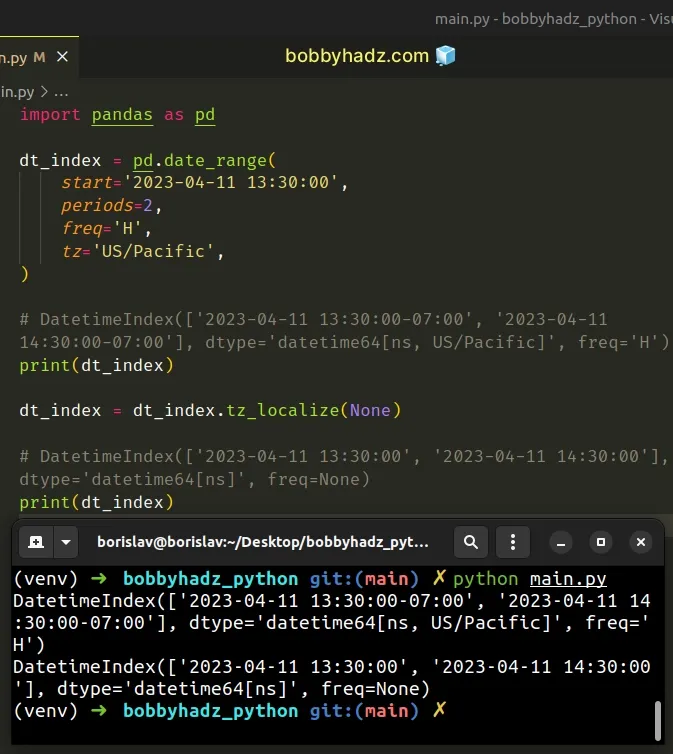
When the
DatetimeIndex.tz_localize()
method is called with a None value, it removes the time zone information and
preserves the local time.
In other words, the result is a naive local time.
# Using the tz_convert() method to get a naive UTC time
If you need to convert a timezone-aware DateTimeIndex to naive UTC time, use
the
DateTimeIndex.tz_convert()
method.
import pandas as pd dt_index = pd.date_range( start='2023-04-11 13:30:00', periods=2, freq='H', tz='US/Pacific', ) # DatetimeIndex(['2023-04-11 13:30:00-07:00', '2023-04-11 14:30:00-07:00'], dtype='datetime64[ns, US/Pacific]', freq='H') print(dt_index) dt_index = dt_index.tz_convert(None) # DatetimeIndex(['2023-04-11 20:30:00', '2023-04-11 21:30:00'], dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='H') print(dt_index)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
DatetimeIndex(['2023-04-11 13:30:00-07:00', '2023-04-11 14:30:00-07:00'], dtype='datetime64[ns, US/Pacific]', freq='H') DatetimeIndex(['2023-04-11 20:30:00', '2023-04-11 21:30:00'], dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='H')
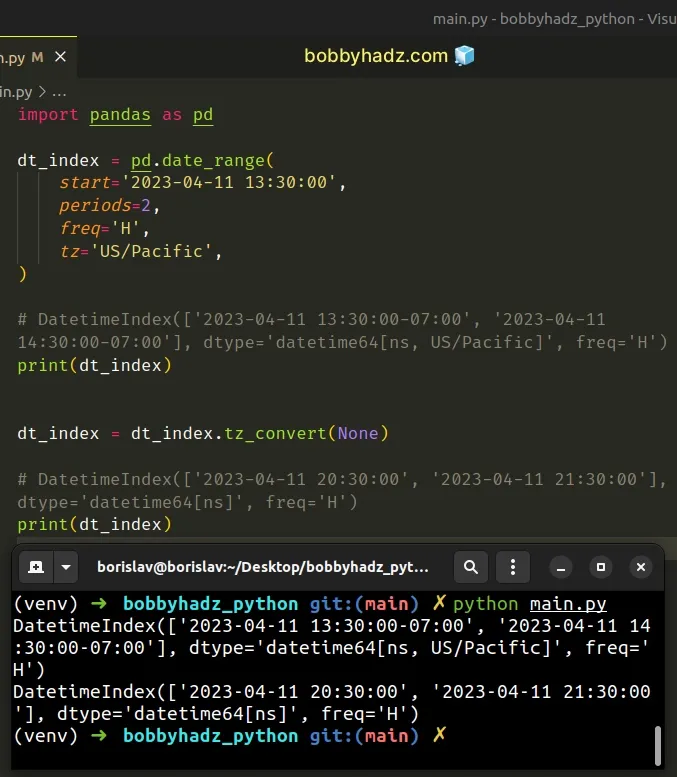
When the DateTimeIndex.tz_convert() method is called with a None value, it
converts the datetime to UTC and removes the timezone information.
In other words, the result is a naive UTC time.
The DatetimeIndex.tz_convert() method is also often used to convert a
timezone-aware Datetime array or index from one timezone to another.
import pandas as pd dt_index = pd.date_range( start='2023-04-11 13:30:00', periods=2, freq='H', tz='US/Pacific', ) # DatetimeIndex(['2023-04-11 13:30:00-07:00', '2023-04-11 14:30:00-07:00'], dtype='datetime64[ns, US/Pacific]', freq='H') print(dt_index) dt_index = dt_index.tz_convert('US/Central') # DatetimeIndex(['2023-04-11 15:30:00-05:00', '2023-04-11 16:30:00-05:00'], dtype='datetime64[ns, US/Central]', freq='H') print(dt_index)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
DatetimeIndex(['2023-04-11 13:30:00-07:00', '2023-04-11 14:30:00-07:00'], dtype='datetime64[ns, US/Pacific]', freq='H') DatetimeIndex(['2023-04-11 15:30:00-05:00', '2023-04-11 16:30:00-05:00'], dtype='datetime64[ns, US/Central]', freq='H')
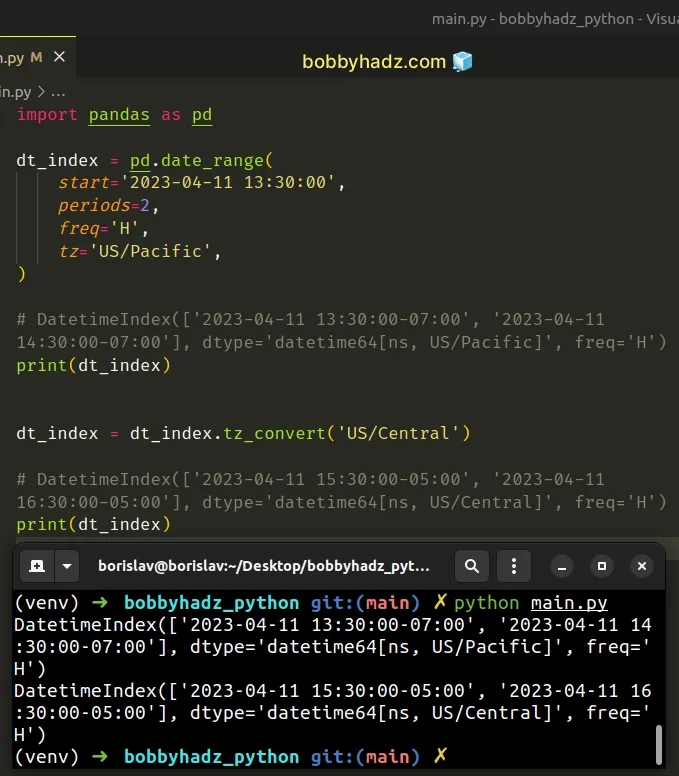
The only argument we passed to the DateTimeIndex.tz_convert() method is the
timezone.
The timestamps in the array/index get converted to the specified timezone.
As previously noted, if the tz argument is set to None, the method converts
the datetime to UTC and removes the timezone information.
# Pandas: Convert timezone-aware DateTimeIndex to naive timestamp using replace()
You can also use the
Timestamp.replace()
method to convert a timezone-aware DateTimeIndex to a naive timestamp.
import pandas as pd dt_index = pd.date_range( start='2023-04-11 13:30:00', periods=2, freq='H', tz='US/Pacific', ) # DatetimeIndex(['2023-04-11 13:30:00-07:00', '2023-04-11 14:30:00-07:00'], dtype='datetime64[ns, US/Pacific]', freq='H') print(dt_index) dt_index = pd.DatetimeIndex( [tstamp.replace(tzinfo=None) for tstamp in dt_index] ) # DatetimeIndex(['2023-04-11 13:30:00', '2023-04-11 14:30:00'], dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq=None) print(dt_index)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
DatetimeIndex(['2023-04-11 13:30:00-07:00', '2023-04-11 14:30:00-07:00'], dtype='datetime64[ns, US/Pacific]', freq='H') DatetimeIndex(['2023-04-11 13:30:00', '2023-04-11 14:30:00'], dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq=None)
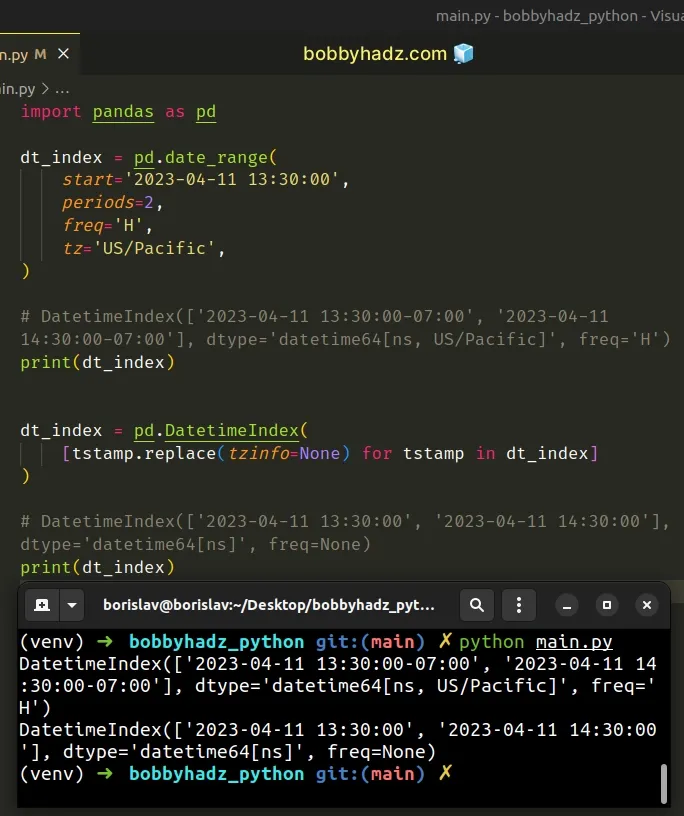
We used a list comprehension to iterate over the DatetimeIndex.
List comprehensions are used to perform some operation for every element or select a subset of elements that meet a condition.
On each iteration, we use the Timestamp.replace() method to create a timezone
unaware object from an aware object.
dt_index = pd.DatetimeIndex( [tstamp.replace(tzinfo=None) for tstamp in dt_index] )
When the tzinfo argument is set to None, the method removes the timezone
information.
# Use apply() if you have a Series with multiple timezones
You can use the Series.apply() method if you have a Series with multiple
different timezones.
import pandas as pd series = pd.Series([pd.Timestamp.now(tz='US/Pacific'), pd.Timestamp.now(tz='Europe/Amsterdam'), pd.Timestamp.now(tz='Europe/Brussels')]) series = series.apply(lambda x: x.tz_localize(None)) # 0 2023-08-22 06:48:19.822881 # 1 2023-08-22 15:48:19.824277 # 2 2023-08-22 15:48:19.824789 # dtype: datetime64[ns] print(series)
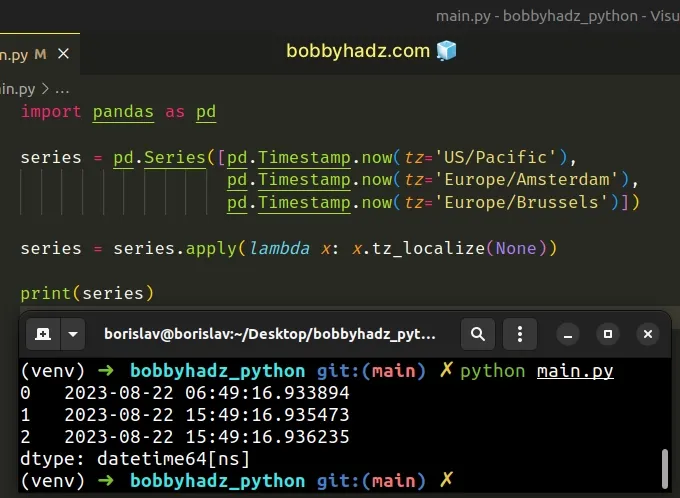
The Series.apply() method invokes a function on each value of the Series.
We called the tz_localize() method on each timestamp.
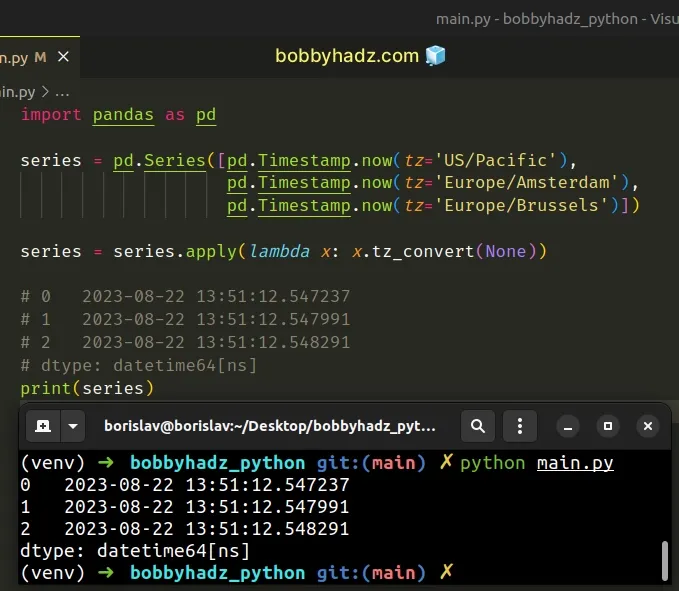
If you need to get the results in UTC, use the tz_convert method instead.
import pandas as pd series = pd.Series([pd.Timestamp.now(tz='US/Pacific'), pd.Timestamp.now(tz='Europe/Amsterdam'), pd.Timestamp.now(tz='Europe/Brussels')]) series = series.apply(lambda x: x.tz_convert(None)) # 0 2023-08-22 13:51:12.547237 # 1 2023-08-22 13:51:12.547991 # 2 2023-08-22 13:51:12.548291 # dtype: datetime64[ns] print(series)
# The same approach can be used for a Pandas Timestamp
The same approach can be used if you have a Pandas Timestamp object.
For example, if you need to convert a timezone-aware Timestamp to a naive
timestamp and get the result in local time, use tz_localize().
import pandas as pd tstamp = pd.Timestamp.now(tz='US/Pacific') # 2023-08-22 06:42:03.820451-07:00 print(tstamp) naive_tstamp = tstamp.tz_localize(None) # 2023-08-22 06:42:03.820451 print(naive_tstamp)
If you need to get the result in UTC, use the tz_convert() method instead.
import pandas as pd tstamp = pd.Timestamp.now(tz='US/Pacific') # 2023-08-22 06:42:03.820451-07:00 print(tstamp) naive_tstamp = tstamp.tz_convert(None) # 2023-08-22 13:42:03.820451 print(naive_tstamp)
This is equivalent to calling the utcnow() method before calling
tz_localize().
import pandas as pd tstamp = pd.Timestamp.now(tz='US/Pacific') # 2023-08-22 06:42:03.820451-07:00 print(tstamp) naive_tstamp = tstamp.utcnow().tz_localize(None) # 2023-08-22 13:42:03.820451 print(naive_tstamp)
Or calling the utcnow() method before calling tz_convert().
import pandas as pd tstamp = pd.Timestamp.now(tz='US/Pacific') # 2023-08-22 06:42:03.820451-07:00 print(tstamp) naive_tstamp = tstamp.utcnow().tz_convert(None) # 2023-08-22 13:42:03.820451 print(naive_tstamp)
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

