ValueError: If using all scalar values, you must pass index
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- ValueError: If using all scalar values, you must pass index
- Wrap each value in a list [] to solve the error
- Creating a DataFrame that contains scalar values with index
- Wrap the dictionary in a list to solve the error
- Solving the error by using Series.to_frame()
- Maybe you meant to use the Series class
- Specifying the columns explicitly to solve the error
- Setting the orient to "index" to solve the error
# ValueError: If using all scalar values, you must pass index
The Pandas "ValueError: If using all scalar values, you must pass an index"
occurs when you try to create a DataFrame containing only scalar values (e.g.
integers, strings or floats).
To solve the error, wrap each value in a list [] or set the index argument
when creating the DataFrame.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': 50, 'B': 100, 'C': 150 }) # ⛔️ ValueError: If using all scalar values, you must pass an index print(df)
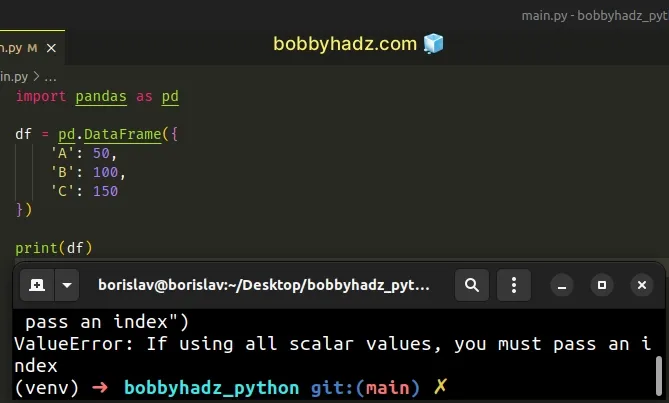
We instantiated the
DataFrame class
with only scalar values (integers) without supplying the index argument.
# Wrap each value in a list [] to solve the error
One way to solve the error is to wrap each value in a list by using square brackets.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': [50], 'B': [100], 'C': [150] }) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
A B C 0 50 100 150
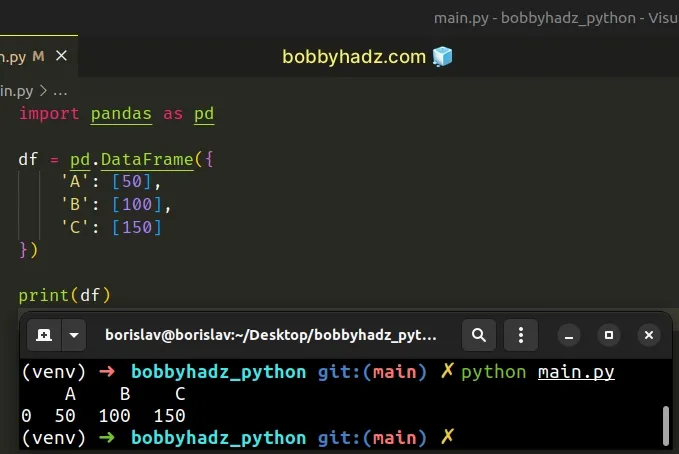
Notice that we wrapped the DataFrame values in square brackets [] to use
lists as values instead of scalars (e.g. integers, strings or floats).
When using this approach, you can specify multiple rows by separating the list items with a comma.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': [50, 60, 70], 'B': [100, 110, 1120], 'C': [150, 160, 170] }) print(df) print('-' * 50) print(df['A']) print('-' * 50) print(df['B'])
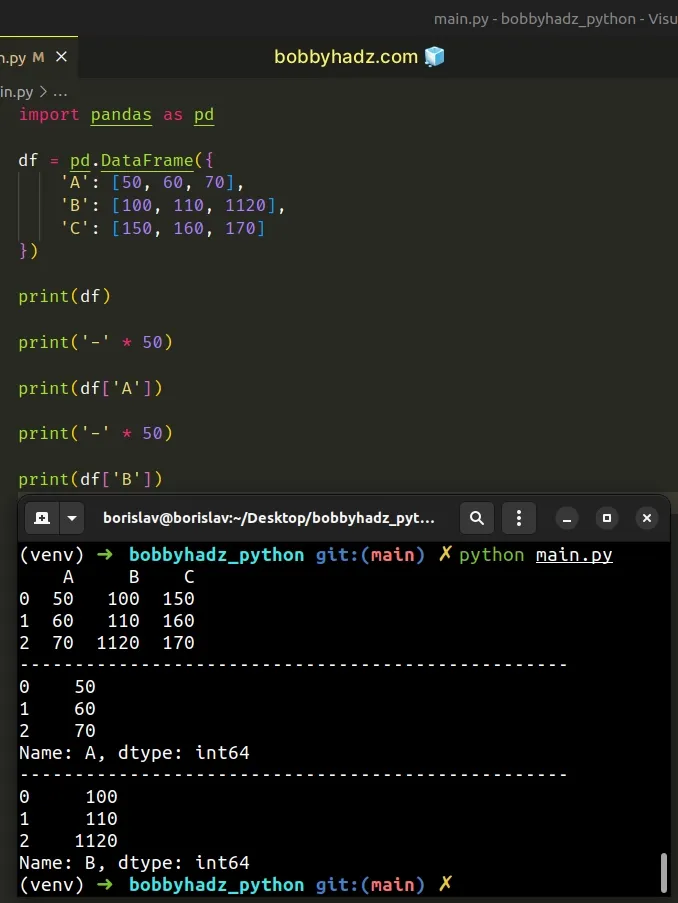
# Creating a DataFrame that contains scalar values with index
If you want to create a DataFrame that only contains scalar values, you have
to supply the index argument.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': 50, 'B': 100, 'C': 150 }, index=[0] ) # A B C # 0 50 100 150 print(df) print('-' * 50) # 0 50 # Name: A, dtype: int64 print(df['A'])
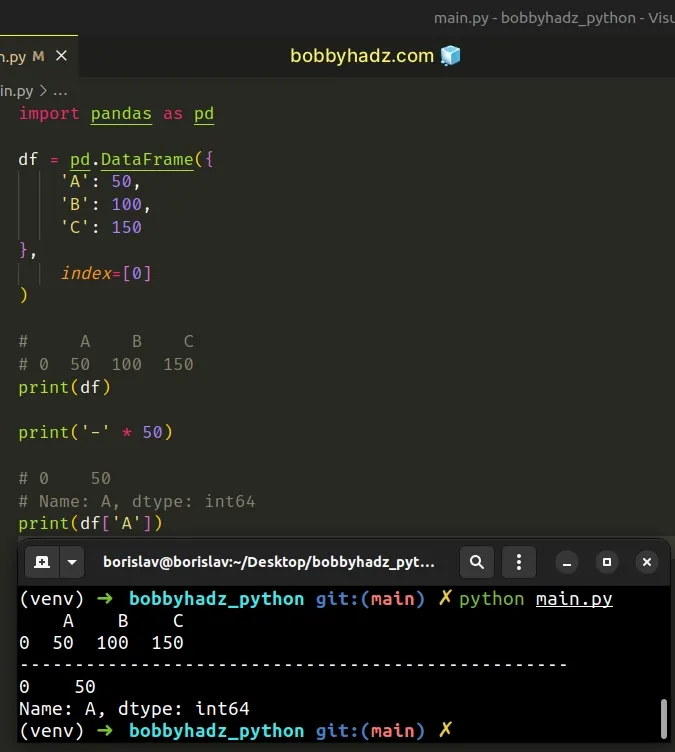
The index argument is used to specify the index to use for the resulting
DataFrame.
When you construct a DataFrame containing only scalar values, you should only
pass a single value in the index list.
# Wrap the dictionary in a list to solve the error
You can also solve the error by wrapping the dictionary in a list [].
import pandas as pd a_dict = { 'A': 50, 'B': 100, 'C': 150 } df = pd.DataFrame([a_dict]) # A B C # 0 50 100 150 print(df)
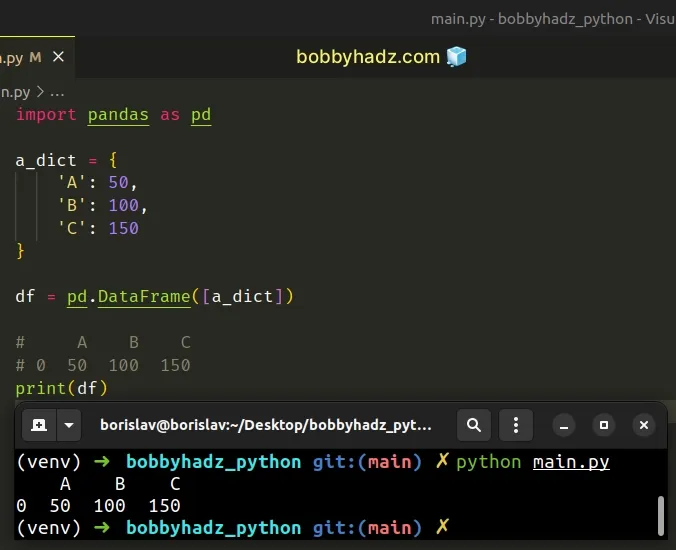
Notice that we wrapped the dictionary in square brackets [].
This way, we passed a list containing a dictionary to the pandas.DataFrame()
class (and not a dictionary with scalar values).
Now the index is implied to be 0.
We could've also used the DataFrame.from_records() method.
import pandas as pd a_dict = { 'A': 50, 'B': 100, 'C': 150 } df = pd.DataFrame.from_records([a_dict]) # A B C # 0 50 100 150 print(df)
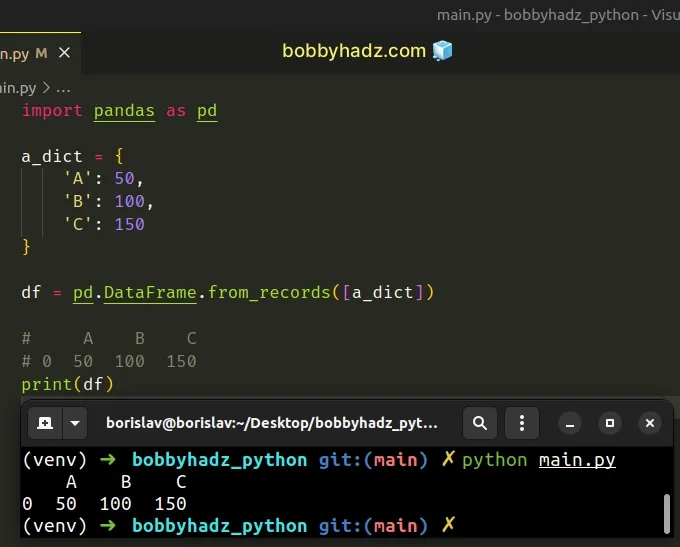
The
DataFrame.from_records()
method converts a structured or record ndarray to a DataFrame.
You don't have to explicitly set the index when calling from_records() but
you could.
import pandas as pd a_dict = { 'A': 50, 'B': 100, 'C': 150 } df = pd.DataFrame.from_records([a_dict], index=[0]) # A B C # 0 50 100 150 print(df)
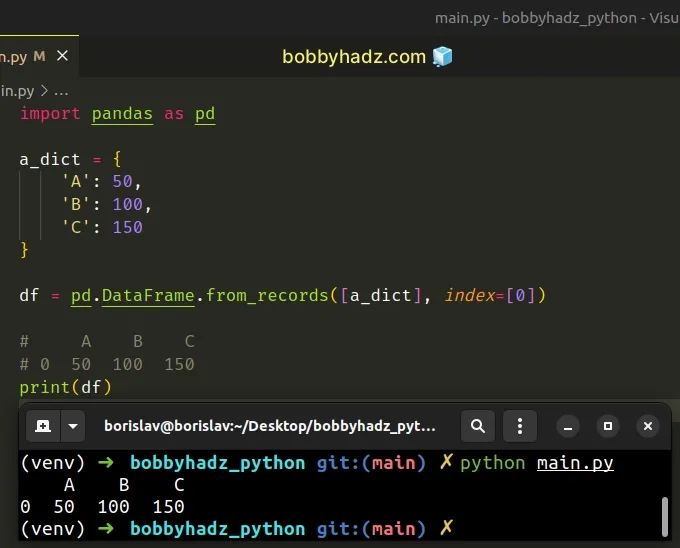
# Solving the error by using Series.to_frame()
You can also use the Series.to_frame method to solve the error.
import pandas as pd a_dict = { 'A': 50, 'B': 100, 'C': 150 } df = pd.Series(a_dict).to_frame() # 0 # A 50 # B 100 # C 150 print(df)
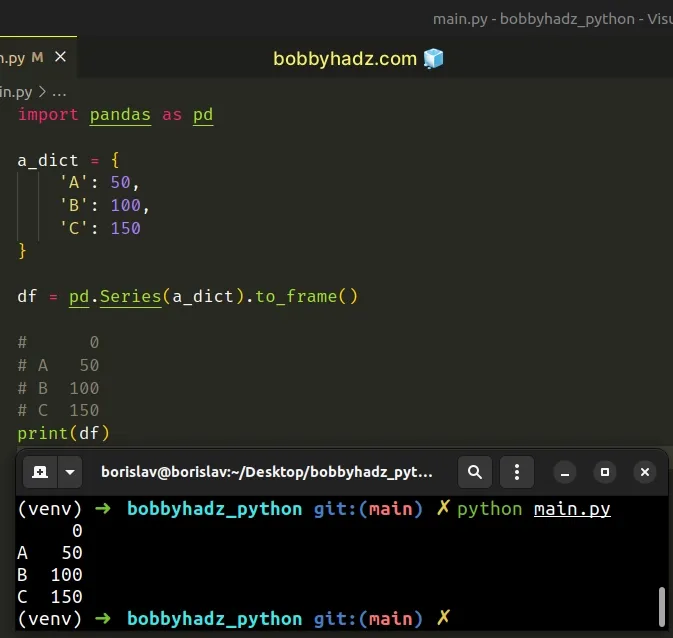
The
pandas.Series
is used to create a one-dimensional ndarray with axis labels.
Series objects have a to_frame() method that converts the Series to a
DataFrame.
The method returns the DataFrame representation of the series.
# Maybe you meant to use the Series class
You might've also meant to use the pandas.Series class instead.
import pandas as pd a_dict = { 'A': 50, 'B': 100, 'C': 150 } series = pd.Series(a_dict) # A 50 # B 100 # C 150 # dtype: int64 print(series) print('-' * 50) df = pd.DataFrame() df = df.assign(col_name=series.values) # col_name # 0 50 # 1 100 # 2 150 print(df)
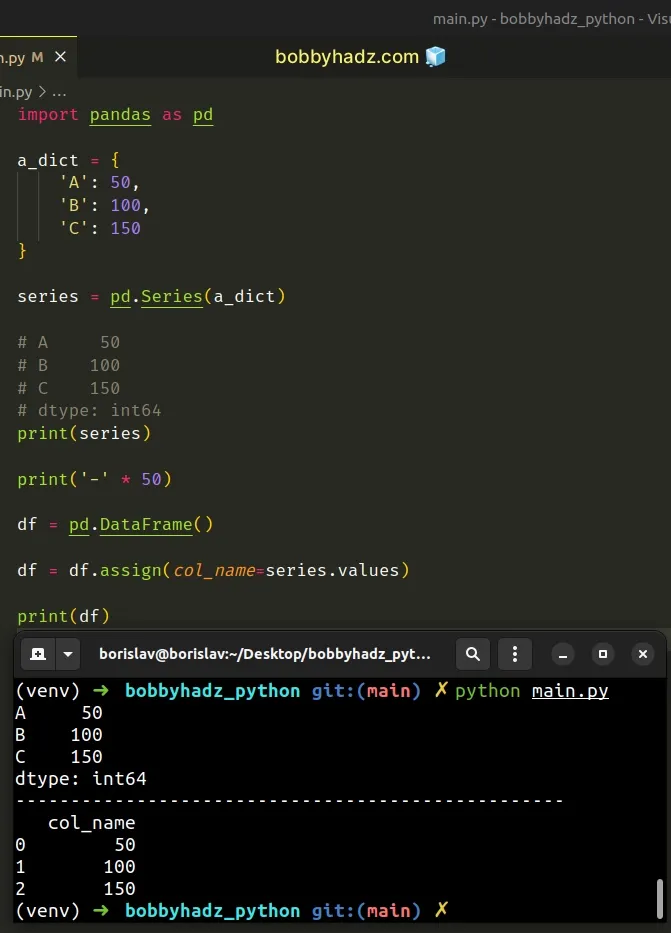
The code sample uses the Series class to create a Series object and then
adds the values of the Series to a DataFrame column.
# Specifying the columns explicitly to solve the error
You can also solve the error by specifying the columns explicitly when
instantiating the DataFrame() class.
import pandas as pd a_dict = { 'A': 50, 'B': 100, 'C': 150 } df = pd.DataFrame(a_dict.items(), columns=['X', 'Y']) # X Y # 0 A 50 # 1 B 100 # 2 C 150 print(df) print('-' * 50) # 0 A # 1 B # 2 C # Name: X, dtype: object print(df['X'])
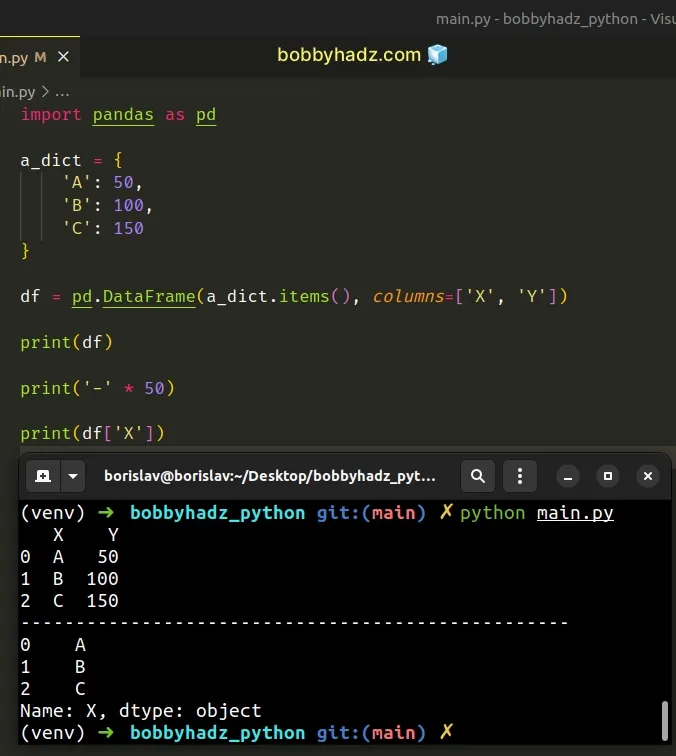
The columns argument is used to set the columns labels to use for the
resulting DataFrame when the supplied data doesn't have any.
# Setting the orient to "index" to solve the error
You can also solve the error by setting the orient argument to "index" when
calling
DataFrame.from_dict.
import pandas as pd a_dict = { 'A': 50, 'B': 100, 'C': 150 } df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(a_dict, orient='index') # 0 # A 50 # B 100 # C 150 print(df)
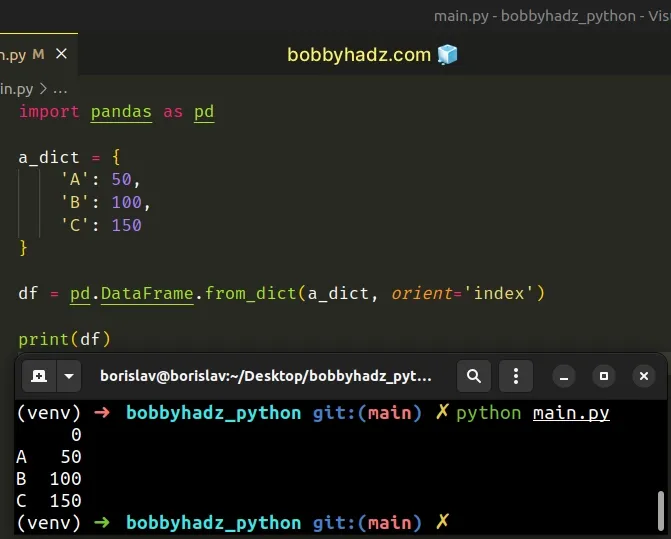
The DataFrame.from_dict() method constructs a DataFrame from a dictionary of
array-like objects or nested dictionaries.
The orient argument is used to specify the "orientation" of the data.
When the orient argument is set to "index", the keys are used as rows.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Multiply the Values in a Dictionary in Python
- Calculate the Average for each Row in a Pandas DataFrame
- How to drop all Rows in a Pandas DataFrame in Python
- How to drop all Rows in a Pandas DataFrame in Python
- Pandas: Get Nth row or every Nth row in a DataFrame
- Pandas: Select Rows between two values in DataFrame

