Python: Can't call numpy() on Tensor that requires grad
Last updated: Apr 11, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- Python: Can't call numpy() on Tensor that requires grad
- Using the
no_grad()context manager to solve the error - Getting the error when drawing a scatter plot in matplotlib
# Python: Can't call numpy() on Tensor that requires grad
The Python "RuntimeError: Can't call numpy() on Tensor that requires grad. Use tensor.detach().numpy() instead" occurs when you try to convert a tensor with a gradient to a NumPy array.
To solve the error, convert your tensor to one that doesn't require a gradient
by using detach().
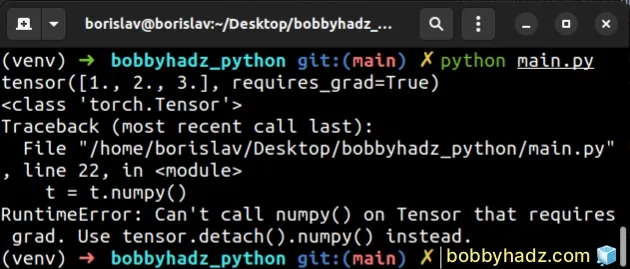
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import torch t = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0, 3.0], requires_grad=True) print(t) # 👉️ tensor([1., 2., 3.], requires_grad=True) print(type(t)) # 👉️ <class 'torch.Tensor'> # ⛔️ RuntimeError: Can't call numpy() on Tensor that requires grad. Use tensor.detach().numpy() instead. t = t.numpy()
When the
requires_grad
attribute is set to True, gradients need to be computed for the Tensor.
To solve the error, use the
tensor.detach()
method to convert the tensor to one that doesn't require a gradient before
calling numpy().
import torch t = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0, 3.0], requires_grad=True) print(t) # 👉️ tensor([1., 2., 3.], requires_grad=True) print(type(t)) # 👉️ <class 'torch.Tensor'> # ✅ Call detach() before calling numpy() t = t.detach().numpy() print(t) # 👉️ [1. 2. 3.] print(type(t)) # 👉️ <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
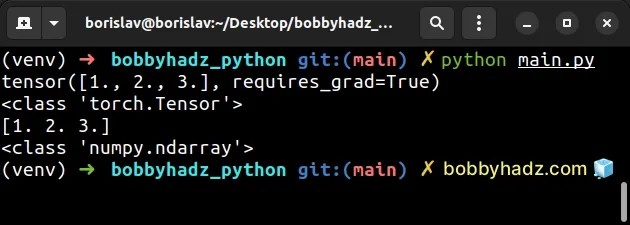
The tensor.detach() method returns a new Tensor that is detached from the
current graph.
The result never requires a gradient.
In other words, the method returns a new tensor that shares the same storage but
doesn't track gradients (requires_grad is set to False).
The new tensor can safely be converted to a NumPy ndarray by calling the
tensor.numpy()
method.
If you have a list of tensors, use a
list comprehension to
iterate over the list and call detach() on each tensor.
import torch t1 = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0, 3.0], requires_grad=True) t2 = torch.tensor([4.0, 5.0, 6.0], requires_grad=True) tensors = [t1, t2] result = [t.detach().numpy() for t in tensors] # 👇️ [array([1., 2., 3.], dtype=float32), array([4., 5., 6.], dtype=float32)] print(result)
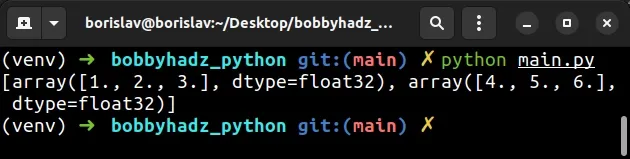
We used a list comprehension to iterate over the list of tensors.
List comprehensions are used to perform some operation for every element or select a subset of elements that meet a condition.
On each iteration, we call detach() before calling numpy() so no error is
raised.
# Using the no_grad() context manager to solve the error
You can also use the no_grad() context manager to solve the error.
The context manager disables gradient calculation.
import torch t = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0, 3.0], requires_grad=True) print(t) # 👉️ tensor([1., 2., 3.], requires_grad=True) print(type(t)) # 👉️ <class 'torch.Tensor'> with torch.no_grad(): t = t.detach().numpy() print(t) # 👉️ [1. 2. 3.] print(type(t)) # 👉️ <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
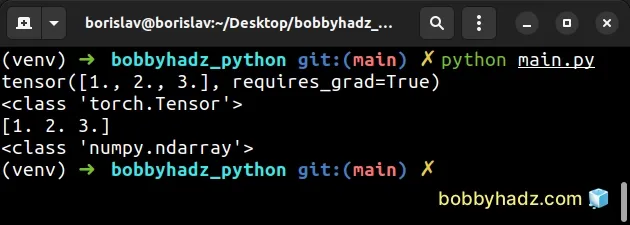
The no_grad context manager disables gradient calculation.
In the context manager (the indented block), the result of every computation
will have requires_grad=False even if the inputs have requires_grad=True.
Calling the numpy() method on a tensor that is attached to a computation graph
is not allowed.
We first have to make sure that the tensor is detached before calling numpy().
# Getting the error when drawing a scatter plot in matplotlib
If you got the error when drawing a scatter plot in matplotlib, try using the
torch.no_grad() method as we did in the previous subheading.
import torch t = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0, 3.0], requires_grad=True) with torch.no_grad(): # 👉️ YOUR CODE THAT CAUSES THE ERROR HERE pass
Make sure to add your code to the indented block inside the no_grad() context
manager.
The context manager will disable gradient calculation which should resolve the
error as long as your code is indented inside the with torch.no_grad()
statement.
If the error persists, try to add an import statement for the fastio.basics
module at the top of your file.
from fastai.basics import * # 👇️ the rest of your code
The no_grad context manager will set requires_grad=False as long as your
code is indented in the block.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Only one element tensors can be converted to Python scalars
- Convert a NumPy array to 0 or 1 based on threshold in Python
- How to get the length of a 2D Array in Python
- TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable in Python
- TypeError: Object of type ndarray is not JSON serializable
- IndexError: too many indices for array in Python [Solved]
- How to replace None with NaN in Pandas DataFrame
- FutureWarning: pandas.Int64Index is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version
- You are trying to merge on int64 and object columns [Fixed]
- Copy a column from one DataFrame to another in Pandas
- AttributeError: Can only use .str accessor with string values
- ValueError: zero-dimensional arrays cannot be concatenated
- ValueError: zero-dimensional arrays cannot be concatenated
- ValueError: all the input array dimensions for the concatenation axis must match exactly
- ValueError: cannot reshape array of size X into shape Y
- lbfgs failed to converge (status=1): STOP: TOTAL NO. of ITERATIONS REACHED LIMIT
- How to draw empty circles on a Scatter Plot in Matplotlib
- TypeError: Image data cannot be converted to float [Solved]
- OverflowError: Python int too large to convert to C long
- How to use numpy.argsort in Descending order in Python
- TypeError: cannot pickle '_thread.lock' object [Solved]
- ValueError: DataFrame constructor not properly called [Fix]
- ufunc 'add' did not contain loop with signature matching types
- TypeError: Field elements must be 2- or 3-tuples, got 1
- ValueError: Expected 2D array, got 1D array instead [Fixed]
- ValueError: Found array with dim 3. Estimator expected 2
- Input contains infinity or value too large for dtype(float64)
- RuntimeWarning: overflow encountered in exp [Solved]
- TypeError: ufunc 'isnan' not supported for the input types
- Arrays used as indices must be of integer (or boolean) type
- Shape mismatch: objects cannot be broadcast to a single shape
- Get the column names of a NumPy ndarray in Python
- Finding the Range of NumPy Array elements in Python
- Remove the Duplicate elements from a NumPy Array
- NumPy: Apply a Mask from one Array to another Array
- How to iterate over the Columns of a NumPy Array
- Pandas: Select rows based on a List of Indices
- Pandas: Find an element's Index in Series [7 Ways]
- TypeError: type numpy.ndarray doesn't define __round__ method

