ValueError: zero-dimensional arrays cannot be concatenated
Last updated: Apr 11, 2024
Reading time·2 min

# ValueError: zero-dimensional arrays cannot be concatenated
The NumPy "ValueError: zero-dimensional arrays cannot be concatenated" occurs
when you pass a single one-dimensional array to the numpy.concatenate()
method.
To solve the error, wrap the argument in square brackets, when calling
concatenate().
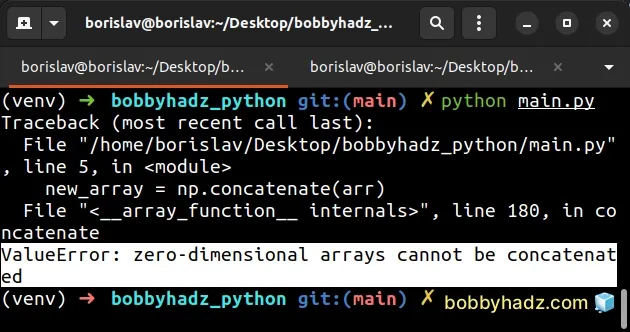
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([1, 2, 3]) # ⛔️ ValueError: zero-dimensional arrays cannot be concatenated new_array = np.concatenate(arr)
The numpy.concatenate() method joins a sequence of arrays along an existing axis.
We only passed a single one-dimensional array to the numpy.concatenate()
method which caused the error.
You can solve the error by wrapping the array in square brackets.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([1, 2, 3]) new_array = np.concatenate([arr]) print(new_array) # 👉️ [1 2 3]
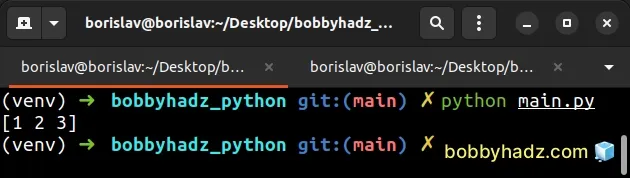
Notice that we wrapped the array in square brackets.
Replace this:
# ⛔️ Error new_array = np.concatenate(arr)
With this:
# ✅ Correct new_array = np.concatenate([arr])
Here is an example of passing an inline list to the np.concatenate() method.
import numpy as np new_array = np.concatenate([[1, 2, 3]]) print(new_array) # 👉️ [1 2 3]
Notice that we have 2 sets of square brackets.
The arrays you want to concatenate have to be placed in a sequence, e.g. a list.
The numpy.concatenate() method joins a sequence of arrays along an existing axis.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3]) arr2 = np.array([4, 5, 6]) new_array = np.concatenate([arr1, arr2]) print(new_array) # 👉️ [1 2 3 4 5 6]
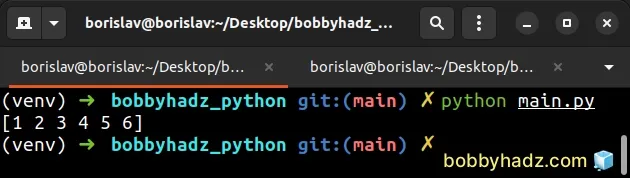
Notice that we placed the arrays in a sequence (a list []) when passing them
to numpy.concatenate().
You can also use a tuple () to achieve the same result.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3]) arr2 = np.array([4, 5, 6]) new_array = np.concatenate((arr1, arr2)) print(new_array) # 👉️ [1 2 3 4 5 6]
Here is an example of calling the numpy.concatenate() method with
two-dimensional arrays.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]]) arr2 = np.array([[5, 6]]) new_arr = np.concatenate((arr1, arr2), axis=0) # [[1 2] # [3 4] # [5 6]] print(new_arr)
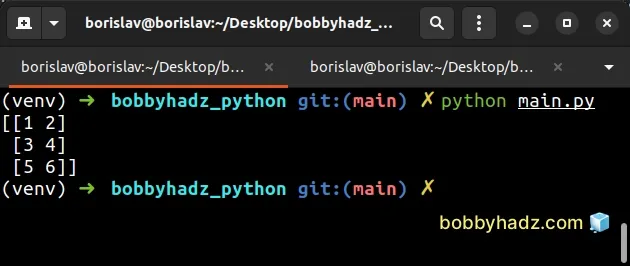
The example joins the two-dimensional arrays along the 0 axis.
0 is the default value for the axis parameter.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- TypeError Invalid comparison between datetime64[ns] and date
- How to replace None with NaN in Pandas DataFrame
- You are trying to merge on int64 and object columns [Fixed]
- Could not broadcast input array from shape into shape [Fix]
- ValueError: object too deep for desired array [Solved]
- Only one element tensors can be converted to Python scalars
- Copy a column from one DataFrame to another in Pandas
- Count number of non-NaN values in each column of DataFrame

