NumPy: Apply a Mask from one Array to another Array
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- NumPy: Apply a Mask from one Array to another Array
- NumPy: Apply a Mask from one 2D Array to another 2D Array
- NumPy: Apply a Mask from one Array to another Array using masked_where()
# NumPy: Apply a Mask from one Array to another Array
To apply a mask from one NumPy array to another array:
- Use the
numpy.ma.masked_where()method to mask the first array where a condition is met. - Use the
numpy.ma.getmask()method to get the mask of the masked array. - Use the
numpy.ma.masked_where()method to mask the second array.
import numpy as np x = np.array([1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 12]) y = np.array([2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 14]) masked_y_array = np.ma.masked_where(y > 8, y) # filter out values in `y` that are greater than 8 print(masked_y_array) # 👉️ [2 4 6 8 -- --] new_x_array = np.ma.masked_where(np.ma.getmask(masked_y_array), x) # apply the mask of `masked_y_array` to `x` print(new_x_array) # 👉️ [1 3 5 7 -- --]
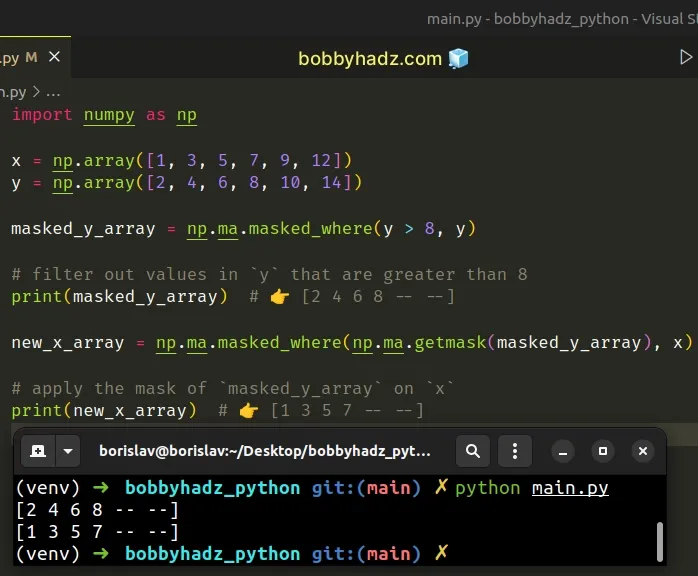
The numpy.ma.masked_where method masks an array where a condition is met.
In other words, the method returns the supplied array as a masked array where
the condition returns True.
import numpy as np x = np.array([1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 12]) y = np.array([2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 14]) masked_y_array = np.ma.masked_where(y > 8, y) # filter out values in `y` that are greater than 8 print(masked_y_array) # 👉️ [2 4 6 8 -- --]
Any masked values of the array are also masked in the output.
Once we've filtered out the values in the array that match the condition, we can apply the mask to the second array using numpy.ma.getmask().
The numpy.ma.getmask() method takes a masked array as a parameter and returns
the mask of the masked array.
import numpy as np x = np.array([1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 12]) y = np.array([2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 14]) masked_y_array = np.ma.masked_where(y > 8, y) # filter out values in `y` that are greater than 8 print(masked_y_array) # 👉️ [2 4 6 8 -- --] # 👇️ [False False False False True True] print(np.ma.getmask(masked_y_array))
The last step is to apply the mask to the other array by using the
numpy.ma.masked_where() method.
import numpy as np x = np.array([1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 12]) y = np.array([2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 14]) masked_y_array = np.ma.masked_where(y > 8, y) # filter out values in `y` that are greater than 8 print(masked_y_array) # 👉️ [2 4 6 8 -- --] new_x_array = np.ma.masked_where(np.ma.getmask(masked_y_array), x) # apply the mask of `masked_y_array` to `x` print(new_x_array) # 👉️ [1 3 5 7 -- --]

You can apply the mask to as many arrays as necessary by using
numpy.ma.getmask() as shown in the code sample.
If you need to get all non-masked data as a 1-D array, use the numpy.ma.compressed() method.
import numpy as np x = np.array([1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 12]) y = np.array([2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 14]) masked_y_array = np.ma.masked_where(y > 8, y) # filter out values in `y` that are greater than 8 print(masked_y_array) # 👉️ [2 4 6 8 -- --] print(np.ma.compressed(masked_y_array)) # 👉️ [2 4 6 8] new_x_array = np.ma.masked_where(np.ma.getmask(masked_y_array), x) # apply the mask of `masked_y_array` to `x` print(new_x_array) # 👉️ [1 3 5 7 -- --] print(np.ma.compressed(new_x_array)) # 👉️ [1 3 5 7]
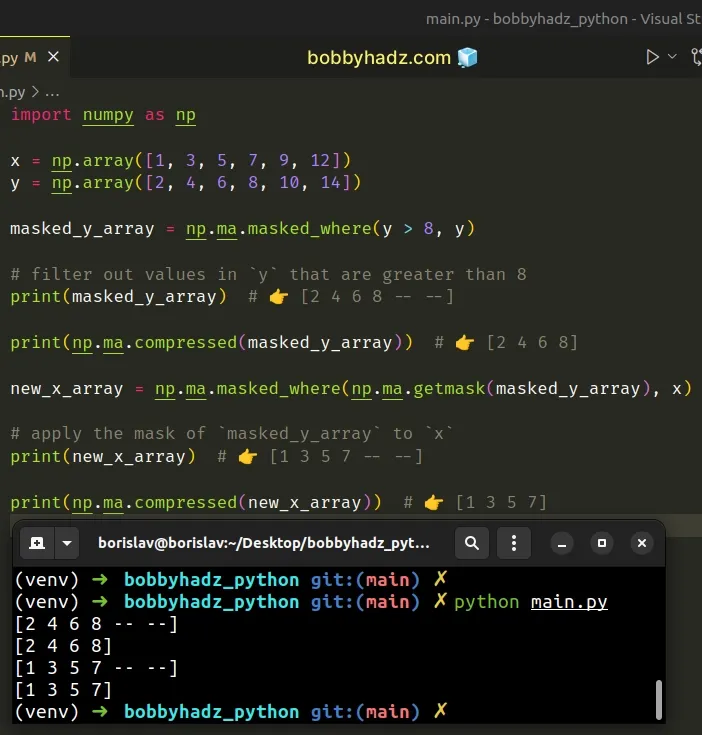
The numpy.ma.compressed() method returns all of the non-masked data in the
supplied array as a 1-D array.
# NumPy: Apply a Mask from one 2D Array to another 2D Array
This approach also works if you need to apply a mask from one 2D array to another 2D array.
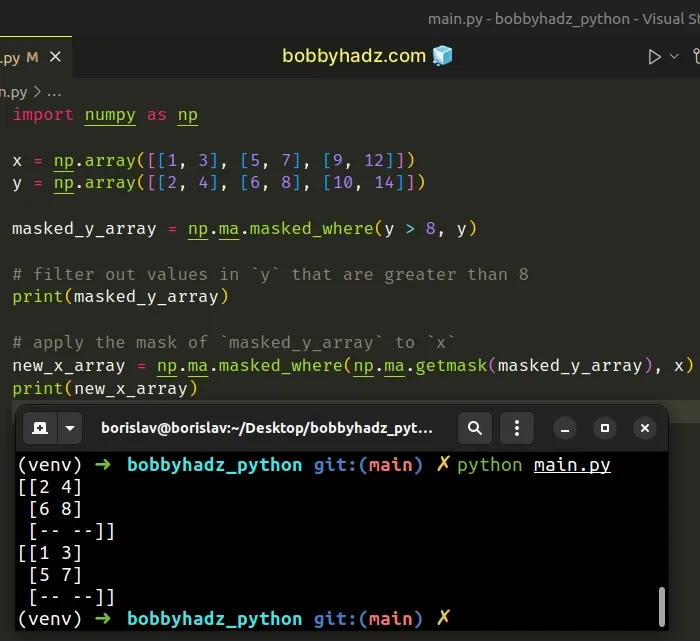
import numpy as np x = np.array([[1, 3], [5, 7], [9, 12]]) y = np.array([[2, 4], [6, 8], [10, 14]]) masked_y_array = np.ma.masked_where(y > 8, y) # filter out values in `y` that are greater than 8 print(masked_y_array) # apply the mask of `masked_y_array` to `x` new_x_array = np.ma.masked_where(np.ma.getmask(masked_y_array), x) print(new_x_array)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
[[2 4] [6 8] [-- --]] [[1 3] [5 7] [-- --]]
# NumPy: Apply a Mask from one Array to another Array using masked_where()
You can also use the numpy.ma.masked_where() method twice, with the same
condition to apply a mask from one array to another.
import numpy as np x = np.array([1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 12]) y = np.array([2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 14]) masked_y_array = np.ma.masked_where(y > 8, y) # filter out values in `y` that are greater than 8 print(masked_y_array) # 👉️ [2 4 6 8 -- --] print(np.ma.compressed(masked_y_array)) # 👉️ [2 4 6 8] new_x_array = np.ma.masked_where(y > 8, x) # apply the mask of `masked_y_array` to `x` print(new_x_array) # 👉️ [1 3 5 7 -- --] print(np.ma.compressed(new_x_array)) # 👉️ [1 3 5 7]
We first masked the y array using the condition y > 8, effectively filtering
out the values in y that are greater than 8.
masked_y_array = np.ma.masked_where(y > 8, y)
We then called the masked_where() method a second time, with the same
condition (y > 8).
new_x_array = np.ma.masked_where(y > 8, x)
However, notice that we passed x as the second argument to the method.
This way, the mask from the y array is applied to the x array.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Pandas: Merge only specific DataFrame columns
- How to Start the Index of a Pandas DataFrame at 1
- Pandas: DataFrame.reset_index() not working [Solved]
- How to Add Axis Labels to a Plot in Pandas [5 Ways]
- How to Create a Set from a Series in Pandas
- Pandas: Remove non-numeric rows in a DataFrame column
- numpy.linalg.LinAlgError: Singular matrix [Solved]
- NumPy RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in divide
- Sklearn ValueError: Unknown label type: 'continuous' [Fixed]

