OverflowError: Python int too large to convert to C long
Last updated: Apr 11, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- OverflowError: Python int too large to convert to C long
- Solving the error when using a pandas DataFrame
- The error is also raised when trying to store integers greater than
sys.maxsize
# OverflowError: Python int too large to convert to C long
The error "OverflowError: Python int too large to convert to C long" occurs when one or more of the supplied Python integers are too large to be converted to C long.
To solve the error, set the data type of the numbers to np.int64 instead of
int.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import numpy as np # ⛔️ OverflowError: Python int too large to convert to C long arr = np.array([1, 5, 2147483648], dtype=int) print(arr)
One of the numbers we passed to the numpy.array() method is too large to be converted to a C long.
- The
int32(orint) data type can store integers from-2147483648to2147483647. - On the other hand, the
int64data type can store integers from-9223372036854775808to9223372036854775807.
To solve the error, set the dtype (data type) argument to np.int64 instead.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([1, 5, 2147483648], dtype=np.int64) print(arr)
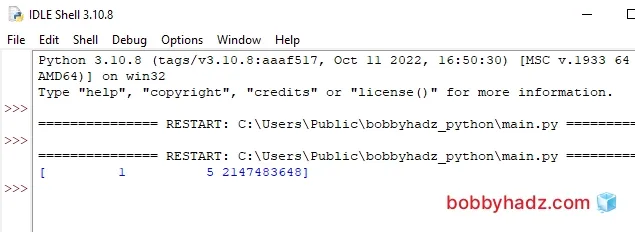
sys.maxsize (more on that below).You can also set the dtype to "int64" to achieve the same result.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([1, 5, 2147483648], dtype='int64') print(arr)
You won't get the error on macOS or Linux if the numbers are in the range from
-2147483648 to 2147483647.
This is because the int (or int32) type uses a C long which is always
32-bit on Windows.
For example, the following code sample runs without any issues on macOS and Linux, but causes the error on Windows.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([1, 5, 2147483648], dtype=int) # [ 1 5 2147483648] print(arr)
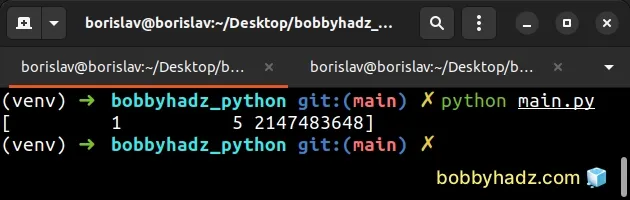
On Windows, C long is 32-bit and on macOS and Linux, it is 64-bit.
# Solving the error when using a pandas DataFrame
If you got the error when using a pandas DataFrame, use the astype() method
to cast the pandas object to the int64 dtype.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({'salary': ['9223372036854775804', '439243294932']}) df['new'] = df['salary'].astype('int64') print(df)
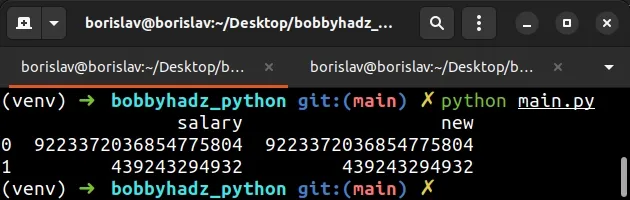
The
DataFrame.astype()
method takes a
dtype (data
type) as a parameter and casts the pandas object to the specified dtype.
# The error is also raised when trying to store integers greater than sys.maxsize
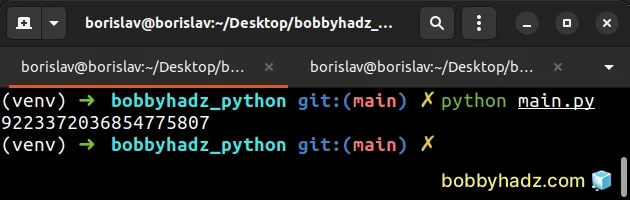
The error is also raised when you try to store integers that are greater than sys.maxsize.
import sys print(sys.maxsize) # 👉️ 9223372036854775807
The sys.maxsize property is an integer that defines the maximum value a
variable of type
Py_ssize_t can take.
On a 32-bit platform, the value is: 2**31 - 1 = 2147483647.
On a 64-bit platform, the value is 2**63 - 1 = 9223372036854775807.
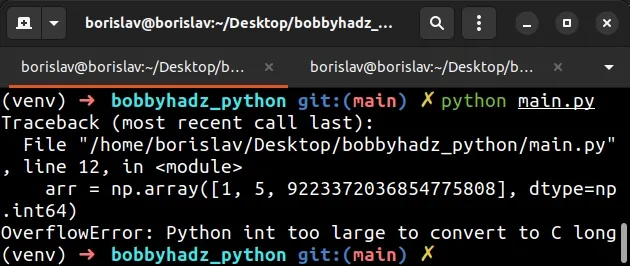
If you try to store a value that is greater than sys.maxsize in a NumPy array,
the error is raised.
import numpy as np # ⛔️ OverflowError: Python int too large to convert to C long arr = np.array([1, 5, 9223372036854775808], dtype=np.int64)
Note that native Python lists can store much larger integer values.
a_list = [1, 5, 92233720368547758088888888] # [1, 5, 92233720368547758088888888] print(a_list)
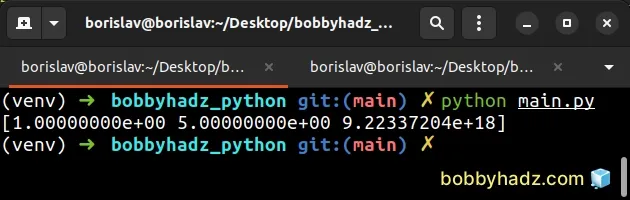
If you have to store the values in a NumPy array, set the type to np.float64
instead.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([1, 5, 9223372036854775808], dtype=np.float64) # [1.00000000e+00 5.00000000e+00 9.22337204e+18] print(arr)
The int type uses a C long under the hood which is quite limited (especially
on Windows).
You can use the np.float64 data type to store larger values in a NumPy array.
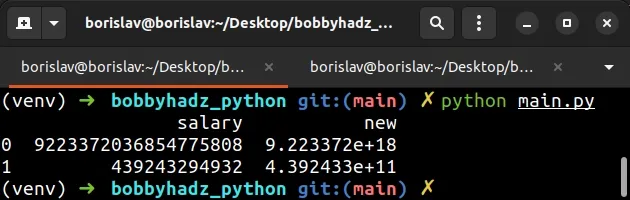
You can also use the float type when working with a pandas DataFrame.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({'salary': ['9223372036854775808', '439243294932']}) df['new'] = df['salary'].astype(float) print(df)
In general, NumPy arrays are not suited for storing extremely large integer values.
You can either use a native Python list or set the data type of the sequence to
float or np.float64.
If you try to store an integer that is greater than sys.maxsize, you will
get the "OverflowError: Python int too large to convert to C long" error.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to filter a JSON array in Python
- AttributeError module 'numpy' has no attribute array or int
- NumPy RuntimeWarning: divide by zero encountered in log10
- ValueError: x and y must have same first dimension, but have shapes
- SystemError: initialization of _internal failed without raising an exception
- TypeError Invalid comparison between datetime64[ns] and date
- How to replace None with NaN in Pandas DataFrame
- You are trying to merge on int64 and object columns [Fixed]
- Add a column with incremental Numbers to a Pandas DataFrame
- ValueError: No axis named X for object type DataFrame
- Process finished with exit code 139 (interrupted by signal 11: SIGSEGV)

