Convert a NumPy array to 0 or 1 based on threshold in Python
Last updated: Apr 10, 2024
Reading time·9 min

# Table of Contents
- Convert a NumPy array to 0 or 1 based on threshold in Python
- Set NumPy array elements to Zero if greater than X in Python
- Set the first N elements of an Array to Zero in Python
# Convert a NumPy array to 0 or 1 based on threshold in Python
Use the numpy.where() method to convert a NumPy array to 0 or 1 based on a
threshold.
The numpy.where() method will set each value of the array based on whether
it meets the condition.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([0.2, 0.1, 0.4, 0.7, 0.3, 0.9]) new_arr = np.where(arr > 0.5, 1, 0) print(new_arr) # 👉️ [0 0 0 1 0 1]
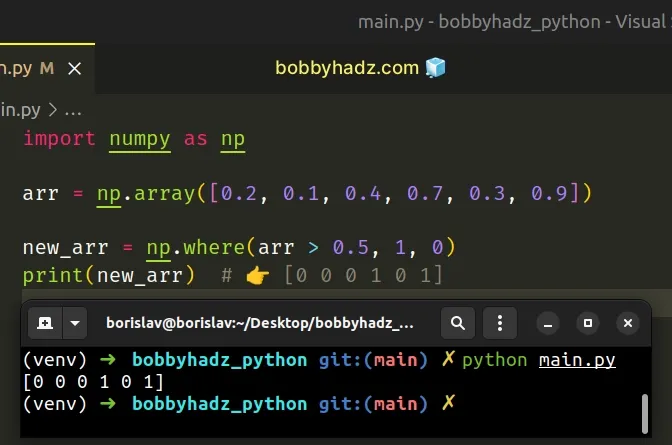
Make sure you have numpy installed to be able to run the code sample.
pip install numpy # 👇️ or with pip3 pip3 install numpy
numpy.where() method to set all values in a numpy array that are greater than 0.5 to 1 and all values that are less than or equal to 0.5 to 0.The numpy.where() method takes the following 3 arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| condition | If the condition is met, return x, otherwise, return y. |
x | Values from which to choose if the condition is met. |
y | Values from which to choose if the condition is NOT met. |
The numpy.where() method returns an array with elements from x where the
condition is True and elements from y where the condition is False.
0.5, it gets set to 1, otherwise, the element gets set to 0.Alternatively, you can use the astype() method with a condition.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([0.2, 0.1, 0.4, 0.7, 0.3, 0.9]) new_arr = (arr > 0.5).astype(int) print(new_arr) # 👉️ [0 0 0 1 0 1]
The expression arr > 0.5 returns a boolean array containing True values for
the elements that meet the condition and False for all other elements.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([0.2, 0.1, 0.4, 0.7, 0.3, 0.9]) # 👇️ [False False False True False True] print(arr > 0.5)
The astype() method is then used to return a copy of the array casting the boolean values to integers.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([0.2, 0.1, 0.4, 0.7, 0.3, 0.9]) new_arr = (arr > 0.5).astype(int) print(new_arr) # 👉️ [0 0 0 1 0 1]
True values get converted to 1 and False values get converted to 0.Alternatively, you can use a list comprehension.
# Convert a NumPy array to 0 or 1 based on threshold using list comprehension
This is a three-step process:
- Use a list comprehension to iterate over the array.
- Check if each item is greater than the threshold and return
0or1. - Optionally, convert the list to an array.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([0.2, 0.1, 0.4, 0.7, 0.3, 0.9]) a_list = [ 1 if element > 0.5 else 0 for element in arr ] print(a_list) # 👉️ [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1] new_array = np.array(a_list) print(new_array) # 👉️ [0 0 0 1 0 1]
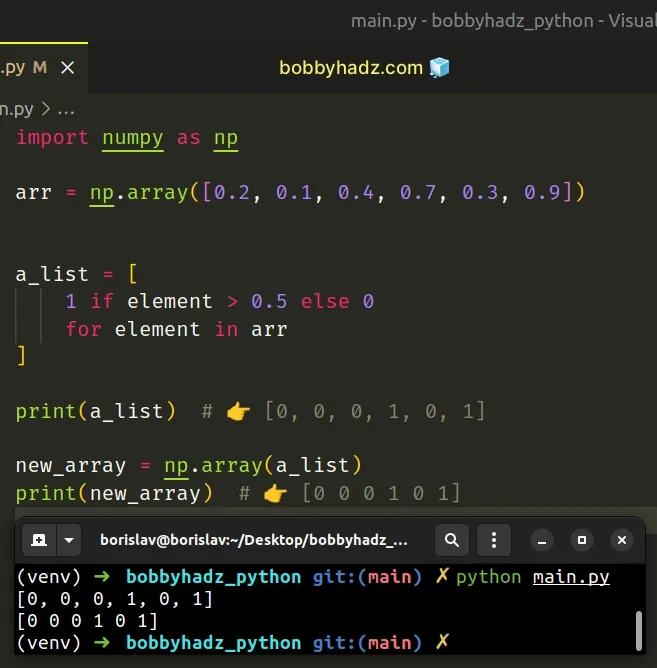
We used a list comprehension to iterate over the numpy array.
On each iteration, we check if the current element is greater than 0.5.
The list comprehension returns a list containing the results.
If you need to convert the list to an array, use the np.array() method.
# Set NumPy array elements to Zero if greater than X in Python
Use NumPy's indexing to set the NumPy array elements to 0 if they are greater
than a certain number.
You can directly assign a zero to the slice of the array that meets the condition.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([8, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]) threshold = 3 arr[arr > threshold] = 0 print(arr) # 👉️ [0 1 2 3 0 0 0 0]
The code sample sets all array elements to 0 if they have a value greater than
3.
The conditional check arr > threshold returns an array of booleans.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([8, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]) threshold = 3 # 👇️ [ True False False False True True True True] print(arr > threshold)
3 have a value of True and the ones that aren't, have a value of False.You can directly use the boolean array to only set the array elements that meet
the condition to 0.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([8, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]) threshold = 3 arr[arr > threshold] = 0 print(arr) # 👉️ [0 1 2 3 0 0 0 0]
# Set NumPy array elements to Zero if greater than X without mutation
If you don't want to mutate the original array, use the numpy.where() method.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([8, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]) threshold = 3 new_arr = np.where(arr > threshold, 0, arr) print(new_arr) # 👉️ [0 1 2 3 0 0 0 0]
The numpy.where() method takes the following 3 arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| condition | If the condition is met, return x, otherwise, return y. |
x | Values from which to choose if the condition is met. |
y | Values from which to choose if the condition is NOT met. |
The numpy.where method returns an array with elements from x where the
condition is True and elements from y where the condition is False.
In other words, if the array element is greater than the specified number, it
gets set to 0, otherwise, the element is returned as is.
Alternatively, you can use a list comprehension.
# Set numpy array elements to Zero if greater than X using list comprehension
To set a NumPy array's elements to zero if they are greater than a certain threshold:
- Use a list comprehension to iterate over the array.
- Check if each item is greater than the threshold.
- If the condition is met, return
0, otherwise, return the element as is.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([8, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]) threshold = 3 a_list = [ 0 if element > threshold else element for element in arr ] print(a_list) # 👉️ [0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0] new_array = np.array(a_list) print(new_array) # 👉️ [0 1 2 3 0 0 0 0]
We used a list comprehension to iterate over the array.
On each iteration, we check if the current element is greater than the specified threshold.
If the condition is met, we return 0, otherwise, we return the current
element.
The list comprehension returns a list containing the results.
If you need to convert the list to an array, use the np.array() method.
# Set the first N elements of an Array to Zero in Python
Use list slicing to set the first N elements of an array to zero.
import numpy as np # ✅ Set the first N elements of a Python list to 0 a_list = [8, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] n = 3 a_list[:n] = [0] * n print(a_list) # 👉️ [0, 0, 0, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] # --------------------------------------------- # ✅ Set the first N elements of NumPy array to 0 arr = np.array([8, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]) n = 3 arr[:n] = 0 print(arr) # 👉️ [0 0 0 3 4 5 6 7]
The first example shows how to set the first N elements of a native Python list
to 0.
a_list = [8, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] n = 3 a_list[:n] = [0] * n print(a_list) # 👉️ [0, 0, 0, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
We used the list-slicing assignment to set the first N elements of the list to
0.
The syntax for list slicing is my_list[start:stop:step].
start index is inclusive and the stop index is exclusive (up to, but not including).If the start index is omitted, it is considered to be 0, if the stop index
is omitted, the slice goes to the end of the list.
Python indexes are zero-based, so the first item in a list has an index of 0,
and the last item has an index of -1 or len(my_list) - 1.
a_list[:n] starts at index 0 and goes up to, but not including index n.We used the multiplication operator to create a list of N zero values on the right-hand side of the assignment.
a_list = [8, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] n = 3 a_list[:n] = [0] * n print(a_list) # 👉️ [0, 0, 0, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
When the multiplication (*) operator is used with a list and an integer, it repeats the items in the list N times.
print([0] * 2) # 👉️ [0, 0] print([0] * 3) # 👉️ [0, 0, 0]
In its entirety, the statement replaces a slice of the first N elements of the list with a new list containing N zeros.
# Directly assigning a value to the first N array elements
If you have a numpy array, you can directly assign a zero to the first N
elements of the array.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([8, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]) n = 3 arr[:n] = 0 print(arr) # 👉️ [0 0 0 3 4 5 6 7]
You can install numpy by running the following command from your terminal.
pip install numpy pip3 install numpy
We can directly assign a zero to multiple elements in a numpy array.
Note that this is not a valid syntax when working with native Python lists.
The following code sample raises a TypeError exception.
a_list = [8, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] n = 3 # ⛔️ TypeError: can only assign an iterable a_list[:n] = 0
We are trying to assign a single 0 to a slice (multiple items) of the list.
This only works with numpy arrays, not with native Python lists.
# Replacing the first N array elements with a list of zeros
You can also replace the first N elements in the numpy array with a list
containing N zeros as we did in the previous example.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([8, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]) n = 3 arr[:n] = [0] * n print(arr) # 👉️ [0 0 0 3 4 5 6 7]
The code sample sets the first N elements of the numpy array to 0 by
replacing the slice with a slice containing N zero values.
You can use the tolist() method if you need to convert the numpy array to a
native Python list.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([8, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]) n = 3 arr[:n] = [0] * n print(arr) # 👉️ [0 0 0 3 4 5 6 7] a_list = arr.tolist() print(a_list) # 👉️ [0, 0, 0, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
The
tolist()
method converts a numpy array to a list.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'numpy' in Python
- Only integers, slices (
:), ellipsis (...), numpy.newaxis (None) and integer or boolean arrays are valid indices - NumPy RuntimeWarning: divide by zero encountered in log10
- How to replace None with NaN in Pandas DataFrame
- ValueError: assignment destination is read-only [Solved]
- You are trying to merge on int64 and object columns [Fixed]
- Could not broadcast input array from shape into shape [Fix]
- ValueError: cannot reindex on an axis with duplicate labels
- AttributeError: Can only use .str accessor with string values
- ValueError: all the input array dimensions for the concatenation axis must match exactly
- ValueError: cannot reshape array of size X into shape Y
- How to draw empty circles on a Scatter Plot in Matplotlib
- OverflowError: Python int too large to convert to C long
- Unable to initialize device PRN in Python [Solved]
- How to use numpy.argsort in Descending order in Python
- Object arrays cannot be loaded when allow_pickle=False
- TypeError: cannot pickle '_thread.lock' object [Solved]
- ufunc 'add' did not contain loop with signature matching types
- RuntimeWarning: overflow encountered in exp [Solved]
- TypeError: ufunc 'isnan' not supported for the input types
- ValueError: No axis named X for object type DataFrame
- How to check if a NumPy Array is multidimensional or 1D
- Numpy: How to extract a Submatrix from an array
- How to flatten only some Dimensions of a NumPy array
- numpy.linalg.LinAlgError: Singular matrix [Solved]
- Removing the Top and Right axis (spines) in Matplotlib
- Only integer scalar arrays can be converted to a scalar index
- ValueError: Index contains duplicate entries, cannot reshape

