IndexError: too many indices for array in Python [Solved]
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# IndexError: too many indices for array in Python
The Python "IndexError: too many indices for array" occurs when we specify too many index values when accessing a one-dimensional NumPy array.
To solve the error, declare a two-dimensional array or correct the index accessor.
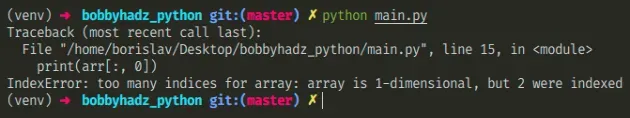
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([1, 2, 3]) print(arr.shape) # 👉️ (3, ) 👈️ This is one-dimensional array # ⛔️ IndexError: too many indices for array: array is 1-dimensional, but 2 were indexed print(arr[:, 0])
We have a one-dimensional NumPy array but we specified 2 indexes which caused the error.
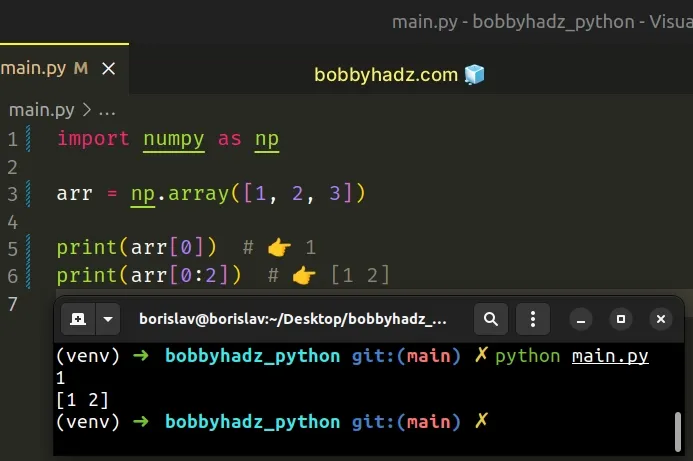
# Use a single index or a slice for one-dimensional arrays
If you have a one-dimensional array, use a single index or a slice.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([1, 2, 3]) print(arr[0]) # 👉️ 1 print(arr[0:2]) # 👉️ [1 2]
The syntax for list slicing is
a_list[start:stop:step].
The start index is inclusive and the stop index is exclusive (up to, but not
including).
start index is omitted, it is considered to be 0, if the stop index is omitted, the slice goes to the end of the list.Python indexes are zero-based, so the first item in a list has an index of 0,
and the last item has an index of -1 or len(a_list) - 1.
# Declaring a 2-dimensional NumPy array
Alternatively, you could declare a 2-dimensional NumPy array.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]) print(arr.shape) # 👉️ (3, 2) 👈️ This is two-dimensional array print(arr[:, 0]) # 👉️ [1 3 5]
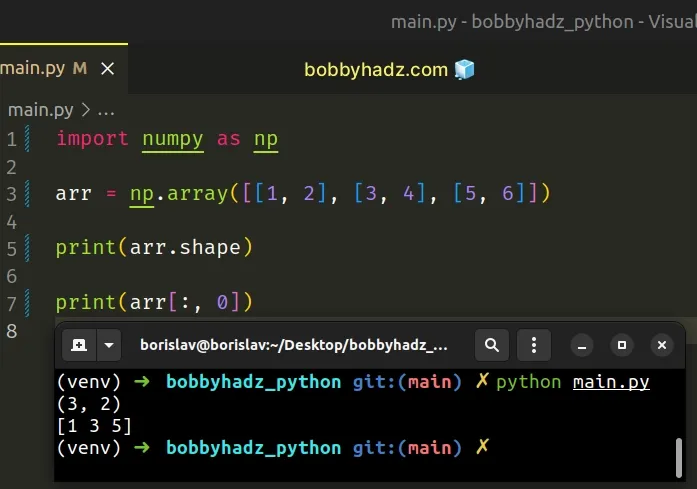
The example uses 2 indexes to get the first element of each nested array.
print the array you are trying to index to check whether it contains what you expect.If you only have a one-dimensional array, use a single index when accessing it,
e.g. arr[0] or arr[0:3].
import numpy as np arr = np.array([1, 2, 3]) print(arr[0]) # 👉️ 1 print(arr[1]) # 👉️ 2 print(arr[2]) # 👉️ 3
# Declaring a 2-d array with sub-arrays of different length
Another common cause of the error is declaring a two-dimensional array where not all nested arrays have items of the same type and size.
import numpy as np # 👇️ Declared one-dimensional array (second nested list has only 1 item) arr = np.array([[1, 2], [3], [5, 6]]) print(arr.shape) # 👉️ (3,) # ⛔️ IndexError: too many indices for array: array is 1-dimensional, but 2 were indexed print(arr[:, 0])
Notice that the second nested array only has 1 item, so we end up declaring a one-dimensional array.
A numpy array is an object that represents a multidimensional, homogenous array of fixed-size items.
If we add a second item to the second nested array, we would declare a two-dimensional array.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]) print(arr.shape) # 👉️ (3, 2) print(arr[:, 0]) # 👉️ [1 3 5]
Notice that the shape of the array is (3, 2) as opposed to the array in the
previous example which had a shape of (3,).
Once you declare a two-dimensional array, you will be able to use two indices to access items in nested arrays.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]) # ✅ Get the first item from the first two nested arrays print(arr[0:2, 0]) # 👉️ [1 3] # ✅ Get the last item from the first two nested arrays print(arr[0:2, -1]) # 👉️ [2 4]
The first example selects the first item from the first two nested arrays.
The second example selects the last item from the first two nested arrays.

