How to get the length of a 2D Array in Python
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Get the length of a 2D Array in Python
- Getting the total number of items in a 2D list
- Get the length of a 2D NumPy array
- Getting the total number of elements in a NumPy 2D array
# Get the length of a 2D Array in Python
To get the length of a 2D Array in Python:
- Pass the entire array to the
len()function to get the number of rows. - Pass the first array element to the
len()function to get the number of columns. - Multiply the number of rows by the number of columns to get the total.
my_arr = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]] # ✅ Get the number of rows rows = len(my_arr) print(rows) # 👉️ 2 # ✅ Get the number of columns cols = len(my_arr[0]) print(cols) # 👉️ 3 # ✅ Get the number of total elements total_elements = rows * cols print(total_elements) # 👉️ 6
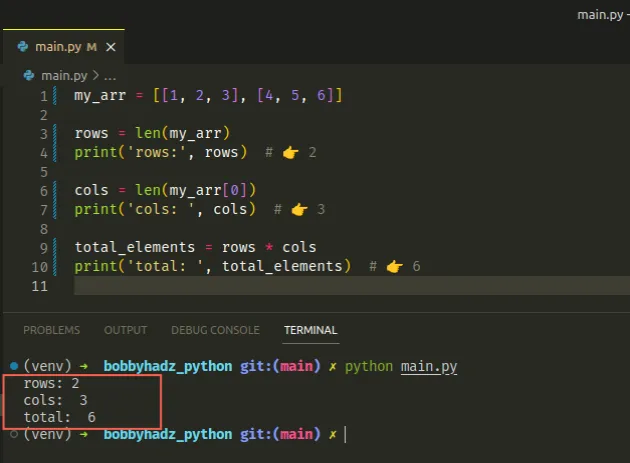
The len() function returns the length (the number of items) of an object.
The argument the function takes may be a sequence (a string, tuple, list, range or bytes) or a collection (a dictionary, set, or frozen set).
We first passed the entire list to the len() function to get the number of
rows (the number of nested lists).
my_arr = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]] rows = len(my_arr) print(rows) # 👉️ 2 cols = len(my_arr[0]) print(cols) # 👉️ 3
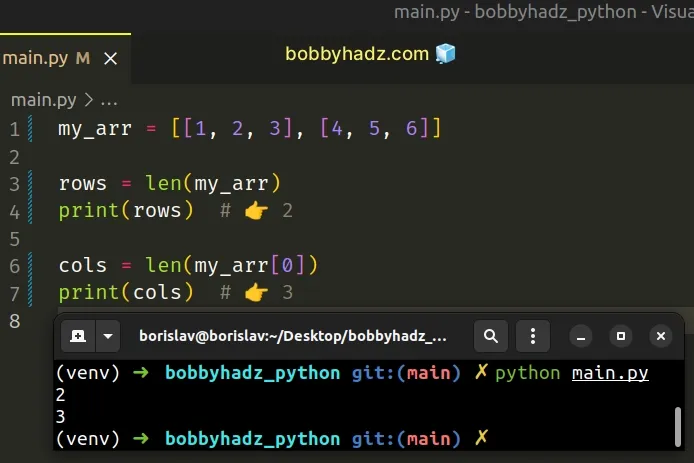
len() function.# Getting the total number of items in a 2D list
You can get the total number of items in the 2D list by multiplying the number of rows by the number of columns.
If the nested lists may be of different sizes, use the sum() function.
my_arr = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6, 7, 8]] rows = len(my_arr) print(rows) # 👉️ 2 total_elements = sum(len(l) for l in my_arr) print(total_elements) # 👉️ 8
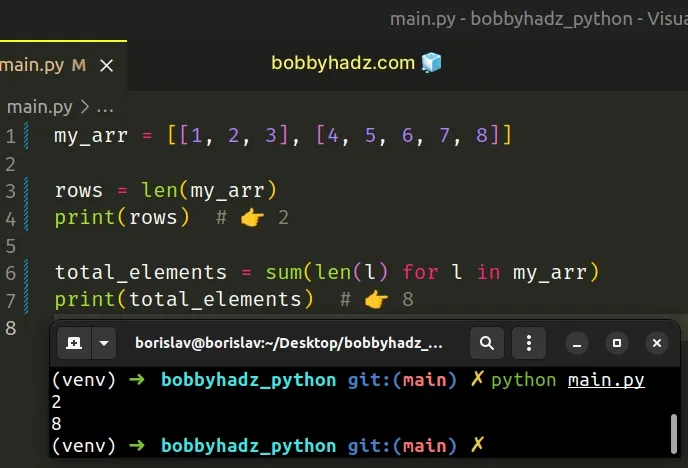
The sum function takes an iterable, sums its items from left to right and returns the total.
We pass each nested list to the len function and calculate the sum.
You can also use a for loop to get the total number of items in a 2D array containing subarrays of different sizes.
my_arr = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6, 7, 8]] total_elements = 0 for subarray in my_arr: total_elements += len(subarray) print(total_elements) # 👉️ 8
We used a for loop to iterate over the 2D array and on each iteration, we use
the add the length of the current array to the total.
# Get the length of a 2D NumPy array
If you need to get the length of a 2D NumPy array, use the shape and size
attributes.
import numpy as np my_2d_arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]) print(my_2d_arr.shape) # 👉️ (2, 3) print(my_2d_arr.size) # 👉️ 6 rows, cols = my_2d_arr.shape total_elements = rows * cols print(total_elements) # 👉️ 6
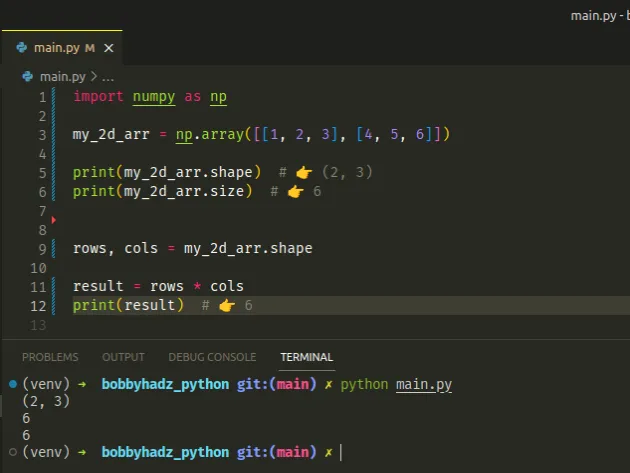
The size attribute returns the number of elements in the NumPy array.
import numpy as np my_2d_arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]) print(my_2d_arr.size) # 👉️ 6 print(my_2d_arr.shape) # 👉️ (2, 3)
The shape attribute returns a tuple of the array's dimensions.
The first value in the tuple is the number of rows, and the second is the number of columns in the array.
The two-dimensional array contains 2 nested arrays with 3 elements each.
# Getting the total number of elements in a NumPy 2D array
If you need to get the total number of elements in a NumPy 2D array, multiply the number of rows by the number of columns.
import numpy as np my_2d_arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]) print(my_2d_arr.shape) # 👉️ (2, 3) rows, cols = my_2d_arr.shape total_elements = rows * cols print(total_elements) # 👉️ 6
The array in the example has 2 rows with 3 columns each, so it has a total of 6 elements.
If the nested arrays may be of different sizes, use the sum() function to
calculate the number of total elements.
import numpy as np my_2d_arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6, 7]], dtype=object) total_elements = sum(len(arr) for arr in my_2d_arr) print(total_elements) # 👉️ 7
On each iteration, we use the len() function to get the length of the current
subarray and pass the result to the sum() function.
You can also use a simple for loop to calculate the number of total elements
in a 2D array.
import numpy as np my_2d_arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6, 7]], dtype=object) total_elements = 0 for arr in my_2d_arr: total_elements += len(my_2d_arr) print(total_elements) # 👉️ 4
On each iteration of the for loop, we add the length of the current array to
the total_elements variable.
I've also written an article on how to check if a value exists in a two-dimensional list.

