TypeError: Field elements must be 2- or 3-tuples, got 1
Last updated: Apr 11, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# TypeError: Field elements must be 2- or 3-tuples, got 1
The NumPy error "TypeError: Field elements must be 2- or 3-tuples, got 1" occurs when you try to create a two-dimensional NumPy array incorrectly.
To solve the error, pass a two-dimensional array to the numpy.array()
method.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import numpy as np # ⛔️ TypeError: Field elements must be 2- or 3-tuples, got '1' arr = np.array([2, 4, 6], [1, 3, 5])
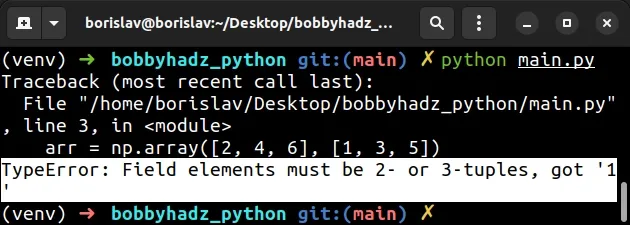
We tried to create a two-dimensional NumPy array incorrectly which caused the error.
Notice that we passed 2 arrays as separate arguments to the numpy.array method.
To solve the error, use two sets of square brackets.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([[2, 4, 6], [1, 3, 5]]) # [[2 4 6] # [1 3 5]] print(arr)
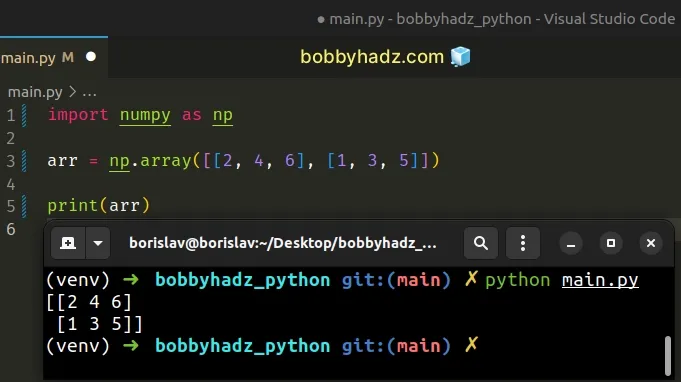
We passed a single, two-dimensional list to the numpy.array() method to create
a NumPy array.
We start with a set of square brackets and then specify the rows using sublists.
Make sure that the sublists contain the same number of elements, otherwise, you would get the Creating ndarray from ragged nested sequences is deprecated warning.
You can also pass a tuple containing the sublists as the first argument to
numpy.array().
import numpy as np arr = np.array(([2, 4, 6], [1, 3, 5])) # [[2 4 6] # [1 3 5]] print(arr)
However, make sure to pass the collection of sublists as a single argument by
wrapping them in curly braces [] or parentheses ().
If you want to create a one-dimensional array, pass a flat list to the
numpy.array() method.
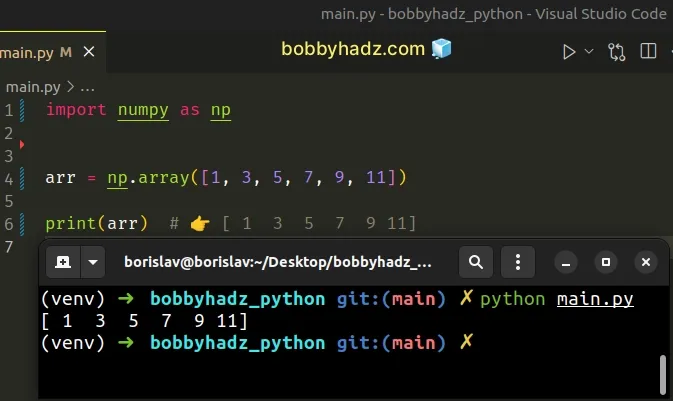
import numpy as np arr = np.array([1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11]) print(arr) # 👉️ [ 1 3 5 7 9 11]
The first argument the numpy.array method takes is an array-like object.
The argument can be:
- an array
- any object that exposes the array interface
- an object whose
__array__method returns an array - any nested sequence
If the supplied value is a scalar, a 0-dimensional array containing the value is returned.
import numpy as np arr = np.array(123) print(arr) # 👉️ 123 print(type(arr)) # 👉️ <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
The second argument the numpy.array() method takes is the
dtype (data
type).
import numpy as np arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], dtype=float) # [[1. 2. 3.] # [4. 5. 6.]] print(arr) print(arr.dtype) # 👉️ float64
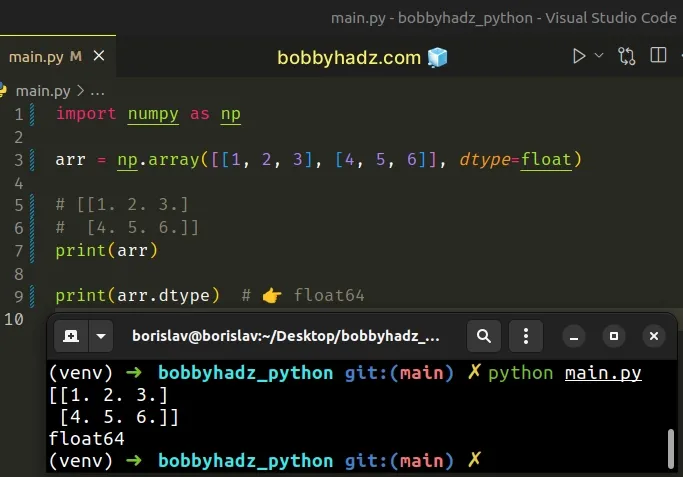
The dtype argument represents the desired data type for the array.
If the argument isn't supplied, NumPy tries to use a default dtype that can
represent the given values.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Could not broadcast input array from shape into shape [Fix]
- ValueError: object too deep for desired array [Solved]
- ValueError: cannot reindex on an axis with duplicate labels
- ValueError: Length mismatch: Expected axis has X elements, new values have Y elements
- ValueError: zero-dimensional arrays cannot be concatenated
- ValueError: all the input array dimensions for the concatenation axis must match exactly
- ValueError: cannot reshape array of size X into shape Y
- lbfgs failed to converge (status=1): STOP: TOTAL NO. of ITERATIONS REACHED LIMIT
- How to draw empty circles on a Scatter Plot in Matplotlib
- TypeError: Image data cannot be converted to float [Solved]
- OverflowError: Python int too large to convert to C long
- Count number of non-NaN values in each column of DataFrame
- Add a column with incremental Numbers to a Pandas DataFrame

