ValueError: Expected 2D array, got 1D array instead [Fixed]
Last updated: Apr 11, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# ValueError: Expected 2D array, got 1D array instead [Fixed]
The Python "ValueError: Expected 2D array, got 1D array instead" occurs when you pass a 1-dimensional array to a function that expects a 2-dimensional array.
To solve the error, reshape the numpy.reshape() method to make the array
two-dimensional.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import numpy as np from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression # 👇️ both arrays are 1-dimensional x = np.array([1, 5, 3, 2, 1]) y = np.array([2, 4, 6, 8, 10]) model = LinearRegression() # ⛔️ ValueError: Expected 2D array, got 1D array instead: # array=[1 5 3 2 1]. # Reshape your data either using array.reshape(-1, 1) if your data has a single feature or array.reshape(1, -1) if it contains a single sample. reg = model.fit(x, y)
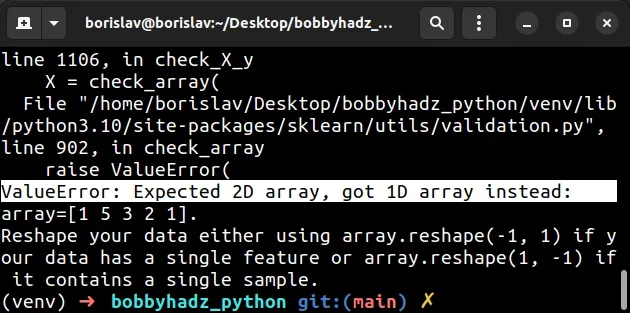
We created two 1-dimensional arrays and instantiated the LinearRegression class.
The error occurs when calling the fit() method.
x) and a 1-dimensional array for the target values (y).Calling the fit() method with two 1-dimensional arrays caused the error.
One way to solve the error is to use the reshape() method to reshape x into
a 2-dimensional array.
import numpy as np from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression # both arrays are 1-dimensional x = np.array([1, 5, 3, 2, 1]) y = np.array([2, 4, 6, 8, 10]) x = x.reshape(-1, 1) # [[1] # [5] # [3] # [2] # [1]] print(x) model = LinearRegression() reg = model.fit(x, y) print(reg.score(x, y)) # 👉️ 0.08035714285714268
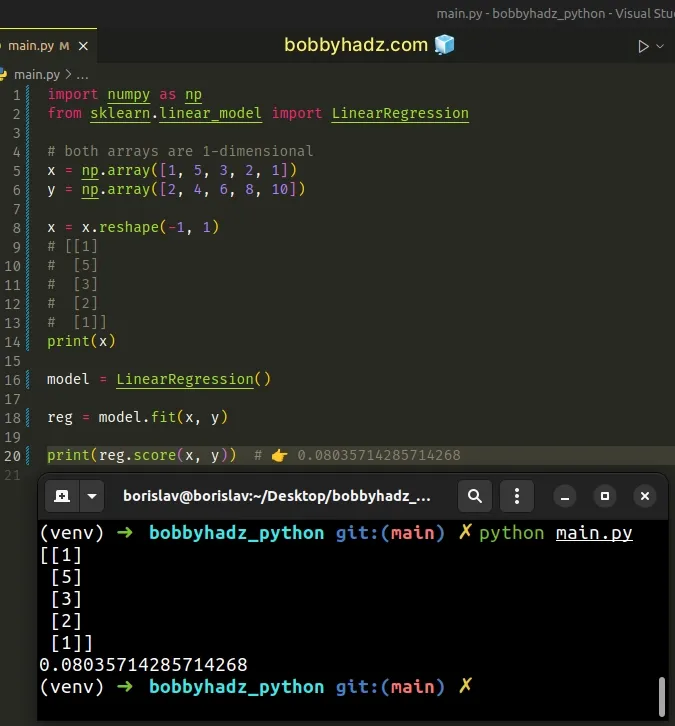
We used the numpy.reshape() method
to give a new shape to the x array without changing its data.
When the shape dimension is set to -1, the value is inferred from the length
of the array and the remaining dimensions.
We used the method to construct a 2-dimensional array where each subarray has 1 element.
# Wrap the one-dimensional array in a set of square brackets
You might also commonly get the error when using the reshape() method.
import numpy as np from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression X = np.array([[1, 1], [1, 2], [2, 2], [2, 3]]) y = np.dot(X, np.array([1, 2])) + 3 reg = LinearRegression().fit(X, y) print(reg.score(X, y)) # ⛔️ ValueError: Expected 2D array, got 1D array instead: # array=[3 5]. # Reshape your data either using array.reshape(-1, 1) if your data has a single feature or array.reshape(1, -1) if it contains a single sample. arr = np.array([3, 5]) print(reg.predict(arr))
Notice that we passed a one-dimensional array to the predict() method.
To solve the error, wrap the array in an extra set of square brackets to make it a two-dimensional array.
import numpy as np from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression X = np.array([[1, 1], [1, 2], [2, 2], [2, 3]]) y = np.dot(X, np.array([1, 2])) + 3 reg = LinearRegression().fit(X, y) print(reg.score(X, y)) arr = np.array([3, 5]) # 👇️ Wrap in square brackets [] print(reg.predict([arr])) # 👉️ [16.]
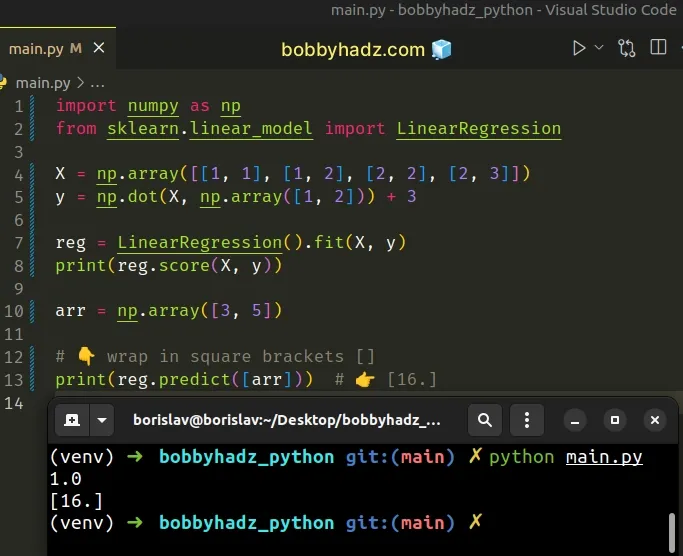
Now the predict() method gets called with a two-dimensional array and
everything works as expected.
This is necessary because the training data (X) is a two-dimensional array.
We have to use the predict() method on data that is of the same dimensionality
as the training data.
You can also use the reshape() method to solve the error.
import numpy as np from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression X = np.array([[1, 1], [1, 2], [2, 2], [2, 3]]) y = np.dot(X, np.array([1, 2])) + 3 reg = LinearRegression().fit(X, y) print(reg.score(X, y)) arr = np.array([3, 5]) arr = arr.reshape(1, -1) print(arr) # 👉️ [[3 5]] print(reg.predict(arr)) # 👉️ [16.]
- We used the
reshape()method to convert the 1-dimensional array to 2-dimensional. - We removed the set of square brackets
[]when callingreshape().
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Copy a column from one DataFrame to another in Pandas
- ValueError: cannot reindex on an axis with duplicate labels
- AttributeError module 'pandas' has no attribute 'DataFrame'
- ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'pandas' in Python
- FutureWarning: pandas.Int64Index is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version
- TypeError Invalid comparison between datetime64[ns] and date
- How to change the Port and Host in a Flask application
- Input contains infinity or value too large for dtype(float64)
- ValueError: columns overlap but no suffix specified [Solved]
- Arrays used as indices must be of integer (or boolean) type
- Shape mismatch: objects cannot be broadcast to a single shape
- AttributeError: Can only use .dt accessor with datetimelike values
- Usecols do not match columns, columns expected but not found
- Converting a Nested Dictionary to a Pandas DataFrame
- Pandas: Sum the values in a Column that match a Condition
- Interpolating NaN values in a NumPy Array in Python
- How to check if a NumPy Array is multidimensional or 1D
- Numpy: How to extract a Submatrix from an array

