ValueError: all the input array dimensions for the concatenation axis must match exactly
Last updated: Apr 11, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- ValueError: all the input array dimensions for the concatenation axis must match exactly
- Using the
numpy.c_attribute to solve the error - Using the
numpy.reshape()method to solve the error - Using the
numpy.hstack()method to solve the error
# ValueError: all the input array dimensions for the concatenation axis must match exactly
The NumPy "ValueError: all the input array dimensions for the concatenation
axis must match exactly" occurs when the arrays you've passed to
numpy.concatenate() don't have the same dimensions for the concatenation
axis.
To solve the error, use the numpy.column_stack method to stack the arrays as
columns into a 2-D array.
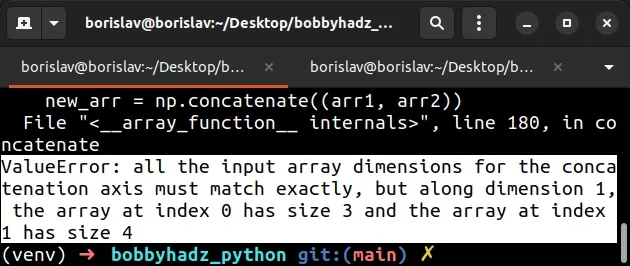
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([[1, 2, 3]]) arr2 = np.array([[4, 5, 6, 7]]) print(arr1.shape) # (1, 3) print(arr2.shape) # (1, 4) # ⛔️ ValueError: all the input array dimensions for the concatenation axis must match exactly, but along dimension 1, the array at index 0 has size 3 and the array at index 1 has size 4 new_arr = np.concatenate((arr1, arr2))
The first array we passed to numpy.concatenate() has 3 columns and the second one has 4 columns.
Both arrays have only 1 row.
The numpy.concatenate method joins a sequence of arrays along an existing
axis.
The error is raised because the dimensions of the arrays for the concatenation axis don't match.
If both arrays had a size of 3 (or a size of 4) along dimension 1, everything would work as expected.
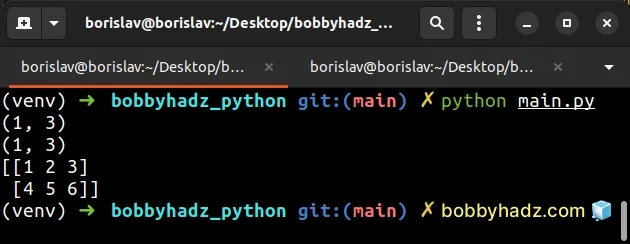
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([[1, 2, 3]]) arr2 = np.array([[4, 5, 6]]) print(arr1.shape) # (1, 3) print(arr2.shape) # (1, 3) new_arr = np.concatenate((arr1, arr2)) # [[1 2 3] # [4 5 6]] print(new_arr)
If you need to stack 1-D arrays as columns into a 2-D array, use the numpy.column_stack method.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([[1, 2, 3]]) arr2 = np.array([[4, 5, 6, 7]]) # [[1 2 3 4 5 6 7]] print(np.column_stack([arr1, arr2]))
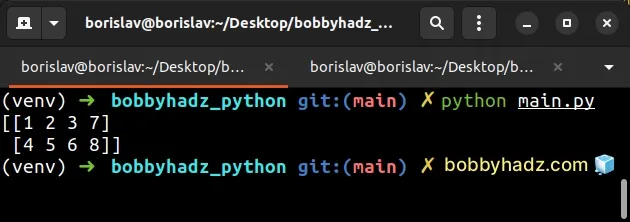
Here is an example that better illustrates how this works.
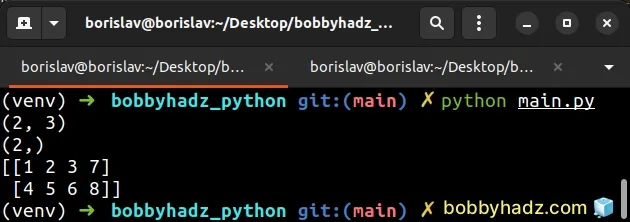
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]) arr2 = np.array([7, 8]) print(arr1.shape) # (2, 3) print(arr2.shape) # (2,) # [[1 2 3 7] # [4 5 6 8]] print(np.column_stack([arr1, arr2]))
The arrays you pass to the column_stack method must all have the same first
dimension.
The column_stack() method returns the two-dimensional array that is formed by
stacking the supplied arrays.
# Using the numpy.c_ attribute to solve the error
You can also use the numpy.c_ attribute to solve the error.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]) arr2 = np.array([7, 8]) print(arr1.shape) # (2, 3) print(arr2.shape) # (2,) # [[1 2 3 7] # [4 5 6 8]] print(np.c_[arr1, arr2])
The numpy.c_ attribute translates slice objects to concatenation along the
second axis.
import numpy as np # [[1 4] # [2 5] # [3 6]] print( np.c_[ np.array([1, 2, 3]), np.array([4, 5, 6]) ] )
The supplied arrays are stacked along their last axis after being upgraded to at least a 2-D array with column vectors made out of 1-D arrays.
# Using the numpy.reshape() method to solve the error
In some cases, you might have to use the numpy.reshape method to solve the error.
Suppose we have the following 2 arrays.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([[0, 1], [2, 3], [4, 5]]) arr2 = np.array([[6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]]) print(arr1.shape) # (3, 2) print(arr2.shape) # (1, 6) # ⛔️ ValueError: all the input array dimensions for the concatenation axis must match exactly, but along dimension 1, the array at index 0 has size 2 and the array at index 1 has size 6 new_arr = np.concatenate((arr1, arr2))
The first array has 3 rows and 2 columns and the second array has 1 row and 6 columns.
We can solve the error by reshaping the second array to 3 rows and 2 columns.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([[0, 1], [2, 3], [4, 5]]) arr2 = np.array([[6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]]) print(arr1.shape) # (3, 2) print(arr2.shape) # (1, 6) arr2 = arr2.reshape((3, 2)) new_arr = np.concatenate((arr1, arr2)) # [[ 0 1] # [ 2 3] # [ 4 5] # [ 6 7] # [ 8 9] # [10 11]] print(new_arr)
The numpy.reshape() method gives a new shape to an array without changing its data.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([[0, 1], [2, 3], [4, 5]]) arr2 = np.array([[6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]]) print(arr1.shape) # (3, 2) print(arr2.shape) # (1, 6) arr2 = arr2.reshape((3, 2)) # [[ 6 7] # [ 8 9] # [10 11]] print(arr2)
The two arrays are compatible after calling reshape(), so we can safely pass
them to the numpy.concatenate() method.
# Using the numpy.hstack() method to solve the error
You can also use the numpy.hstack() method to solve the error.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([[1, 2, 3]]) arr2 = np.array([[4, 5, 6, 7]]) new_array = np.hstack((arr1, arr2)) # 👇️ [[1 2 3 4 5 6 7]] print(new_array)
The numpy.hstack() method takes a sequence of arrays and stacks the arrays in
the sequence horizontally (column-wise).
This is equivalent to concatenation along the second axis, except for one-dimensional arrays where it concatenates along the first axis.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to replace None with NaN in Pandas DataFrame
- FutureWarning: pandas.Int64Index is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version
- You are trying to merge on int64 and object columns [Fixed]
- Copy a column from one DataFrame to another in Pandas
- AttributeError: Can only use .str accessor with string values
- ValueError: zero-dimensional arrays cannot be concatenated
- ValueError: zero-dimensional arrays cannot be concatenated
- ValueError: cannot reshape array of size X into shape Y

