Remove the Duplicate elements from a NumPy Array
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Table of Contents
- Remove the Duplicate elements from a NumPy Array
- Removing the duplicate Rows from a 2D NumPy array
- Removing the duplicate Columns from a 2D NumPy array
- Remove the duplicate rows from a NumPy array using lexsort()
# Remove the Duplicate elements from a NumPy Array
Use the numpy.unique() method to remove the duplicate elements from a NumPy
array.
The method will return a new array, containing the sorted, unique elements of the original array.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([[3, 3, 5, 6, 7], [1, 1, 4, 5, 6], [7, 7, 8, 9, 10]]) print(arr) print('-' * 50) unique_1d = np.unique(arr) print(unique_1d) # 👉️ [ 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10]
Running the code sample produces the following output.
[[ 3 3 5 6 7] [ 1 1 4 5 6] [ 7 7 8 9 10]] -------------------------------------------------- [ 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10]
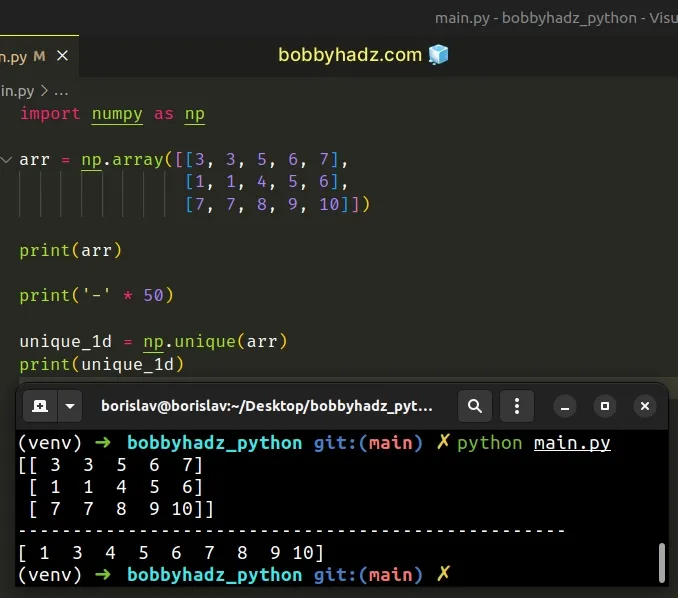
The numpy.unique() method finds the unique elements of an array.
The method returns a new ndarray containing the sorted, unique elements of the
original array.
# Removing the duplicate Rows from a 2D NumPy array
If you need to remove the duplicate rows from a 2D NumPy array, set the axis
argument to 0.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([[3, 3, 5, 6, 7], [3, 3, 5, 6, 7], [7, 7, 8, 9, 10]]) print(arr) print('-' * 50) unique_2d = np.unique(arr, axis=0) print(unique_2d)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
[[ 3 3 5 6 7] [ 3 3 5 6 7] [ 7 7 8 9 10]] -------------------------------------------------- [[ 3 3 5 6 7] [ 7 7 8 9 10]]
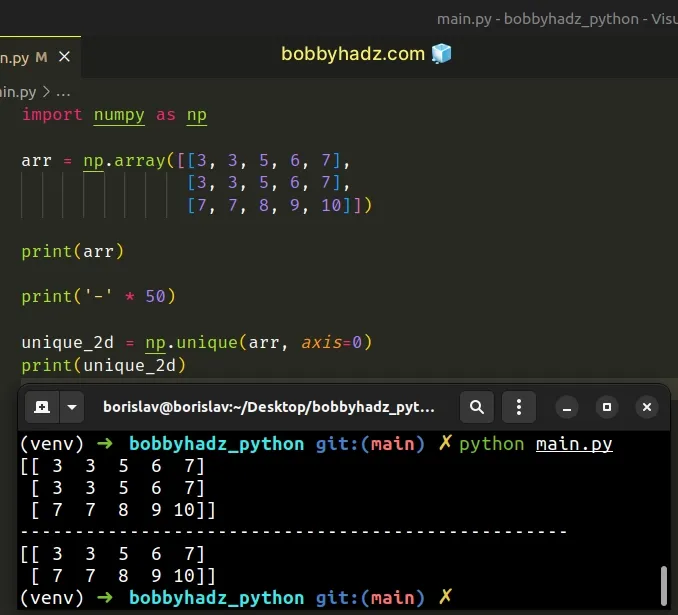
When the axis argument is set to 0, the numpy.unique() method returns the
unique rows of the 2D array.
The axis argument determines the axis to operate on.
If set to None or not supplied, the NumPy array is flattened.
# Removing the duplicate Columns from a 2D NumPy array
If you need to remove the duplicate columns from a 2D NumPy array, set the
axis argument to 1 when calling numpy.unique().
import numpy as np arr = np.array([[3, 3, 5, 6, 7], [1, 1, 4, 5, 6], [7, 7, 8, 9, 10]]) print(arr) print('-' * 50) unique_2d = np.unique(arr, axis=1) print(unique_2d)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
[[ 3 3 5 6 7] [ 1 1 4 5 6] [ 7 7 8 9 10]] -------------------------------------------------- [[ 3 5 6 7] [ 1 4 5 6] [ 7 8 9 10]]
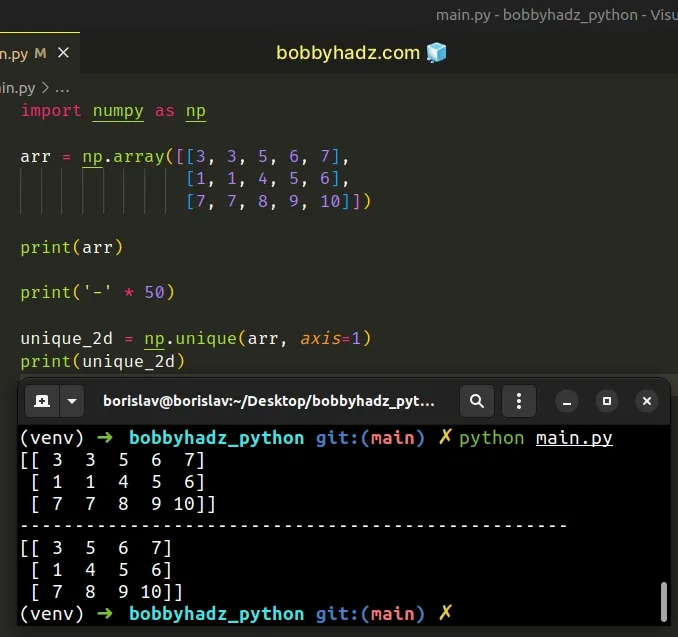
When the axis argument is set to 1, the numpy.unique() method returns the
unique columns of the 2D array.
# Remove the duplicate rows from a NumPy array using lexsort()
You can also use the numpy.lexsort() method if you need to remove the duplicate rows from a NumPy array.
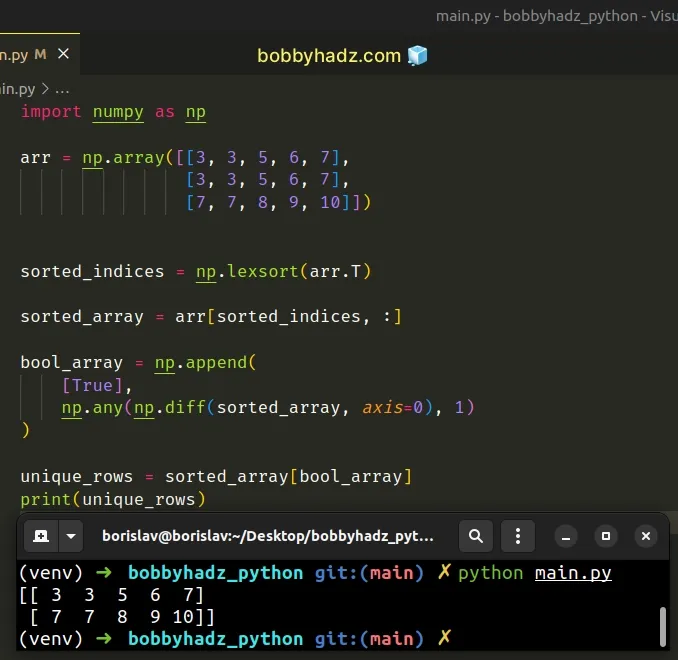
import numpy as np arr = np.array([[3, 3, 5, 6, 7], [3, 3, 5, 6, 7], [7, 7, 8, 9, 10]]) print(arr) print('-' * 50) sorted_indices = np.lexsort(arr.T) print(sorted_indices) print('-' * 50) sorted_array = arr[sorted_indices, :] print(sorted_array) print('-' * 50) bool_array = np.append( [True], np.any(np.diff(sorted_array, axis=0), 1) ) print(bool_array) print('-' * 50) unique_rows = sorted_array[bool_array] print(unique_rows)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
[[ 3 3 5 6 7] [ 3 3 5 6 7] [ 7 7 8 9 10]] -------------------------------------------------- [0 1 2] -------------------------------------------------- [[ 3 3 5 6 7] [ 3 3 5 6 7] [ 7 7 8 9 10]] -------------------------------------------------- [ True False True] -------------------------------------------------- [[ 3 3 5 6 7] [ 7 7 8 9 10]]
The numpy.lexsort() method returns an array of indices that sort the supplied
array.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([[3, 3, 5, 6, 7], [3, 3, 5, 6, 7], [7, 7, 8, 9, 10]]) sorted_indices = np.lexsort(arr.T) print(sorted_indices) # 👉️ [0 1 2]
We used the
numpy.append()
method to construct a boolean array containing True values for unique rows and
False values for duplicate rows.
bool_array = np.append( [True], np.any(np.diff(sorted_array, axis=0), 1) )
The last step is to use bracket notation to select only the unique rows.
unique_rows = sorted_array[bool_array]
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to swap two DataFrame columns in Pandas
- Pandas: Make new Column from string Slice of another Column
- Get N random Rows from a NumPy Array in Python
- Create Date column from Year, Month and Day in Pandas
- How to flatten only some Dimensions of a NumPy array
- NumPy: Unable to allocate array with shape and data type
- NumPy RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in divide
- All the input arrays must have same number of dimensions
- ValueError: Index contains duplicate entries, cannot reshape
- TypeError: type numpy.ndarray doesn't define __round__ method

