Pandas: How to keep the Index when merging DataFrames
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Pandas: How to keep the Index when merging DataFrames
- Pandas: Keep the Index when merging DataFrames using an index copy
- Pandas: Keep the Index when merging DataFrames using join()
# Pandas: How to keep the Index when merging DataFrames
To keep the index when merging DataFrames in Pandas:
- Use the
reset_index()to reset the index of the firstDataFrame. - Call the
merge()method on the result. - Use the
set_index()method to set the index on the mergedDataFrame.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'profit': [1500, 2500, 3500, 4500], }, index=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D']) df2 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'employees': [10, 15, 20, 25], }) df3 = df1.reset_index().merge(df2, how='left').set_index('index') # year profit employees # index # A 2020 1500 10 # B 2021 2500 15 # C 2022 3500 20 # D 2023 4500 25 print(df3)
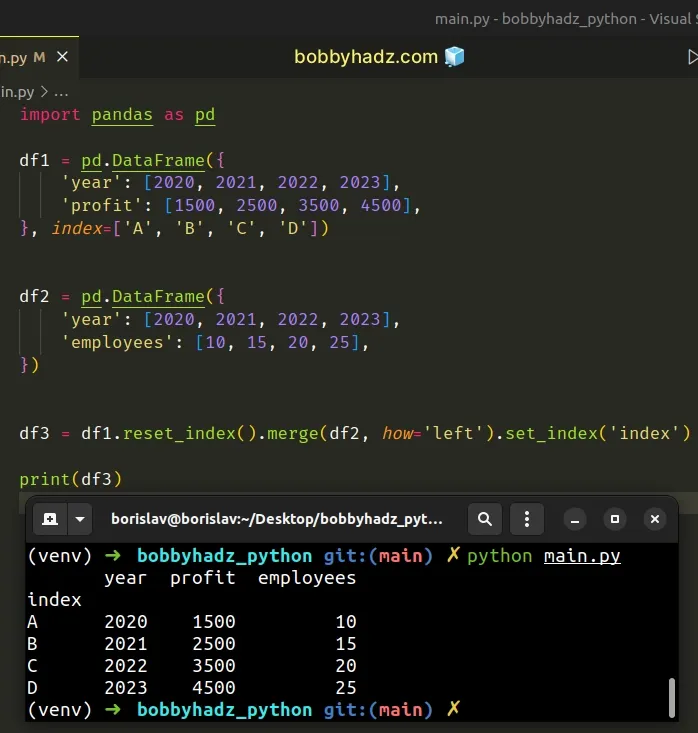
By default, when merging DataFrames, the new DataFrame will have a brand-new
index, starting at 0.
However, you will often have to change the default behavior.
We first used the
reset_index()
method to reset the index of the first DataFrame.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'profit': [1500, 2500, 3500, 4500], }, index=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D']) # index year profit # 0 A 2020 1500 # 1 B 2021 2500 # 2 C 2022 3500 # 3 D 2023 4500 print(df1.reset_index())
Once its index is reset, we can merge the two DataFrames.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'profit': [1500, 2500, 3500, 4500], }, index=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D']) df2 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'employees': [10, 15, 20, 25], }) # index year profit employees # 0 A 2020 1500 10 # 1 B 2021 2500 15 # 2 C 2022 3500 20 # 3 D 2023 4500 25 print(df1.reset_index().merge(df2, how='left'))
The last step is to set the index of the merged DataFrame.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'profit': [1500, 2500, 3500, 4500], }, index=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D']) df2 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'employees': [10, 15, 20, 25], }) # year profit employees # index # A 2020 1500 10 # B 2021 2500 15 # C 2022 3500 20 # D 2023 4500 25 print(df1.reset_index().merge(df2, how='left').set_index('index'))
The DataFrame.set_index()
method sets the DataFrame index (row labels) using existing columns.
If you need to remove the duplicates after merging the DataFrames, use the DataFrame.drop_duplicates method.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'profit': [1500, 2500, 3500, 4500], }, index=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D']) df2 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'employees': [10, 15, 20, 25], }) df3 = df1.reset_index().merge(df2, how='left').set_index('index') df3.drop_duplicates(inplace=True) # year profit employees # index # A 2020 1500 10 # B 2021 2500 15 # C 2022 3500 20 # D 2023 4500 25 print(df3)
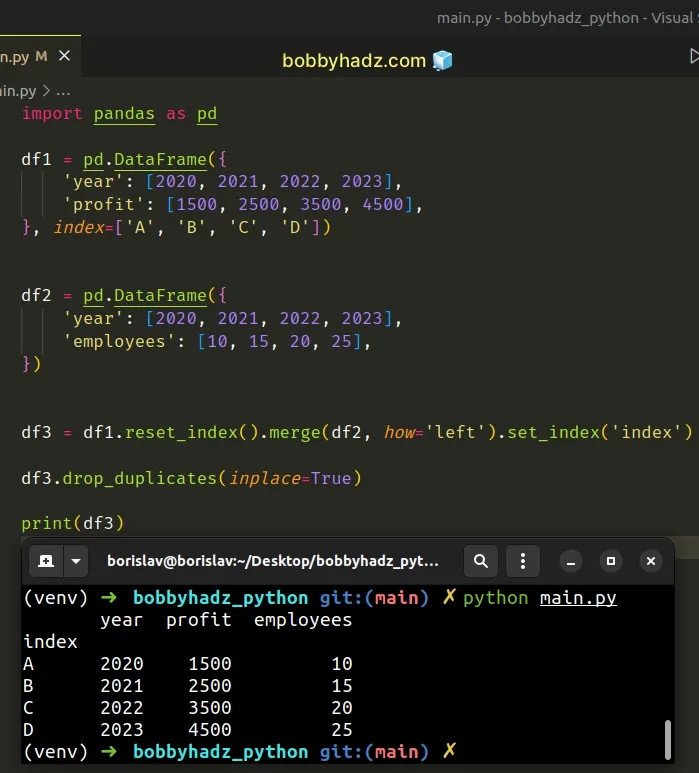
# Pandas: Keep the Index when merging DataFrames using an index copy
You can also create a
copy of the index column in
the first DataFrame before merging to keep the index.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'profit': [1500, 2500, 3500, 4500], }, index=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D']) df2 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'employees': [10, 15, 20, 25], }) df1['index_copy'] = df1.index df3 = df1.merge(df2, how='left') # year profit index_copy employees # 0 2020 1500 A 10 # 1 2021 2500 B 15 # 2 2022 3500 C 20 # 3 2023 4500 D 25 print(df3)
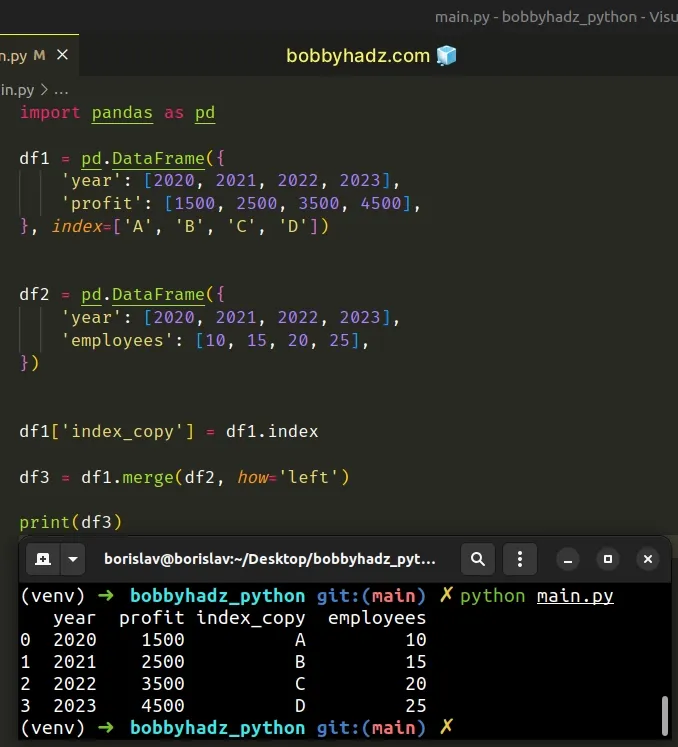
The DataFrame.index attribute returns
the index (row labels) of the DataFrame.
We used the attribute to add a new "index_copy" column to the first
DataFrame
You can then call the merge() method and the "index_copy" column will be
contained in the resulting DataFrame.
# Pandas: Keep the Index when merging DataFrames using join()
You can also use the DataFrame.join() method to keep the index when merging DataFrames.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'profit': [1500, 2500, 3500, 4500], }, index=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D']) df2 = pd.DataFrame({ 'year': [2020, 2021, 2022, 2023], 'employees': [10, 15, 20, 25], }) df3 = df1.join(df2.set_index('year'), on='year') print(df3) print(df3.index)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
year profit employees A 2020 1500 10 B 2021 2500 15 C 2022 3500 20 D 2023 4500 25 Index(['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'], dtype='object')
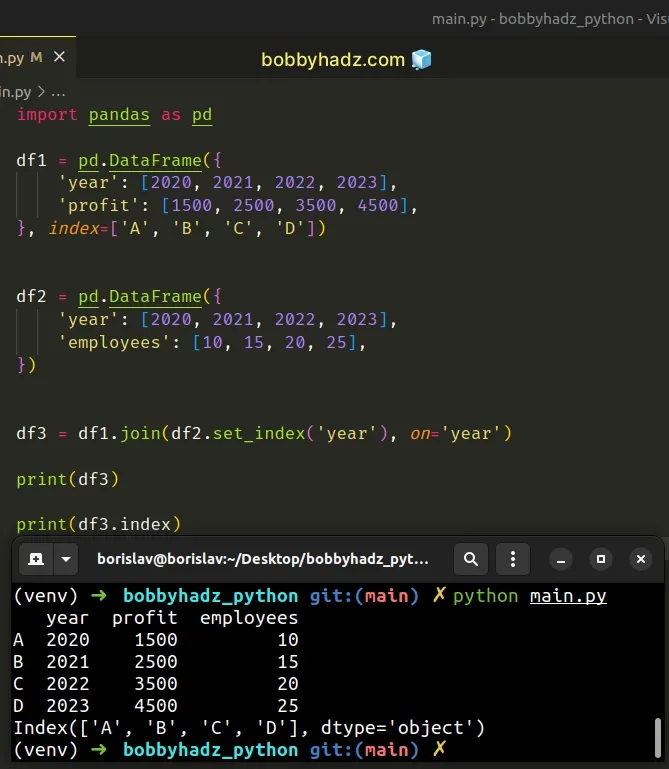
The DataFrame.join() method joins the columns of two DataFrames, either on the
index or on a key column.
Make sure to call the set_index() method and to set the on argument to the
column you want to merge on (year in the example).
df3 = df1.join(df2.set_index('year'), on='year')
I've also written an article on how to Start the Index of a Pandas DataFrame at 1.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Pandas ValueError: Cannot index with multidimensional key
- ValueError: Grouper for 'X' not 1-dimensional [Solved]
- Cannot subset columns with tuple with more than one element
- Pandas: Get Nth row or every Nth row in a DataFrame
- Pandas: Select first N or last N columns of DataFrame
- Pandas: DataFrame.reset_index() not working [Solved]
- How to Create a Set from a Series in Pandas
- NumPy: Apply a Mask from one Array to another Array
- Pandas: Find an element's Index in Series [7 Ways]
- Matplotlib: No artists with labels found to put in legend
- ValueError: Index contains duplicate entries, cannot reshape
- Pandas: How to Query a Column name with Spaces
- Annotate Bars in Barplot with Pandas and Matplotlib
- Pandas: Create a Tuple from two DataFrame Columns
- RuntimeError: Expected scalar type Float but found Double
- Pandas: Convert timezone-aware DateTimeIndex to naive timestamp
- RuntimeError: Input type (torch.FloatTensor) and weight type (torch.cuda.FloatTensor) should be the same
- How to read a .mat (Matplotlib) file in Python
- Python: How to center the Title in Plotly
- ValueError: Expected object or value with
pd.read_json() - Mixing dicts with non-Series may lead to ambiguous ordering
- PyTorch: Trying to backward through the graph a second time
- Pandas: Unalignable boolean Series provided as indexer

