Pandas: Select distinct across multiple DataFrame columns
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Pandas: Select distinct across multiple DataFrame columns
- Select distinct across multiple DataFrame columns using a
forloop - Getting the unique values across multiple columns in a single array
# Pandas: Select distinct across multiple DataFrame columns
Use the drop_duplicates() method to "select distinct" across multiple
DataFrame columns in Pandas.
The method will return a new DataFrame object with the duplicate rows
removed.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'Animal': ['Cat', 'Cat', 'Cat', 'Dog', 'Dog', 'Dog'], 'Max Speed': [25, 25, 40, 45, 45, 65] }) # Animal Max Speed # 0 Cat 25 # 2 Cat 40 # 3 Dog 45 # 5 Dog 65 print(df.drop_duplicates())
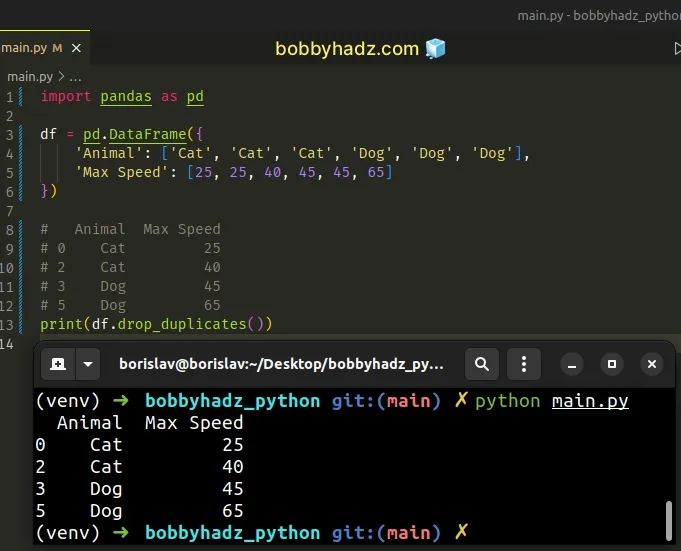
The code sample shows how to get the unique values across multiple DataFrame
columns.
Note: if you need to get the unique values across multiple columns contained
in a single array, use the pandas.unique() method.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'Animal': ['Cat', 'Cat', 'Cat', 'Dog', 'Dog', 'Dog'], 'Animal2': ['Cat', 'Dog', 'Lizzard', 'Monkey', 'Lizzard', 'Cat'] }) # 👇️ ['Cat' 'Dog' 'Lizzard' 'Monkey'] print(pd.unique(df[['Animal', 'Animal2']].values.ravel('K')))
The ravel() method returns a multi-dimensional array which we then flatten.
The
DataFrame.drop_duplicates()
method returns a new DataFrame object with the duplicate rows removed.
By default, the method doesn't mutate the DataFrame in place, so make sure to
assign the result of calling it into a variable.
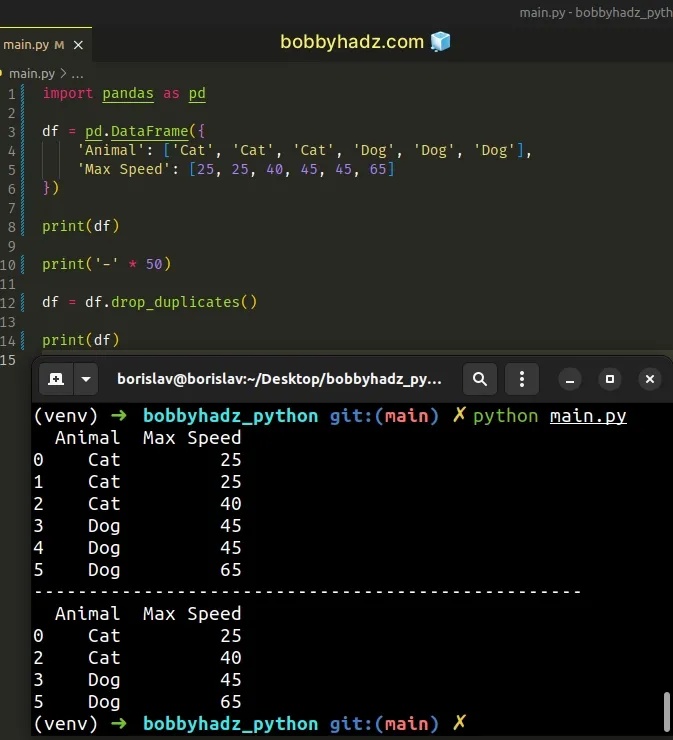
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'Animal': ['Cat', 'Cat', 'Cat', 'Dog', 'Dog', 'Dog'], 'Max Speed': [25, 25, 40, 45, 45, 65] }) print(df) print('-' * 50) df = df.drop_duplicates() print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
Animal Max Speed 0 Cat 25 1 Cat 25 2 Cat 40 3 Dog 45 4 Dog 45 5 Dog 65 -------------------------------------------------- Animal Max Speed 0 Cat 25 2 Cat 40 3 Dog 45 5 Dog 65
Alternatively, you can set the inplace argument to True to mutate the
original DataFrame object.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'Animal': ['Cat', 'Cat', 'Cat', 'Dog', 'Dog', 'Dog'], 'Max Speed': [25, 25, 40, 45, 45, 65] }) print(df) print('-' * 50) df.drop_duplicates(inplace=True) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
Animal Max Speed 0 Cat 25 1 Cat 25 2 Cat 40 3 Dog 45 4 Dog 45 5 Dog 65 -------------------------------------------------- Animal Max Speed 0 Cat 25 2 Cat 40 3 Dog 45 5 Dog 65
When the inplace argument is set to True, the DataFrame is modified in
place and None is returned.
By default, the DataFrame.drop_duplicates method considers all of the columns
when identifying duplicates.
If you only want to consider some of the columns, supply the subset argument.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'Animal': ['Cat', 'Cat', 'Cat', 'Dog', 'Dog', 'Dog'], 'Max Speed': [25, 25, 40, 45, 45, 65] }) print(df) print('-' * 50) df.drop_duplicates(subset=['Animal'], inplace=True) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
Animal Max Speed 0 Cat 25 1 Cat 25 2 Cat 40 3 Dog 45 4 Dog 45 5 Dog 65 -------------------------------------------------- Animal Max Speed 0 Cat 25 3 Dog 45
We only passed the Animal column to the subset list, so the method will only
consider the specified column for identifying duplicates.
# Select distinct across multiple DataFrame columns using a for loop
You can also use a for loop with pandas.unique() to select the distinct
values across multiple DataFrame columns.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'Animal': ['Cat', 'Cat', 'Cat', 'Dog', 'Dog', 'Dog'], 'Max Speed': [25, 25, 40, 45, 45, 65] }) a_dict = {} for column in df: a_dict[column] = df[column].unique() # {'Animal': array(['Cat', 'Dog'], dtype=object), # 'Max Speed': array([25, 40, 45, 65])} print(a_dict)
We used a for loop to iterate over the DataFrame.
On each iteration, we use the pandas.unique() method to get an array that stores the unique values for the current column.
You should also use the unique() method if you need to find the unique values
in a specific column.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'Animal': ['Cat', 'Cat', 'Cat', 'Dog', 'Dog', 'Dog'], 'Max Speed': [25, 25, 40, 45, 45, 65] }) print(df['Animal'].unique()) # ['Cat' 'Dog'] print(df['Max Speed'].unique()) # [25 40 45 65]
Note: if you need to get the unique values across multiple columns contained
in a single array, use the pandas.unique() method.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'Animal': ['Cat', 'Cat', 'Cat', 'Dog', 'Dog', 'Dog'], 'Animal2': ['Cat', 'Dog', 'Lizzard', 'Monkey', 'Lizzard', 'Cat'] }) # 👇️ ['Cat' 'Dog' 'Lizzard' 'Monkey'] print(pd.unique(df[['Animal', 'Animal2']].values.ravel('K')))
# Getting the unique values across multiple columns in a single array
You can also use the numpy.unique() method if you need to get the unique
values across multiple columns in a single array.
First, make sure you
have the numpy module installed.
Open your terminal and run the following command.
pip install numpy # or with pip3 pip3 install numpy
Now, import the module and use numpy.unique().
import pandas as pd import numpy as np df = pd.DataFrame({ 'Animal': ['Cat', 'Cat', 'Cat', 'Dog', 'Dog', 'Dog'], 'Animal2': ['Cat', 'Dog', 'Lizzard', 'Monkey', 'Lizzard', 'Cat'] }) # 👇️ ['Cat' 'Dog' 'Lizzard' 'Monkey'] print(np.unique(df[['Animal', 'Animal2']].values))
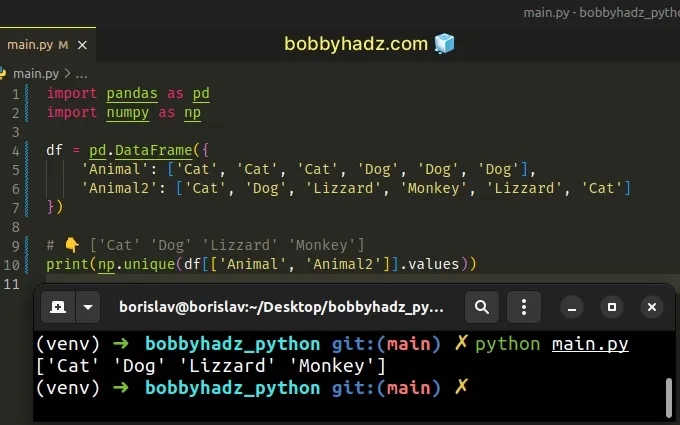
We used bracket notation to select the Animal and Animal2 columns and passed
the resulting DataFrame to numpy.unique().
The numpy.unique method takes an array-like object and returns the unique elements of the array.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Using pandas.read_csv() with multiple delimiters in Python
- ValueError: Cannot merge a Series without a name [Solved]
- Index(...) must be called with a collection of some kind
- ValueError: Shape of passed values is X, indices imply Y
- ValueError: Length of values does not match length of index
- Convert Epoch to Datetime in a Pandas DataFrame
- How to get the Memory size of a DataFrame in Pandas
- Convert column Values to Columns in a Pandas DataFrame
- How to check if a NumPy Array is multidimensional or 1D
- Numpy: How to extract a Submatrix from an array
- Pandas: Cannot setitem on a Categorical with a new category
- Only valid with DatetimeIndex, TimedeltaIndex or PeriodIndex, but got an instance of X
- Pandas SpecificationError: nested renamer is not supported
- Cannot perform 'rand_' with a dtyped [int64] array and scalar of type [bool]

