How to read a .mat (Matplotlib) file in Python
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# How to read a .mat (Matplotlib) file in Python
To read a .mat (Matplotlib) file in Python:
- Install the
scipymodule and importscipy.io. - Pass the path to the file to the
scipy.io.loadmat()method. - The
loadmat()method will load the file into your Python script.
First, make sure that you've installed scipy.
Open your terminal in your project's root directory and issue the following command.
pip install scipy # or with pip3 pip3 install scipy
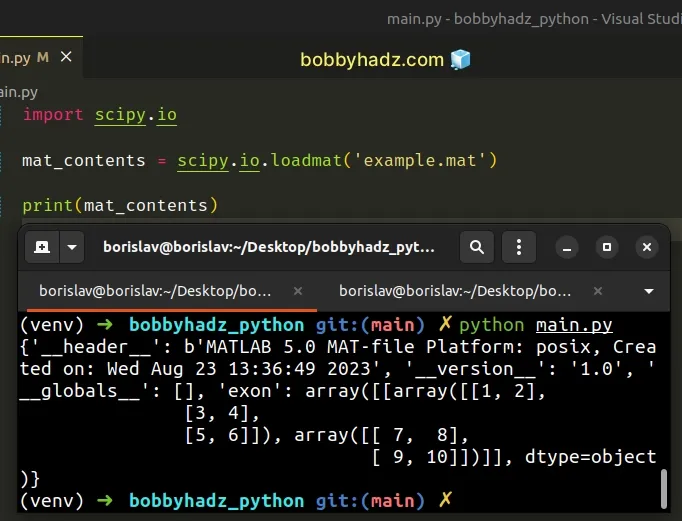
Now, import and use the scipy.io module to read the .mat file.
import scipy.io mat_contents = scipy.io.loadmat('example.mat') print(mat_contents)
Make sure to replace the example.mat placeholder with the path to your .mat
file.
Running the code sample produces the following output.
{'__header__': b'MATLAB 5.0 MAT-file Platform: posix, Created on: Wed Aug 23 13:36:49 2023', '__version__': '1.0', '__globals__': [], 'exon': array([[array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]), array([[ 7, 8], [ 9, 10]])]], dtype=object)}
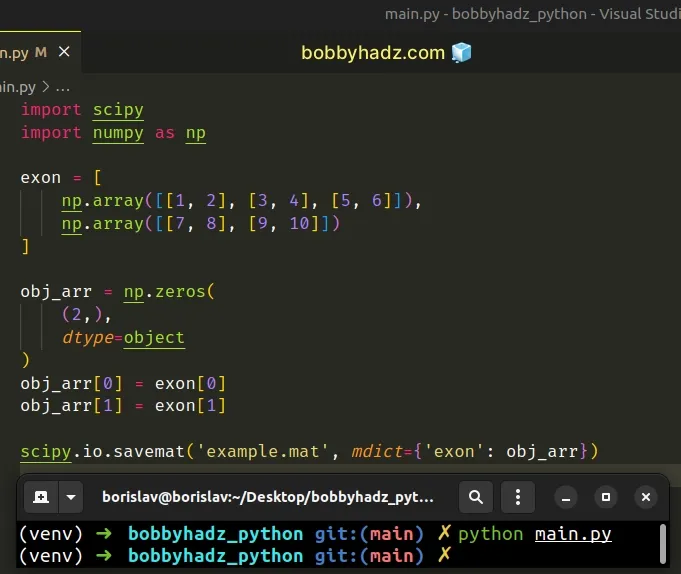
And here is the code that I used to create the example.mat file.
import scipy import numpy as np exon = [ np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]), np.array([[7, 8], [9, 10]]) ] obj_arr = np.zeros( (2,), dtype=object ) obj_arr[0] = exon[0] obj_arr[1] = exon[1] scipy.io.savemat('example.mat', mdict={'exon': obj_arr})
We used the scipy.io.loadmat method to load the Matlab file into a Python script.
import scipy.io mat_contents = scipy.io.loadmat('example.mat') print(mat_contents) print('-' * 50) # 👇️ <class 'dict'> print(type(mat_contents))
The only parameter we passed to the method is the filename.
The method returns a dictionary with variable names as keys and loaded matrices as values.
You can use the dict.keys() method if you only want to print the keys of the dictionary.
import scipy.io mat_contents = scipy.io.loadmat('example.mat') # ['__globals__', '__header__', '__version__', 'exon'] print(sorted(mat_contents.keys())) # [[array([[1, 2], # [3, 4], # [5, 6]]) array([[ 7, 8], # [ 9, 10]])]] print(mat_contents['exon'])
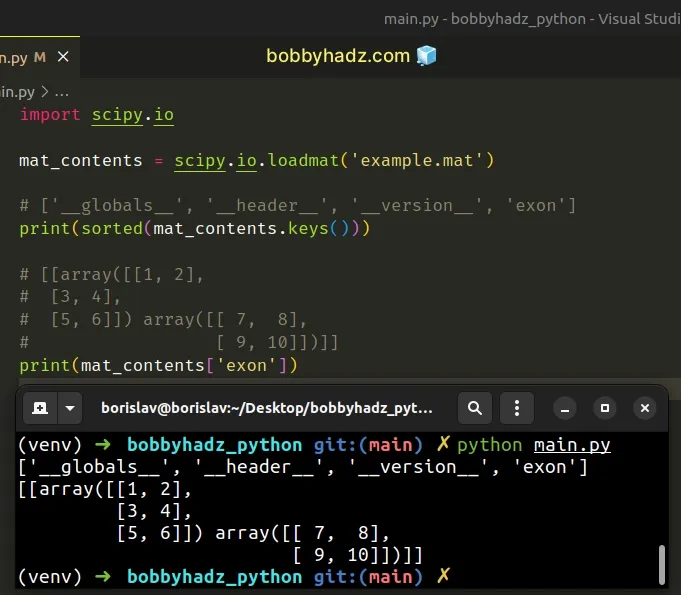
As shown in the code sample, use bracket notation to access a specific dictionary key.
If you need to convert the data from the .mat file to a DataFrame, use the
pandas.DataFrame()
constructor.
import pandas as pd import scipy.io mat_contents = scipy.io.loadmat('example.mat') print(mat_contents.keys()) print('-' * 50) print(mat_contents['exon']) print('-' * 50) df = pd.DataFrame(mat_contents['exon'], columns=['A', 'B']) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
dict_keys(['__header__', '__version__', '__globals__', 'exon']) -------------------------------------------------- [[array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]) array([[ 7, 8], [ 9, 10]])]] -------------------------------------------------- A B 0 [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]] [[7, 8], [9, 10]]
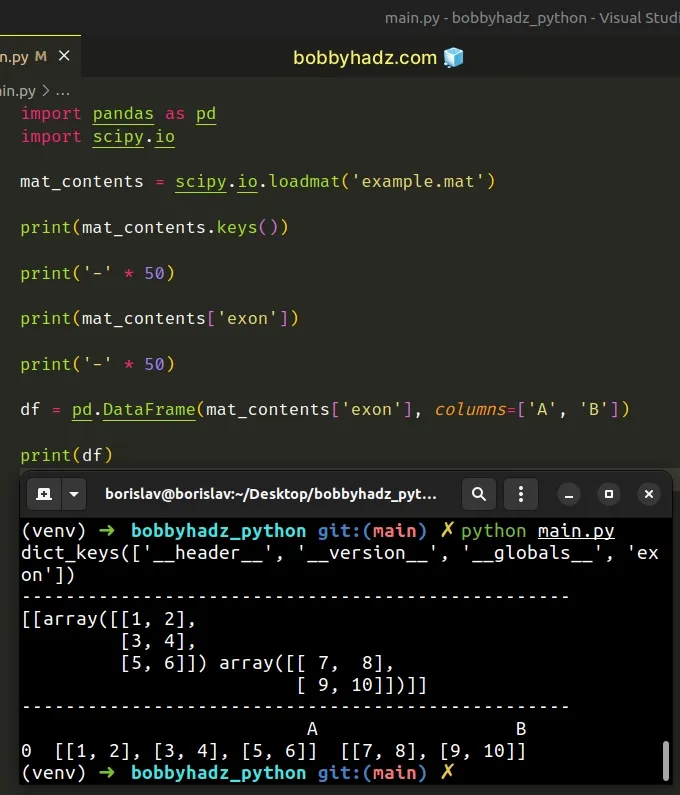
Make sure to adjust the column names and/or massage the data depending on your needs.
# How to read a .mat (Matplotlib) file in Python using pymatreader
You can also use the pymatreader
package to read a .mat file in Python.
First install the module by opening your terminal in your project's root directory and running the following command.
pip install pymatreader # or with pip3 pip3 install pymatreader
Now, import and use the module as follows.
from pymatreader import read_mat mat_contents = read_mat('example.mat') # dict_keys(['__header__', '__version__', '__globals__', 'exon']) print(mat_contents.keys()) # [array([[1, 2], # [3, 4], # [5, 6]]), array([[ 7, 8], # [ 9, 10]])] print(mat_contents['exon'])
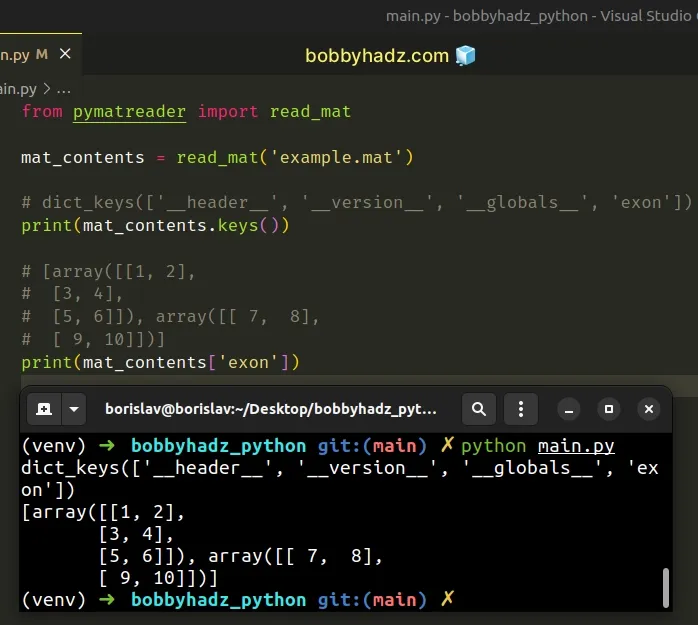
The pymatreader module enables us to read Matlab files.
The read_mat() method returns a Python dictionary that contains all variables
of the .mat file.
As shown in the example, you can use the .keys() method to find where the data
is actually stored.
The only key that is not surrounded by double underscores is xon, so we used
bracket notation to access it.
Depending on the stored data, you will have to access a key with a different name.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Panda: Using fillna() with specific columns in a DataFrame
- Pandas: Split a Column of Lists into Multiple Columns
- How to Split a Pandas DataFrame into Chunks
- Pandas: Count the unique combinations of two Columns
- Remove __pycache__ folders and .pyc files in Python Project
- ValueError: invalid mode: 'rU' while trying to load binding.gyp
- SyntaxError: future feature annotations is not defined
- Python: How to ignore #comment lines in a File

