NumPy: Get the indices of the N largest values in an Array
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- NumPy: Get the indices of the N largest values in an Array
- NumPy: Get the indices of the N largest values in an Array using argsort()
- NumPy: Get the indices of the N largest values in an Array using nlargest
# NumPy: Get the indices of the N largest values in an Array
To get the indices of the N largest values in an array:
- Use the
numpy.argpartition()method to get an array of indices that partition the array. - Access the last N elements of the array.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([100, 50, 20, 30, 90, 1, 5]) indices_2_largest = np.argpartition(arr, -2)[-2:] print(indices_2_largest) # 👉️ [4 0] print(arr[indices_2_largest]) # 👉️ [ 90 100]
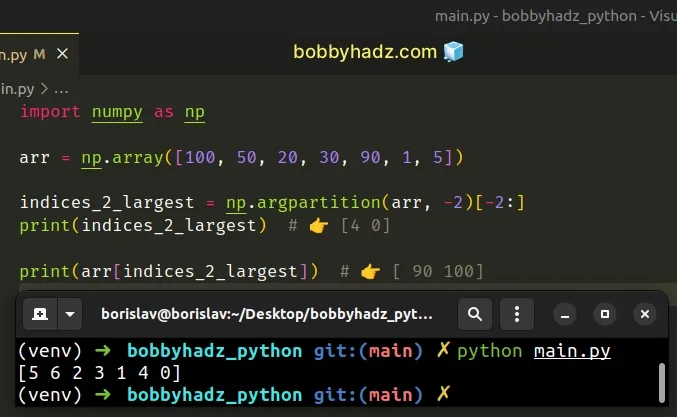
The code sample finds the indices of the 2 largest values in the NumPy array using numpy.argpartition().
The same approach can be used to find the indices of the 3 (or N) largest values in the array.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([100, 50, 20, 30, 90, 1, 5]) indices_3_largest = np.argpartition(arr, -3)[-3:] print(indices_3_largest) # 👉️ [1 4 0] print(arr[indices_3_largest]) # 👉️ [ 50 90 100]
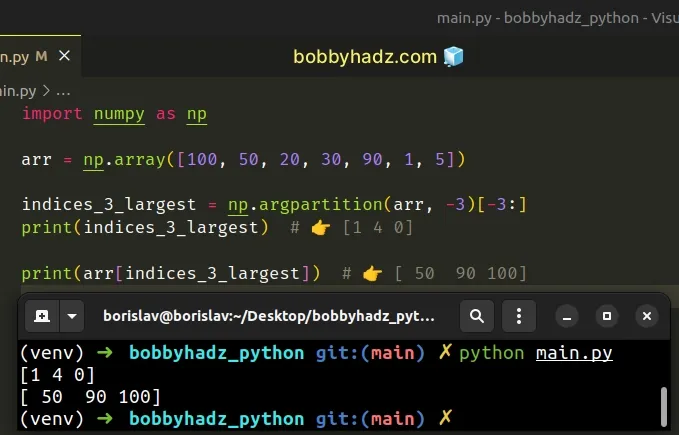
If you have to do this often, define a reusable function.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([100, 50, 20, 30, 90, 1, 5]) def find_indices_n_largest(array, n): return np.argpartition(array, -n)[-n:] print(find_indices_n_largest(arr, 2)) # 👉️ [4 0] print('-' * 50) print(find_indices_n_largest(arr, 3)) # 👉️ [1 4 0]
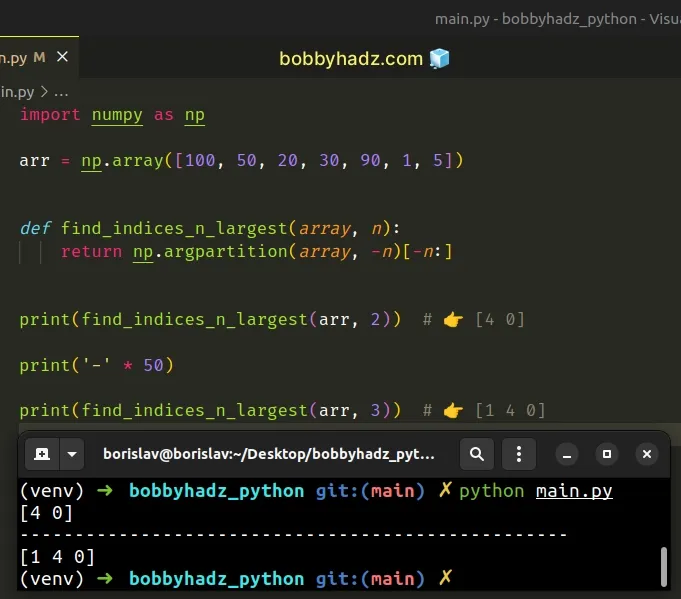
The function takes the array and n as parameters and returns the indices of
the largest n values in the array.
# NumPy: Get the indices of the N largest values in an Array using argsort()
You can also use the numpy.argsort() method to find the indices of the N largest values in an array.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([100, 50, 20, 30, 90, 1, 5]) def find_indices_n_largest(array, n): return array.argsort()[-n:][::-1] print(find_indices_n_largest(arr, 2)) # 👉️ [0 4] print('-' * 50) print(find_indices_n_largest(arr, 3)) # 👉️ [0 4 1]
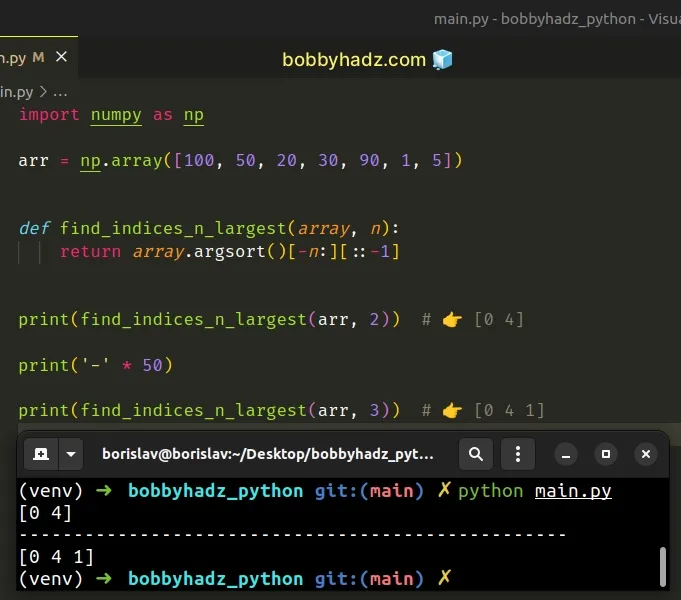
The numpy.argsort() method returns the indices that would sort an array.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([100, 50, 20, 30, 90, 1, 5]) # [5 6 2 3 1 4 0] print(arr.argsort())
The next step is to get the last N elements from the indices array.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([100, 50, 20, 30, 90, 1, 5]) # [5 6 2 3 1 4 0] print(arr.argsort()) # [4 0] print(arr.argsort()[-2:])
The last step is to reverse the slice.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([100, 50, 20, 30, 90, 1, 5]) # [5 6 2 3 1 4 0] print(arr.argsort()) # [4 0] print(arr.argsort()[-2:]) # [0 4] print(arr.argsort()[-2:][::-1])
You can imagine that the [::-1] part of the code sample simply reverses the
indices array.
I've written a detailed guide on how to use numpy.argsort in descending order.
You can also simplify this a little by passing the negated array to argsort().
import numpy as np arr = np.array([100, 50, 20, 30, 90, 1, 5]) def find_indices_n_largest(array, n): return np.argsort(-array)[:n] print(find_indices_n_largest(arr, 2)) # 👉️ [0 4] print('-' * 50) print(find_indices_n_largest(arr, 3)) # 👉️ [0 4 1]
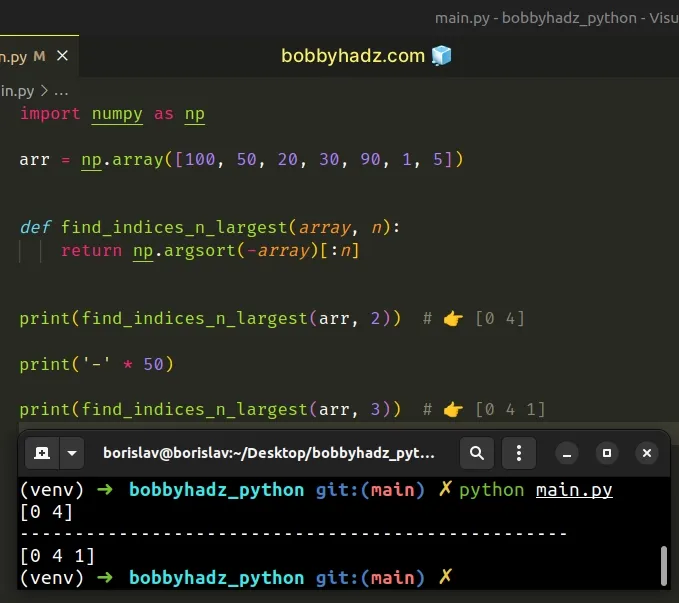
Notice that we didn't have to reverse the array in the example.
If the supplied n value is 0, an empty array is returned.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([100, 50, 20, 30, 90, 1, 5]) def find_indices_n_largest(array, n): return np.argsort(-array)[:n] print(find_indices_n_largest(arr, 0)) # 👉️ []
This can also be done by negating the array elements before calling argsort().
import numpy as np arr = np.array([100, 50, 20, 30, 90, 1, 5]) def find_indices_n_largest(array, n): return (-array).argsort()[:n] print(find_indices_n_largest(arr, 0)) # 👉️ [] print('-' * 50) print(find_indices_n_largest(arr, 2)) # 👉️ [0 4] print('-' * 50) print(find_indices_n_largest(arr, 3)) # 👉️ [0 4 1]
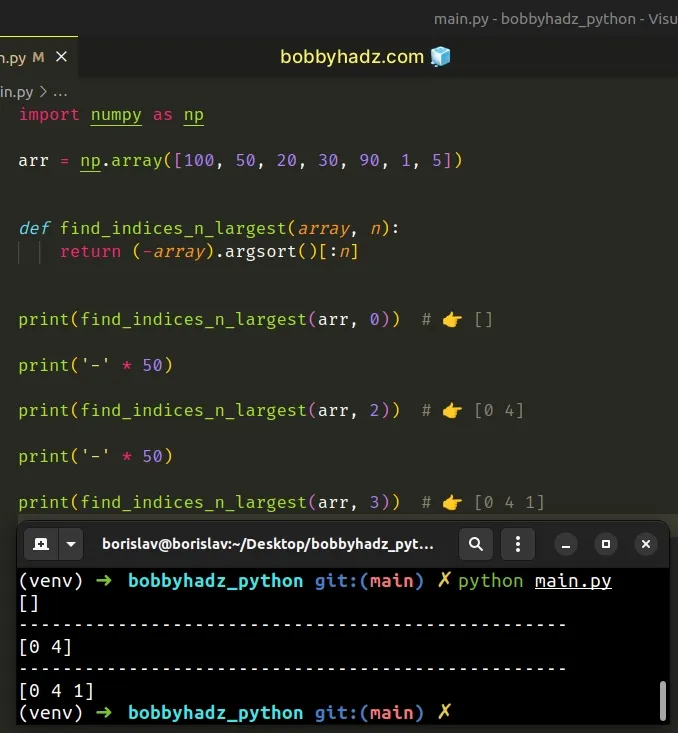
You can also achieve the same result by reversing the array before selecting the first N elements.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([100, 50, 20, 30, 90, 1, 5]) def find_indices_n_largest(array, n): return array.argsort()[::-1][:n] print(find_indices_n_largest(arr, 0)) # 👉️ [] print('-' * 50) print(find_indices_n_largest(arr, 2)) # 👉️ [0 4] print('-' * 50) print(find_indices_n_largest(arr, 3)) # 👉️ [0 4 1]
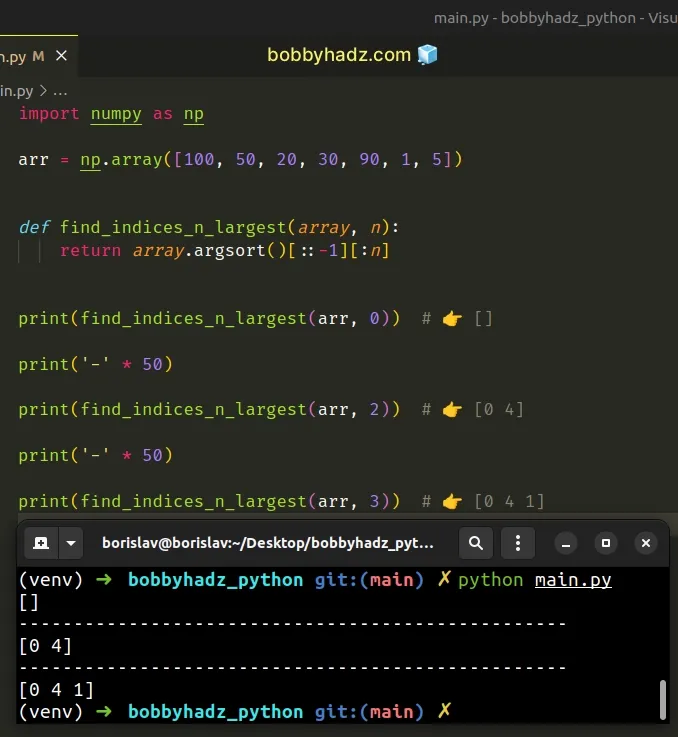
# NumPy: Get the indices of the N largest values in an Array using nlargest
You can also use the nlargest method from the built-in heapq module to get the indices of the N largest values in an array.
from heapq import nlargest import numpy as np arr = np.array([100, 50, 20, 30, 90, 1, 5]) def find_indices_n_largest(array, n): return nlargest(n, range(len(array)), array.take) print(find_indices_n_largest(arr, 0)) # 👉️ [] print('-' * 50) print(find_indices_n_largest(arr, 2)) # 👉️ [0, 4] print('-' * 50) print(find_indices_n_largest(arr, 3)) # 👉️ [0, 4, 1]
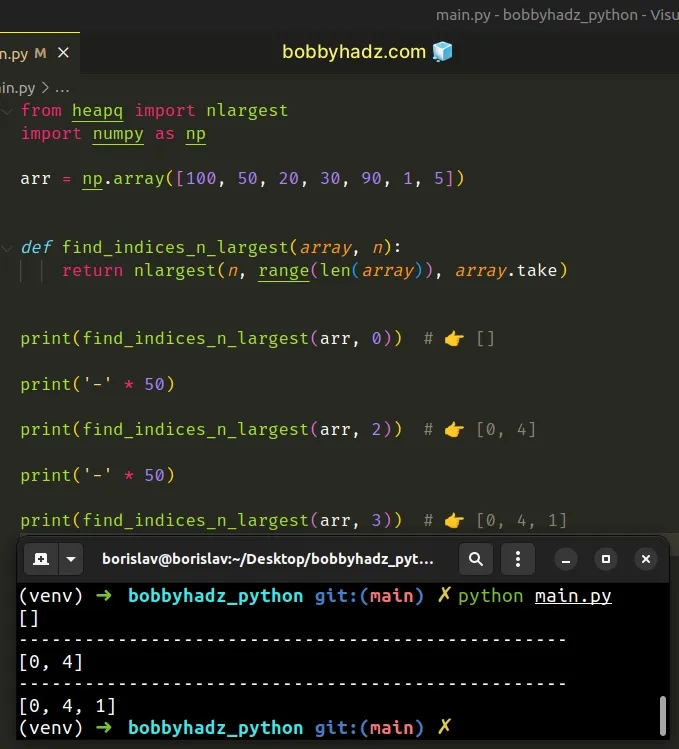
The heapq.nlargest() method takes n and an iterable as parameters and
returns a list with the n largest elements from the iterable.
We used the range() class with the len() function to get the indices of the NumPy array.
The third argument we passed to the heapq.nlargest method is a key function.
The key function is used to extract a comparison key from each element in the
iterable.
The numpy.take() method selects the elements from an array by the given indices.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Cannot set a DataFrame with multiple columns to single column
- Pandas ValueError: cannot insert X, already exists [Solved]
- How to Multiply two or more Columns in Pandas
- How to swap two DataFrame columns in Pandas
- Remove the Duplicate elements from a NumPy Array
- NumPy: Apply a Mask from one Array to another Array
- How to iterate over the Columns of a NumPy Array
- Pandas: Find an element's Index in Series [7 Ways]
- All the input arrays must have same number of dimensions
- Only integer scalar arrays can be converted to a scalar index
- ValueError: Index contains duplicate entries, cannot reshape

