Calculate the Average for each Row in a Pandas DataFrame
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Calculate the Average for each Row in a Pandas DataFrame
- Calculate the Row Average in a Pandas DataFrame using df.iloc
- Calculating the row average based on the column names in a Pandas DataFrame
# Calculate the Average for each Row in a Pandas DataFrame
To calculate the average for each row in a Pandas DataFrame:
- Call the
mean()method on theDataFrame. - Set the
axisargument to1to calculate the average for each row.
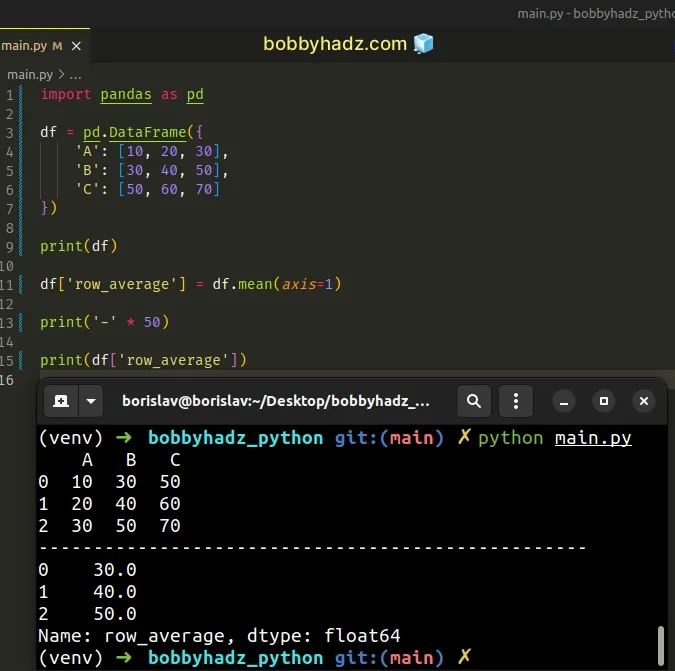
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': [10, 20, 30], 'B': [30, 40, 50], 'C': [50, 60, 70] }) print(df) df['row_average'] = df.mean(axis=1) print('-' * 50) print(df['row_average'])
Running the code sample produces the following output.
A B C 0 10 30 50 1 20 40 60 2 30 50 70 -------------------------------------------------- 0 30.0 1 40.0 2 50.0 Name: row_average, dtype: float64
The
DataFrame.mean()
method returns the mean of the values over the specified axis.
By default, the axis argument is set to 0, which means that the column
average is calculated.
We set the axis argument to 1 to compute the mean along the rows' axis.
df['row_average'] = df.mean(axis=1)
When running the code sample you might get a warning that "A value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame. Try using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead".
If you get the warning, try to use the
DataFrame.assign()
method when adding the row average column to the DataFrame.
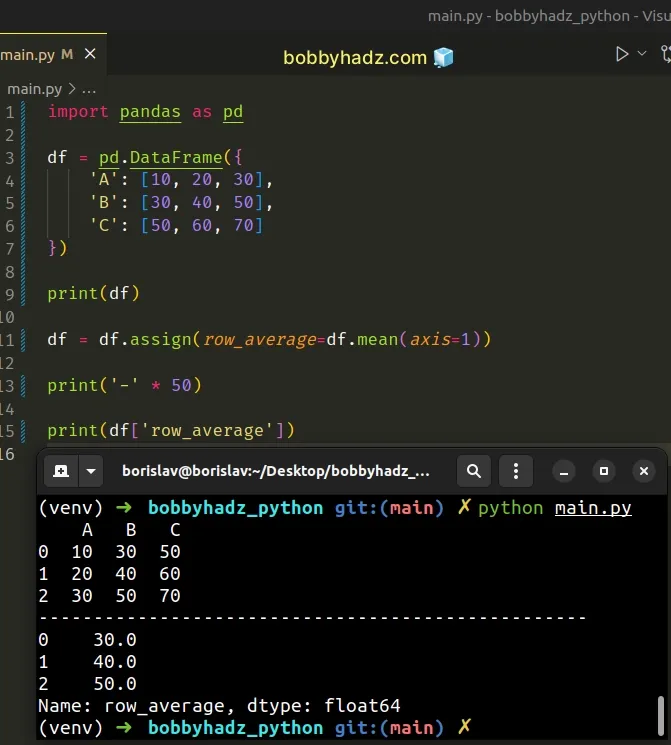
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': [10, 20, 30], 'B': [30, 40, 50], 'C': [50, 60, 70] }) print(df) df = df.assign(row_average=df.mean(axis=1)) print('-' * 50) print(df['row_average'])
Running the code sample produces the same output.
A B C 0 10 30 50 1 20 40 60 2 30 50 70 -------------------------------------------------- 0 30.0 1 40.0 2 50.0 Name: row_average, dtype: float64
# Calculate the Row Average in a Pandas DataFrame using df.iloc
If you only want to calculate the row average for specific columns, use the df.iloc position-based indexer.
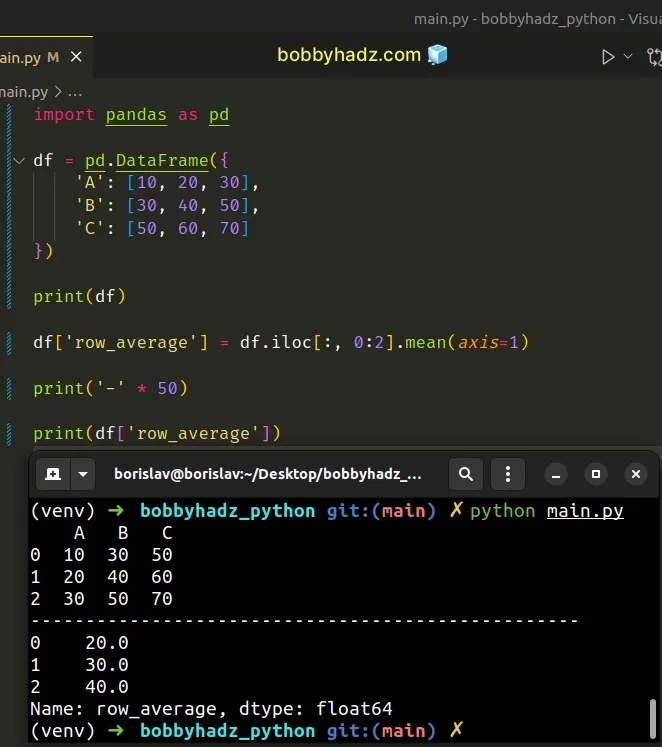
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': [10, 20, 30], 'B': [30, 40, 50], 'C': [50, 60, 70] }) print(df) df['row_average'] = df.iloc[:, 0:2].mean(axis=1) print('-' * 50) print(df['row_average'])
Running the code sample produces the following output.
A B C 0 10 30 50 1 20 40 60 2 30 50 70 -------------------------------------------------- 0 20.0 1 30.0 2 40.0 Name: row_average, dtype: float64
We used the df.iloc indexer to calculate the row average for the A and B
columns.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': [10, 20, 30], 'B': [30, 40, 50], 'C': [50, 60, 70] }) print(df) print('-' * 50) print(df.iloc[:, 0:2])
Running the code sample produces the following output.
A B C 0 10 30 50 1 20 40 60 2 30 50 70 -------------------------------------------------- A B 0 10 30 1 20 40 2 30 50
Once you select the specific columns, you just have to call the mean() method
with the axis argument set to 1.
df['row_average'] = df.iloc[:, 0:2].mean(axis=1)
You can also use the df.iloc position-based indexer to specify individual
columns by index before calculating the row average.
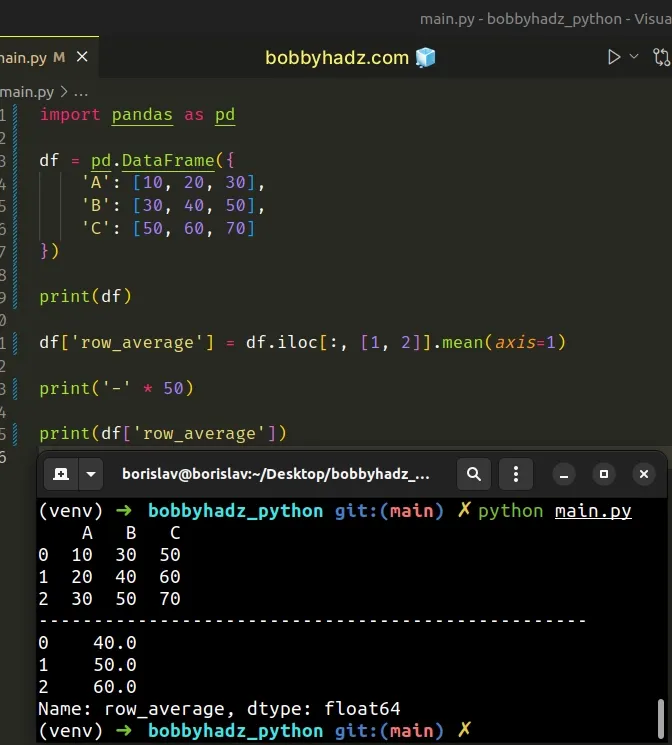
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': [10, 20, 30], 'B': [30, 40, 50], 'C': [50, 60, 70] }) print(df) df['row_average'] = df.iloc[:, [1, 2]].mean(axis=1) print('-' * 50) print(df['row_average'])
Running the code sample produces the following output.
A B C 0 10 30 50 1 20 40 60 2 30 50 70 -------------------------------------------------- 0 40.0 1 50.0 2 60.0 Name: row_average, dtype: float64
We calculated the row average for the columns with indexes 1 and 2.
Note that Python indices are zero-based, so the first index is 0 and the last
is len(columns) - 1.
# Calculating the row average based on the column names in a Pandas DataFrame
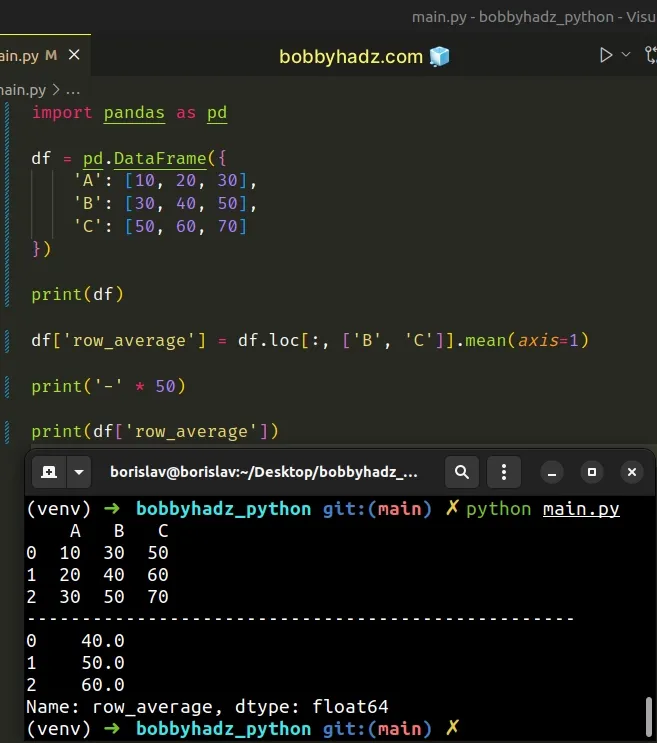
You can use the DataFrame.loc label-based indexer to calculate the row average based on specific column names.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': [10, 20, 30], 'B': [30, 40, 50], 'C': [50, 60, 70] }) print(df) df['row_average'] = df.loc[:, ['B', 'C']].mean(axis=1) print('-' * 50) print(df['row_average'])
Running the code sample produces the following output.
A B C 0 10 30 50 1 20 40 60 2 30 50 70 -------------------------------------------------- 0 40.0 1 50.0 2 60.0 Name: row_average, dtype: float64
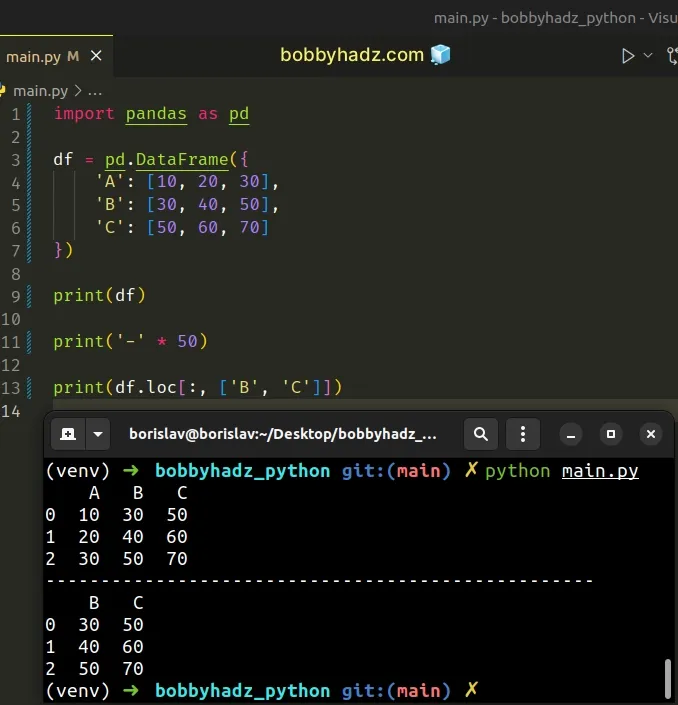
The df.loc indexer is label-based, so it enables you to select specific
columns based on their name.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': [10, 20, 30], 'B': [30, 40, 50], 'C': [50, 60, 70] }) print(df) print('-' * 50) print(df.loc[:, ['B', 'C']])
Running the code sample produces the following output.
A B C 0 10 30 50 1 20 40 60 2 30 50 70 -------------------------------------------------- B C 0 30 50 1 40 60 2 50 70
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Pandas: Sum the values in a Column that match a Condition
- Pandas ValueError: cannot insert X, already exists [Solved]
- How to swap two DataFrame columns in Pandas
- Interpolating NaN values in a NumPy Array in Python
- Numpy: How to extract a Submatrix from an array
- Pandas ValueError: ('Lengths must match to compare')
- Pandas: Out of bounds nanosecond timestamp [Solved]
- How to get a Quarter from a Date in Pandas [4 Ways]
- Create Date column from Year, Month and Day in Pandas
- Pandas: Select Rows between two values in DataFrame
- Pandas: Convert a DataFrame to a List of Dictionaries
- Pandas: GroupBy columns with NaN (missing) values
- Pandas: Remove non-numeric rows in a DataFrame column
- NumPy: Apply a Mask from one Array to another Array
- How to iterate over the Columns of a NumPy Array
- Pandas: Select rows based on a List of Indices
- Pandas: Find an element's Index in Series [7 Ways]
- Pandas: Unalignable boolean Series provided as indexer

