For or While loop to print Numbers from 1 to 10 in Python
Last updated: Apr 9, 2024
Reading time·6 min

# Table of Contents
- Using a For loop to print the numbers from 1 to 10
- Using a While loop to print the numbers from 1 to 10
- Using a For loop to print the numbers from 10 to 1
- Using a While loop to print the numbers from 10 to 1
# Using a For loop to print the numbers from 1 to 10
Use the range() class to loop from 1 to 10 in a for loop, e.g.
for num in range(1, 11):.
The range class takes start (inclusive) and stop (exclusive) arguments
and enables us to loop a specific number of times in for loops.
# ✅ `for` loop 1 to 10 (including 10) for num in range(1, 11): print(num) # 👇️ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] print(list(range(1, 11)))
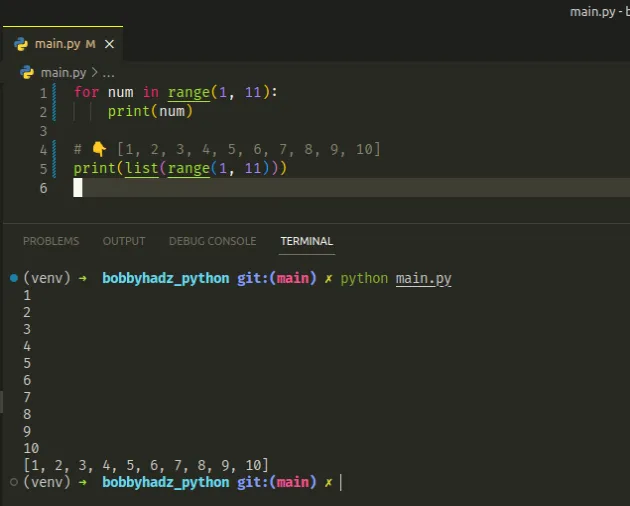
If you need to exclude 10 from the range, use the following code sample instead.
# ✅ `for` loop 1 to 10 (excluding 10) for num in range(1, 10): print(num) # 👇️ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] print(list(range(1, 10)))
We used the range() class to loop from 1 to 10 in a
for loop.
range() class (the start value) is inclusive, whereas the stop value is exclusive.The range() class is
commonly used for looping a specific number of times in for loops and takes
the following arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
start | An integer representing the start of the range (defaults to 0) |
stop | Go up to, but not including the provided integer |
step | Range will consist of every N numbers from start to stop (defaults to 1) |
If you only pass a single argument to the range() constructor, it is
considered to be the value for the stop parameter.
for num in range(10): print(num) # 👇️ [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] print(list(range(10)))
start argument is omitted, it defaults to 0 and if the step argument is omitted, it defaults to 1.Note that the range() class returns a range object, not a list.
# 👇️ range(0, 10) print(range(10)) # 👇️ [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] print(list(range(10)))
If you need to convert the range object to a list, pass it to the
list() class.
# The stop value is exclusive (up to, but not including)
If values for the start and stop parameters are provided, the start value
is inclusive, whereas the stop value is exclusive.
# 👇️ for loop 1 to 10 (including 10) for num in range(1, 11): print(num) # 👇️ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] print(list(range(1, 11)))
If you need to exclude 10 from the range that is being iterated, use a stop
value of 10.
for num in range(1, 10): print(num) # 👇️ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] print(list(range(1, 10)))
# Using a While loop to print the numbers from 1 to 10
To print the numbers from 1 to 10 in a while loop:
- Declare a new variable and initialize it to 1.
- Use a while loop to iterate for as long as the variable is less than or equal
to
10. - Increment the variable by 1 on each iteration.
number = 1 while number <= 10: print(number) number += 1
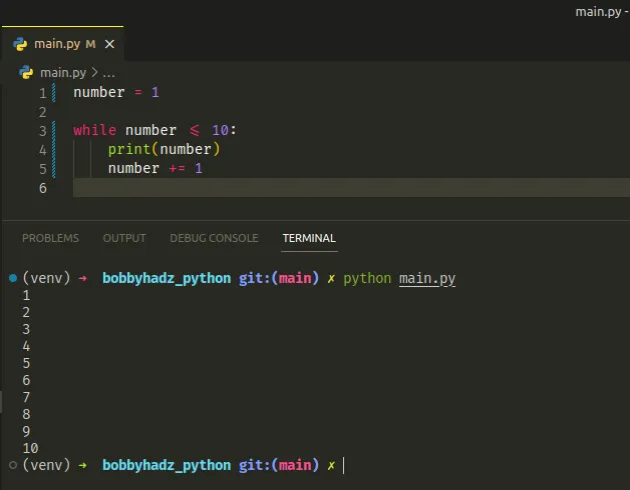
We declared a new variable and initialized it to 1.
The while loop iterates for as long as the number variable is less than or
equal to 10.
On each iteration, we print the current value and increment the variable by 1.
Once the number variable is equal to 11, the condition is no longer met and
we exit the while loop.
# Using a while True loop to print the numbers from 1 to 10
You can also use a while True loop to print the numbers from 1 to 10 in
Python.
number = 1 while True: if number > 10: break print(number) number += 1
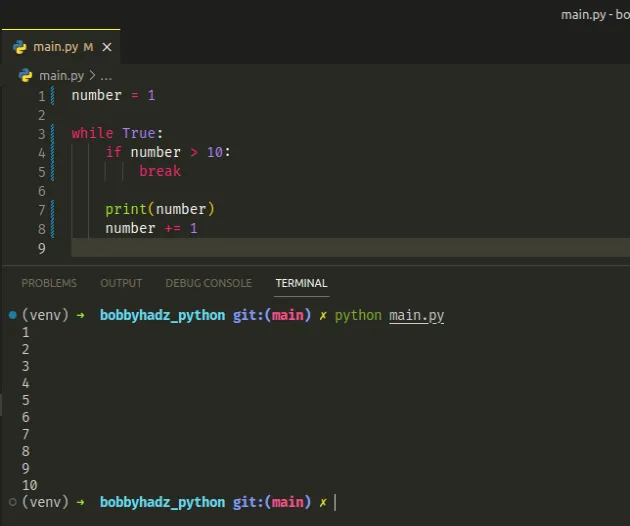
The while True loop iterates until the break statement is used.
We initialized the number variable to 1 just like we did in the previous
example.
On each iteration of the while loop, we check if the number variable is
greater than 10.
If the condition is met, we use the break statement to exit the while loop.
The break statement breaks out of the
innermost enclosing for or while loop.
If the condition isn't met, the number variable is in the specified range (1
to 10), so we print its value and increment it by 1.
# Using a For loop to print the numbers from 10 to 1
To print the numbers from 10 to 1 using a for loop:
- Use the
rangeclass to get a range of the numbers from 1 to 10. - Use the
reversed()function to reverse the range. - Use a
forloop to iterate over the range from 10 to 1.
for num in reversed(range(1, 11)): print(num) # 👇️ [10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1] print(list(reversed(range(1, 11))))
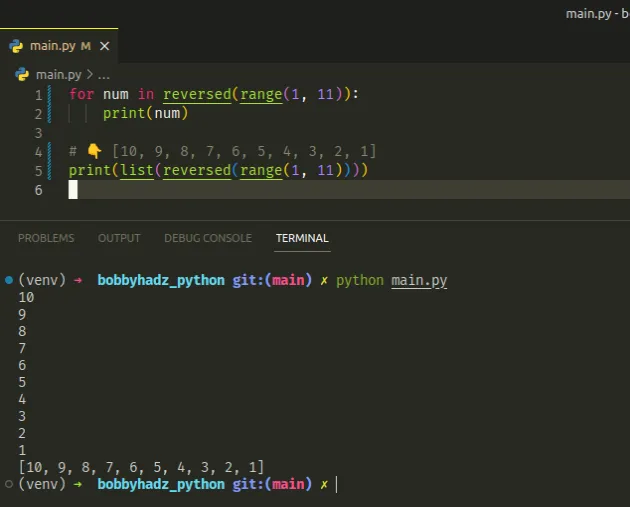
We used the range class to get a range object containing the numbers from
1 to 10.
# 👇️ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] print(list(range(1, 11)))
The next step is to use the reversed() function to reverse the range.
# 👇️ [10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1] print(list(reversed(range(1, 11))))
The reversed function takes an iterator, reverses it and returns the result.
Once the range is reversed, we can use a for loop to iterate and print the
numbers from 10 to 1.
# Using a While loop to print the numbers from 10 to 1
To print the numbers from 10 to 1 using a while loop:
- Declare a new variable and initialize it to 10.
- Use a
whileloop to iterate for as long as the variable's value is greater than or equal to1. - Print the value of the variable and decrement it by
1.
number = 10 while number >= 1: print(number) number -= 1
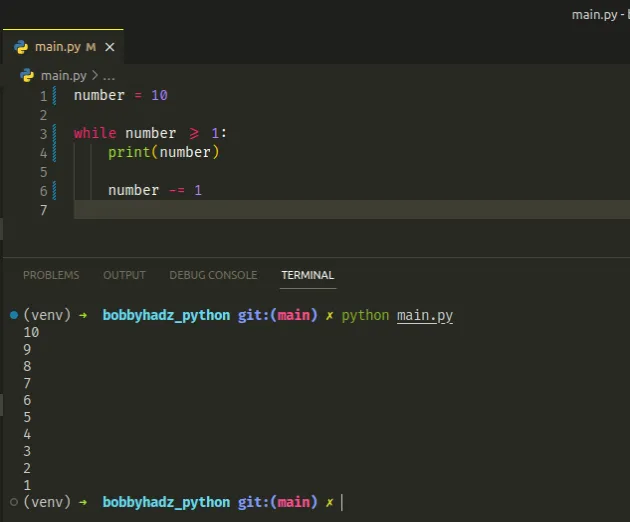
The number variable is initially set to 10.
On each iteration of the while loop, we print the current value of the
variable and decrement it by 1.
Once the number variable is set to 0, the condition is no longer met and we
exit the while loop.
# Using a While True loop to print the numbers from 10 to 1
You can also use a while True loop to print the numbers from 10 to 1.
number = 10 while True: if number < 1: break print(number) number -= 1
The while True loop iterates until the break statement is used.
On each iteration, we check if the number variable is less than 1.
If the condition is met, we use the break statement to exit the loop.
Otherwise, we print the variable and decrement its value by 1.
Once the number variable is set to 0, the condition is no longer met and we
exit the while loop.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Using multiple variables in a For loop in Python
- Using a For or While Loop to take user input in Python
- Detect the Last item in a List using a for loop in Python
- How to restart a Loop in Python
- Python: How to calculate the MD5 Hash of a File
- python.exe: can't find
__main__module in Path - How to exit an if statement in Python [5 Ways]
- -215:Assertion failed !_src.empty() in function 'cvtColor'

