Pandas: Sum the values in a Column that match a Condition
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·6 min

# Table of Contents
- Pandas: Sum the values in a Column that match a Condition
- Pandas: Sum the values in a Column based on multiple conditions
- Pandas: Sum the values in a Column if at least one condition is met
- Sum values in a column based on a condition using query()
- Pandas: Sum the values in a Column that match a Condition without loc
# Pandas: Sum the values in a Column that match a Condition
You can use boolean indexing to sum the values in a column in a Pandas
DataFrame that match a condition.
Once you select the matching values, call the DataFrame.sum() method.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': [3, 5, 7, 10, 5, 19, 5], 'B': [1, 2, 4, 9, 15, 30, 4] }) print(df) result = df.loc[df['A'] == 5, 'B'].sum() print('-' * 50) print(result) # 👉️ 21
Running the code sample produces the following output.
A B 0 3 1 1 5 2 2 7 4 3 10 9 4 5 15 5 19 30 6 5 4 -------------------------------------------------- 21
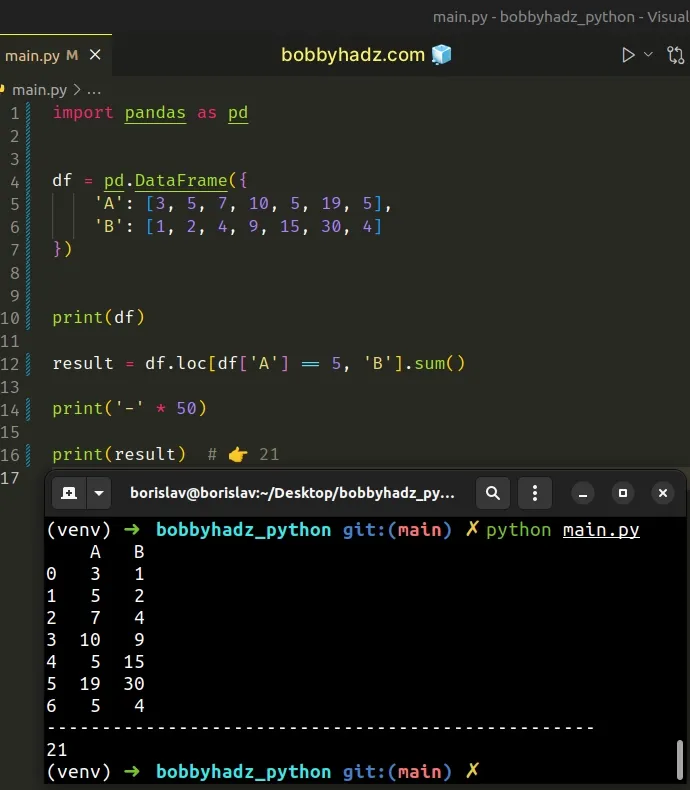
The code sample sums the values in the B column where the corresponding value
in the A column is equal to 5.
df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': [3, 5, 7, 10, 5, 19, 5], 'B': [1, 2, 4, 9, 15, 30, 4] }) result = df.loc[df['A'] == 5, 'B'].sum() print(result) # 👉️ 21
The expression df['A'] == 5 returns a boolean array that contains True for
the values in the A column that are equal to 5 and False for the other
values.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': [3, 5, 7, 10, 5, 19, 5], 'B': [1, 2, 4, 9, 15, 30, 4] }) # 0 False # 1 True # 2 False # 3 False # 4 True # 5 False # 6 True # Name: A, dtype: bool print(df['A'] == 5)
The example then uses boolean indexing to only sum the matching values from the
B column.
# Pandas: Sum the values in a Column based on multiple conditions
The same approach can be used to sum the values in a column based on multiple conditions.
The following example sums the values in column B where:
- The corresponding value in column
Ais equal to5. - And the corresponding value in column
Cis equal to6.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': [3, 5, 7, 10, 5, 19, 5], 'B': [1, 9, 4, 9, 15, 30, 4], 'C': [4, 6, 8, 2, 10, 11, 6] }) result = df.loc[(df['A'] == 5) & (df['C'] == 6), 'B'].sum() print(result) # 👉️ 13
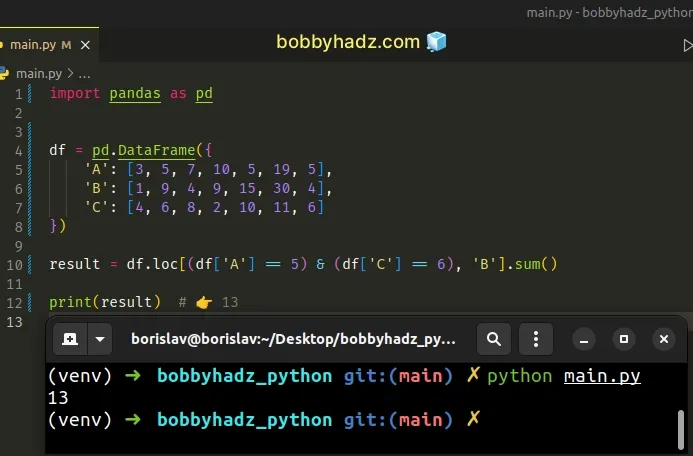
The two conditions are wrapped in parentheses ().
The first condition returns a boolean array that contains True values for the
elements that are equal to 5 in column A.
The second condition returns a boolean array that contains True values for the
elements in column B that are equal to 6.
& to produce an array where both conditions have to be met for a True value to be returned.The sum of the matching numbers in the B column is returned.
# Pandas: Sum the values in a Column if at least one condition is met
The previous example showed how to use the & operator to sum the values in a
column if 2 conditions are met.
In some cases, you might want to sum the values in a column if at least one condition is met.
You can do this with the pipe | operator.
The following example sums the values in the B column where:
- The corresponding value in the
Acolumn is greater than9. - Or the corresponding value in the
Ccolumn is greater than10.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': [3, 5, 7, 10, 5, 19, 5], 'B': [1, 9, 4, 9, 15, 5, 4], 'C': [4, 1, 8, 2, 11, 1, 2] }) result = df.loc[(df['A'] > 9) | (df['C'] > 10), 'B'].sum() print(result) # 👉️ 29
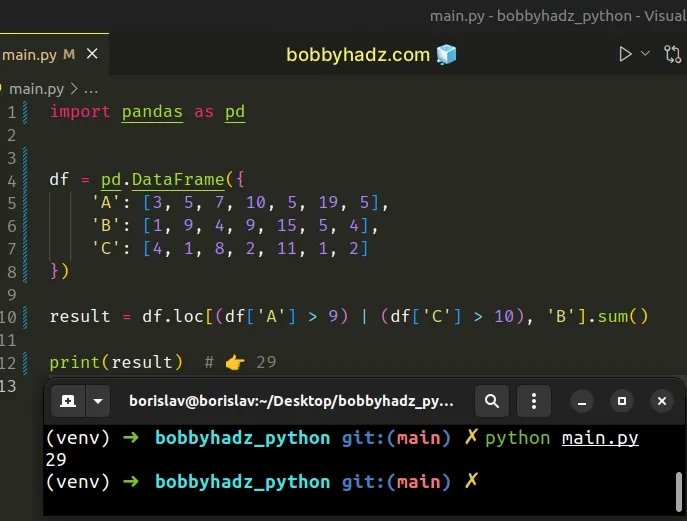
Either of the 2 conditions has to be met for the boolean array to contain a
True value.
The expression calculates the sum of 9 + 15 + 5 and returns 29.
# Sum values in a column based on a condition using query()
You can also use the DataFrame.query() method to sum the values in a column based on a condition.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': [3, 5, 7, 10, 5, 19, 3], 'B': [1, 9, 4, 9, 15, 5, 4], 'C': [4, 1, 8, 2, 11, 1, 2] }) result = df.query('A == 5')['B'].sum() print(result) # 👉️ 24
The DataFrame.query() method takes an expression as a parameter and returns a
DataFrame resulting from the supplied expression.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': [3, 5, 7, 10, 5, 19, 3], 'B': [1, 9, 4, 9, 15, 5, 4], 'C': [4, 1, 8, 2, 11, 1, 2] }) # A B C # 1 5 9 1 # 4 5 15 11 print(df.query('A == 5')) result = df.query('A == 5')['B'].sum() print(result) # 👉️ 24
The result variable stores the sum of the matching numbers from column B
(9 and 15).
You can also use the and keyword to check if multiple conditions are met.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': [3, 5, 7, 10, 5, 19, 5], 'B': [1, 9, 4, 9, 15, 5, 4], 'C': [4, 1, 8, 2, 11, 1, 1] }) result = df.query('A == 5 and C == 1')['B'].sum() print(result) # 👉️ 13
The code sample sums the values in B where:
- The corresponding value in
Ais equal to5. - And the corresponding value in
Cis equal to1.
If you need to check if at least one condition is met before calculating the
sum, use the or keyword.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': [3, 4, 7, 10, 5, 19, 3], 'B': [1, 9, 4, 9, 15, 5, 4], 'C': [1, 4, 8, 2, 11, 0, 3] }) result = df.query('A == 5 or C == 1')['B'].sum() print(result) # 👉️ 16
The code sample sums the values in B where:
- The corresponding value in
Ais equal to5. - Or the corresponding value in
Cis equal to1.
# Pandas: Sum the values in a Column that match a Condition without loc
You can also sum the values in a column based on a condition without using the
loc indexer.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': [3, 4, 7, 10, 5, 19, 5], 'B': [1, 9, 4, 9, 15, 5, 4], 'C': [1, 4, 8, 2, 11, 0, 3] }) result = df[df['A'] == 5]['B'].sum() print(result) # 👉️ 19
We used bracket notation [] to get a boolean DataFrame that stores True
values if the corresponding number in A is equal to 5.
Then, bracket notation is used to select the matching indices in column B
before calling sum().
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': [3, 4, 7, 10, 5, 19, 5], 'B': [1, 9, 4, 9, 15, 5, 4], 'C': [1, 4, 8, 2, 11, 0, 3] }) result = sum(df[df['A'] == 5]['B']) print(result) # 👉️ 19
Using the DataFrame.sum() method is equivalent to passing the resulting
DataFrame to the sum() function.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Convert a NumPy array to 0 or 1 based on threshold in Python
- How to get the length of a 2D Array in Python
- TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable in Python
- TypeError: Object of type ndarray is not JSON serializable
- IndexError: too many indices for array in Python [Solved]
- How to filter a JSON array in Python
- ValueError: object too deep for desired array [Solved]
- Cannot set a DataFrame with multiple columns to single column
- Pandas ValueError: cannot insert X, already exists [Solved]
- How to Multiply two or more Columns in Pandas
- Add columns of a different Length to a DataFrame in Pandas
- Reading specific columns from an Excel File in Pandas
- Only valid with DatetimeIndex, TimedeltaIndex or PeriodIndex, but got an instance of X
- Pandas ValueError: ('Lengths must match to compare')
- Pandas: How to get the Max and Min Dates in a DataFrame
- Reduction operation 'argmax' not allowed for this dtype
- Pandas: Select the Rows where two Columns are Equal
- Pandas: Remove non-numeric rows in a DataFrame column
- NumPy: Apply a Mask from one Array to another Array
- Pandas: Select rows based on a List of Indices

