Pandas: Changing the column type to Categorical
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Pandas: Changing the column type to Categorical
- Pandas: Changing the data type of multiple columns to Categorical
- Change column type to Categorical using a For loop
- Change column type to Categorical using a Lambda function
- Change column type to categorical for all, except some columns
# Pandas: Changing the column type to Categorical
To change the column type to Categorical in Pandas:
- Use square bracket notation to select the specific column.
- Call the
astype()method on the selected column, passing it"category"as a parameter.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'experience': [1, 5, 3, 8], 'salary': [189.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) df['name'] = df['name'].astype('category') print(df) print('-' * 50) print(df.dtypes)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name experience salary 0 Alice 1 189.1 1 Bobby 5 180.2 2 Carl 3 190.3 3 Dan 8 205.4 -------------------------------------------------- name category experience int64 salary float64 dtype: object
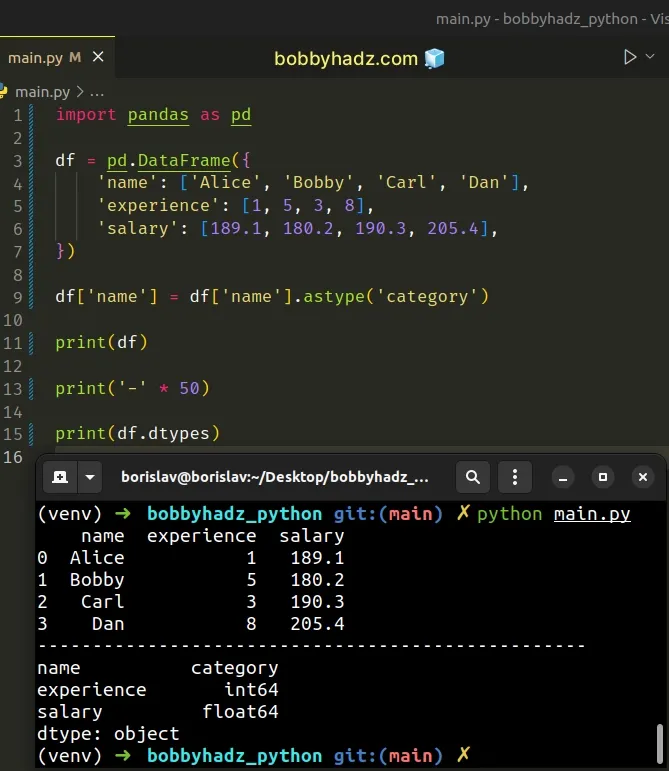
We used bracket notation to select the name column and called the
astype
method on it.
df['name'] = df['name'].astype('category')
The astype() method casts a pandas object to the supplied data type.
You can access the
dtypes
attribute on the DataFrame to verify that the column has been converted to
category.
# name category # experience int64 # salary float64 # dtype: object print(df.dtypes)
The dtypes attribute returns the data types in the DataFrame.
To be more precise, a Series with the data type of each column is returned.
# Pandas: Changing the data type of multiple columns to Categorical
You can use the same approach if you need to change the data type of multiple columns to Categorical.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'experience': [1, 5, 3, 8], 'salary': [189.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) columns = ['name', 'experience'] df[columns] = df[columns].astype('category') # name category # experience category # salary float64 # dtype: object print(df.dtypes)
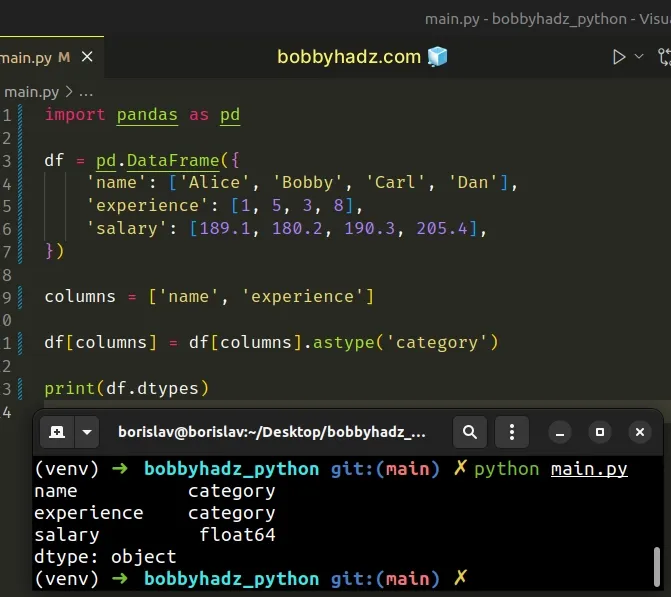
We passed a list of columns between the square brackets [] to change the type
of the name and experience columns to category.
You can also specify the column names inline.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'experience': [1, 5, 3, 8], 'salary': [189.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) df[['name', 'experience']] = df[['name', 'experience']].astype('category') # name category # experience category # salary float64 # dtype: object print(df.dtypes)
However, notice that we have 2 sets of square brackets next to one another.
# Change column type to Categorical using a For loop
In older versions of Pandas, you used to use a for loop to change the type of multiple columns.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'experience': [1, 5, 3, 8], 'salary': [189.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) columns = ['name', 'experience'] for column in columns: df[column] = df[column].astype('category') # name category # experience category # salary float64 # dtype: object print(df.dtypes)
However, in recent Pandas versions, iterating over the columns collection is not necessary.
# Change column type to Categorical using a Lambda function
You might also see examples online that use a lambda function.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'experience': [1, 5, 3, 8], 'salary': [189.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) columns = ['name', 'experience'] df[columns] = df[columns].apply(lambda x: x.astype('category')) # name category # experience category # salary float64 # dtype: object print(df.dtypes)
The lambda function gets called with each column name and sets its type to
category.
However, using a lambda is not needed in recent Pandas versions, as you can directly specify the list of columns between the square brackets.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'experience': [1, 5, 3, 8], 'salary': [189.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) columns = ['name', 'experience'] df[columns] = df[columns].astype('category') # name category # experience category # salary float64 # dtype: object print(df.dtypes)

# Change column type to categorical for all, except some columns
If you need to convert all columns, except for columns that have a specific data
type to categorical, use the select_dtypes() method.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'id': ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'], 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'experience': [1, 5, 3, 8], 'salary': [189.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) columns = df.select_dtypes(exclude='int').columns.to_list() df[columns] = df[columns].astype('category') # id category # name category # experience int64 # salary category # dtype: object print(df.dtypes)
The DataFrame.select_dtypes() method returns a subset of the DataFrame's columns based on the column data types.
We excluded the int column (experience) and converted all other columns to
categorical.
I've also written an article on how to get a list of categories or categorical columns.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- TypeError: Image data cannot be converted to float [Solved]
- OverflowError: Python int too large to convert to C long
- TypeError: Field elements must be 2- or 3-tuples, got 1
- ValueError: Expected 2D array, got 1D array instead [Fixed]
- TypeError: ufunc 'isnan' not supported for the input types
- Convert a Row to a Column Header in a Pandas DataFrame
- Arrays used as indices must be of integer (or boolean) type
- Pandas SpecificationError: nested renamer is not supported
- Pandas: Find first and last non-NaN values in a DataFrame
- How to shuffle two NumPy Arrays together (in Unison)
- Pandas TypeError: no numeric data to plot [Solved]
- ValueError: If using all scalar values, you must pass index
- Pandas: How to Convert a Pivot Table to a DataFrame
- Pandas: Count the unique combinations of two Columns
- Pandas: Find the closest value to a Number in a Column
- Pandas: Create a Tuple from two DataFrame Columns
- Disable the TOKENIZERS_PARALLELISM=(true | false) warning
- RuntimeError: Expected scalar type Float but found Double
- Pandas: Convert timezone-aware DateTimeIndex to naive timestamp
- RuntimeError: Input type (torch.FloatTensor) and weight type (torch.cuda.FloatTensor) should be the same
- ValueError: Failed to convert a NumPy array to a Tensor (Unsupported object type float)
- Mixing dicts with non-Series may lead to ambiguous ordering
- Cannot convert non-finite values (NA or inf) to integer
- Pandas: How to efficiently Read a Large CSV File

