Calculate the average (mean) of 2 NumPy arrays
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- Calculate the average (mean) of 2 NumPy arrays
- Calculate the average (mean) of multiple 2-dimensional NumPy arrays
- Calculate the average of 2 two-dimensional NumPy arrays using division
- Calculate the weighted average of 2 NumPy arrays
- Calculate the weighted average of 2 NumPy arrays using numpy.average()
# Calculate the average (mean) of 2 NumPy arrays
To calculate the average (mean) of 2 NumPy arrays:
- Use the addition operator to sum the 2 arrays element-wise.
- Divide the resulting array by 2 to get the average.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4]) arr2 = np.array([5, 6, 7, 8]) # 👇️ [ 6 8 10 12] print(arr1 + arr2) arr3 = (arr1 + arr2) / 2 # 👇️ [3. 4. 5. 6.] print(arr3)
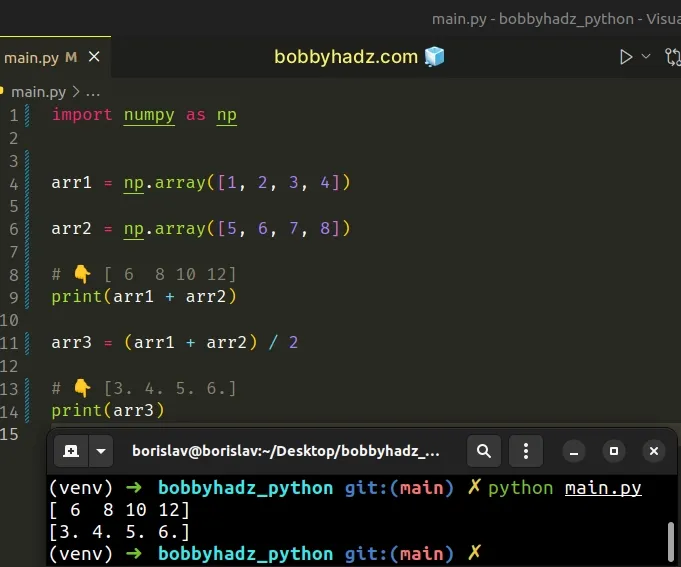
We used the addition (+) operator to sum the two arrays element-wise and then divided by 2.
The average (or mean) of 2 NumPy arrays is calculated by:
- Adding the two arrays element-wise.
- Dividing the numbers in the resulting array by the number of arrays (2 in the example).
The same approach can be used to calculate the average of 3 or more NumPy arrays.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4]) arr2 = np.array([5, 6, 7, 8]) arr3 = np.array([3, 4, 5, 6]) # 👇️ [ 9 12 15 18] print(arr1 + arr2 + arr3) arr3 = (arr1 + arr2 + arr3) / 3 # 👇️ [3. 4. 5. 6.] print(arr3)
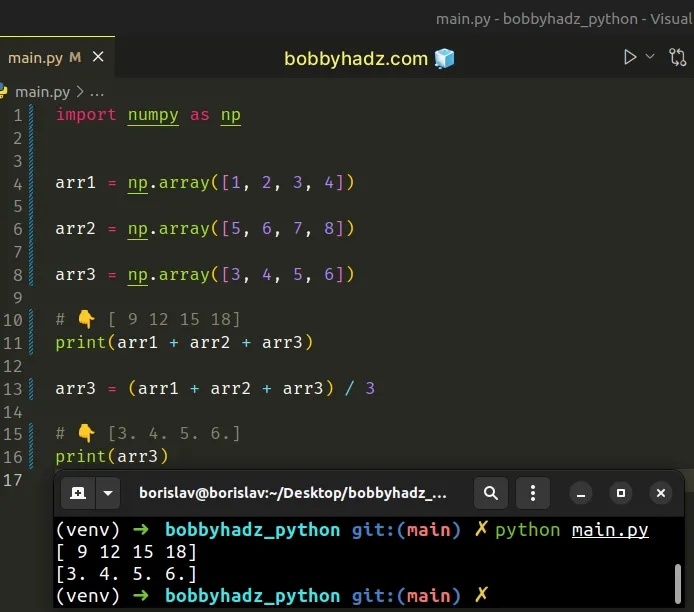
We used the addition (+) operator to sum the 3 arrays element-wise and then divided the resulting array by 3 to get the average.
# Calculate the average (mean) of multiple 2-dimensional NumPy arrays
If you need to calculate the average (mean) of multiple 2-dimensional NumPy arrays:
- Create a 3-dimensional array from your 2-dimensional arrays.
- Call the
numpy.mean()method with the resulting array. - Set the
axisargument to0.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]]) arr2 = np.array([[3, 4], [5, 6]]) arr3 = np.mean(np.array([arr1, arr2]), axis=0) # [[2. 3.] # [4. 5.]] print(arr3)
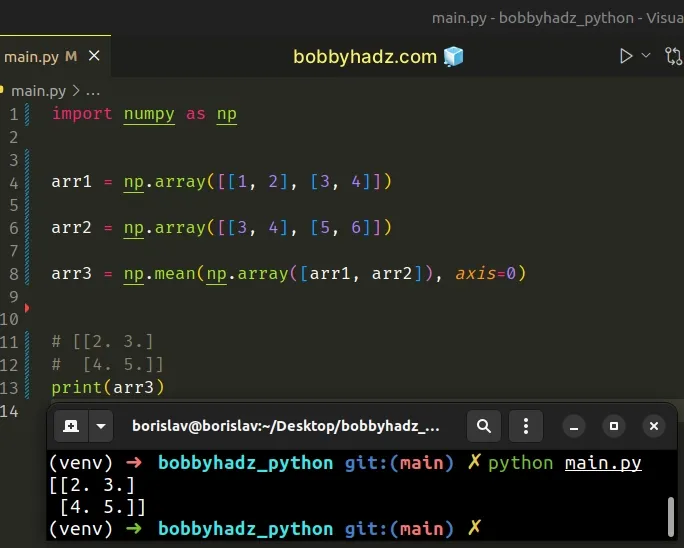
We used the numpy.array() method to create a 3-dimensional array from the two 2-dimensional arrays.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]]) arr2 = np.array([[3, 4], [5, 6]]) # [[[1 2] # [3 4]] # [[3 4] # [5 6]]] print(np.array([arr1, arr2]))
The last step is to get the average (mean) of the arrays by using numpy.mean.
arr3 = np.mean(np.array([arr1, arr2]), axis=0) # [[2. 3.] # [4. 5.]] print(arr3)
The numpy.mean() method computes the arithmetic mean along the specified axis.
The same approach can be used to calculate the average (mean) of more than two 2-dimensional NumPy arrays.
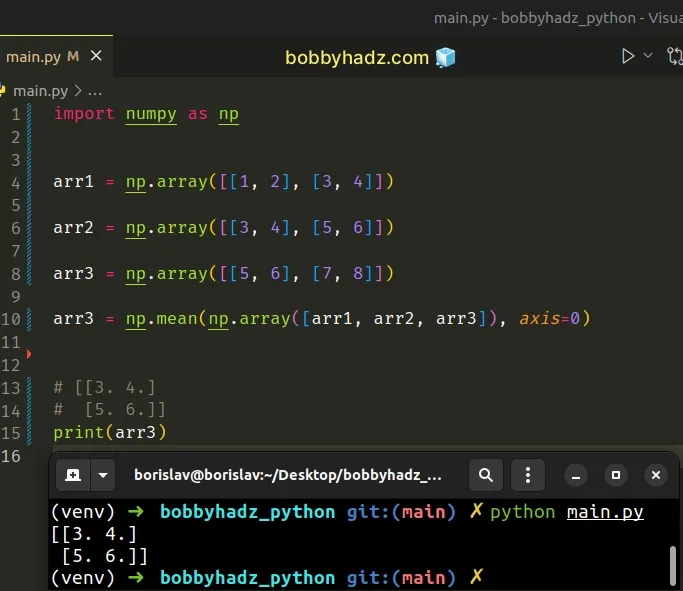
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]]) arr2 = np.array([[3, 4], [5, 6]]) arr3 = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]]) arr4 = np.mean(np.array([arr1, arr2, arr3]), axis=0) # [[3. 4.] # [5. 6.]] print(arr4)
# Calculate the average of 2 two-dimensional NumPy arrays using division
You can also use division to calculate the average of 2 two-dimensional NumPy arrays.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]]) arr2 = np.array([[3, 4], [5, 6]]) arr3 = (arr1 + arr2) / 2 # [[2. 3.] # [4. 5.]] print(arr3)
We used the addition (+) operator to sum the two 2-dimensional arrays.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]]) arr2 = np.array([[3, 4], [5, 6]]) # [[ 4 6] # [ 8 10]] print(arr1 + arr2)
The last step is to divide the resulting array by the number of arrays to get the mean.
arr3 = (arr1 + arr2) / 2 # [[2. 3.] # [4. 5.]] print(arr3)
The same approach can be used to calculate the average of more than 2 two-dimensional NumPy arrays.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]]) arr2 = np.array([[3, 4], [5, 6]]) arr3 = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]]) arr3 = (arr1 + arr2 + arr3) / 3 # [[3. 4.] # [5. 6.]] print(arr3)
We used the addition (+) operator to sum the 3 two-dimensional NumPy arrays element-wise.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]]) arr2 = np.array([[3, 4], [5, 6]]) arr3 = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]]) # [[ 9 12] # [15 18]] print(arr1 + arr2 + arr3)
The last step is to divide the resulting array by 3 to get the average values.
arr3 = (arr1 + arr2 + arr3) / 3 # [[3. 4.] # [5. 6.]] print(arr3)
# Calculate the weighted average of 2 NumPy arrays
If you need to calculate the weighted average of 2 NumPy arrays:
- Multiply each array by the weight.
- Use the addition (+) operator to sum the resulting arrays element-wise.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4]) arr2 = np.array([5, 6, 7, 8]) weight1 = 0.5 weight2 = 0.5 arr3 = arr1 * weight1 + arr2 * weight2 # 👇️ [3. 4. 5. 6.] print(arr3)
We used the multiplication operator to multiply each array by the weight.
The last step is to use the addition (+) operator to get the average of the 2 arrays.
# Calculate the weighted average of 2 NumPy arrays using numpy.average()
You can also use the numpy.average() method to calculate the weighted average of 2 NumPy arrays.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4]) arr2 = np.array([5, 6, 7, 8]) weight1 = 0.5 weight2 = 0.5 arr3 = np.average( [arr1, arr2], axis=0, weights=[weight1, weight2] ) # 👇️ [3. 4. 5. 6.] print(arr3)
The numpy.average() method computes the weighted average along the specified
axis.
The method takes a weights argument - an array of weights associated with the
values in the supplied arrays.
The weights array can either be 1-dimensional (in which case its length must
be the size of along the given axis) or the same shape as the supplied arrays.
# Table of Contents
- IndexError: too many indices for array in Python [Solved]
- How to filter a JSON array in Python
- ValueError: object too deep for desired array [Solved]
- Only one element tensors can be converted to Python scalars
- Replace negative Numbers in a Pandas DataFrame with Zero
- Pandas: Sum the values in a Column that match a Condition
- Pandas: Make new Column from string Slice of another Column
- Interpolating NaN values in a NumPy Array in Python
- How to check if a NumPy Array is multidimensional or 1D
- Numpy: How to extract a Submatrix from an array
- Reading specific columns from an Excel File in Pandas
- Only valid with DatetimeIndex, TimedeltaIndex or PeriodIndex, but got an instance of X
- Pandas ValueError: ('Lengths must match to compare')
- Calculate the Average for each Row in a Pandas DataFrame
- How to drop all Rows in a Pandas DataFrame in Python
- How to repeat Rows N times in a Pandas DataFrame
- How to convert a Pandas DataFrame to a Markdown Table
- Pandas SpecificationError: nested renamer is not supported
- Cannot perform 'rand_' with a dtyped [int64] array and scalar of type [bool]
- Get N random Rows from a NumPy Array in Python
- How to remove Time from DateTime in Pandas [5 Ways]
- Create Date column from Year, Month and Day in Pandas
- NumPy: Unable to allocate array with shape and data type
- Only integer scalar arrays can be converted to a scalar index
- ValueError: Index contains duplicate entries, cannot reshape

