NumPy: Unable to allocate array with shape and data type
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- NumPy: Unable to allocate array with shape and data type
- Setting the overcommit mode to 1
- NumPy: Unable to allocate array with shape and data type on Windows
- Make sure your Python installation is 64-bit
- Try setting the dtype argument to uint8
- Splitting the data structure or reading it in chunks
# NumPy: Unable to allocate array with shape and data type
The NumPy error "Unable to allocate array with shape and data type" occurs most commonly because of the system's default overcommit handling.
By default, the overcommit mode is set to 0.
This means that overcommits of address space are refused automatically.
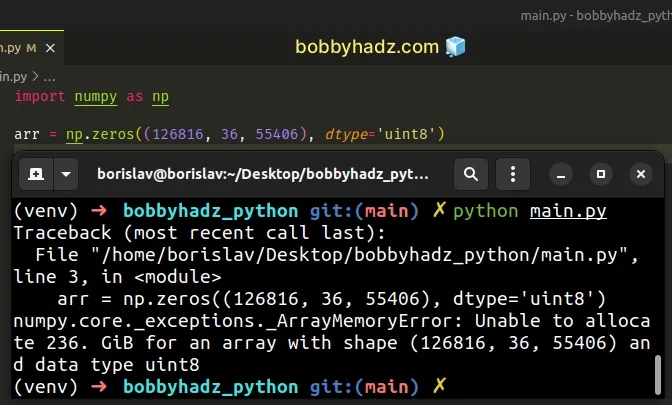
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import numpy as np # ⛔️ numpy.core._exceptions._ArrayMemoryError: Unable to allocate 236. GiB for an array with shape (126816, 36, 55406) and data type uint8 arr = np.zeros((126816, 36, 55406), dtype='uint8')
Note, if you got the error on Windows, click on the following subheading:
On Linux, you can check your overcommit mode by issuing the following command.
cat /proc/sys/vm/overcommit_memory
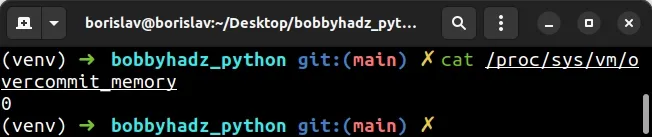
The default overcommit mode is 0.
When we tried to create the array, we tried to allocate 236 GiB.
import numpy as np # ⛔️ numpy.core._exceptions._ArrayMemoryError: Unable to allocate 236. GiB for an array with shape (126816, 36, 55406) and data type uint8 arr = np.zeros((126816, 36, 55406), dtype='uint8')
Here is how this is calculated.
# 👇️ 235.37039217029948 print(126816*36*55406 / 1024.3 ** 3)
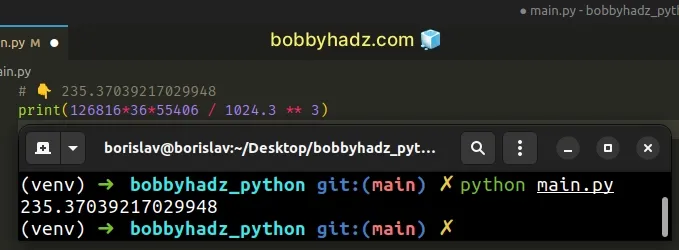
Trying to allocate 236 GiB fails when the overcommit mode is set to 0.
# Setting the overcommit mode to 1
One way to resolve the issue is to set the overcommit mode to 1.
You can do this by issuing the following 2 commands.
# switch to super user sudo su # set overcommit mode to 1 echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/overcommit_memory
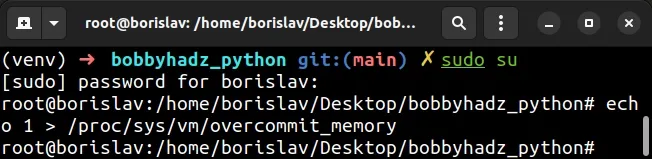
Note that you have to have super user privileges when running the echo
command, otherwise, you'd get a permission denied error.
When the overcommit mode is set to 1 ("always commit"), the system allows you
to commit the necessary amount of memory.
import numpy as np arr = np.zeros((126816, 36, 55406), dtype='uint8') print(arr)
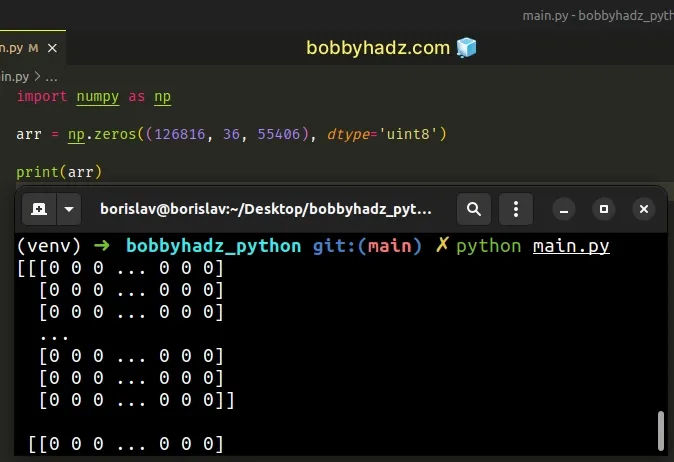
Notice that we are now able to create the NumPy array, after setting the
overcommit mode to 1.
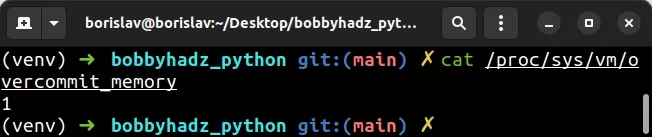
You can use the cat command to verify that the overcommit mode has been set to
1.
cat /proc/sys/vm/overcommit_memory
Note that changing your overcommit mode as shown above will not persist after a reboot.
You might have to rerun the following 2 commands after each reboot if you want
to change the overcommit mode to 1.
# switch to super user sudo su # set overcommit mode to 1 echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/overcommit_memory

There are also ways to update your /proc/sys settings in a persistent manner
but they are distribution-specific.
# NumPy: Unable to allocate array with shape and data type on Windows
If you got the NumPy "Unable to allocate array with shape and data type" error on Windows:
- Click on the Windows key or on the search bar and type "SystemPropertiesAdvanced".
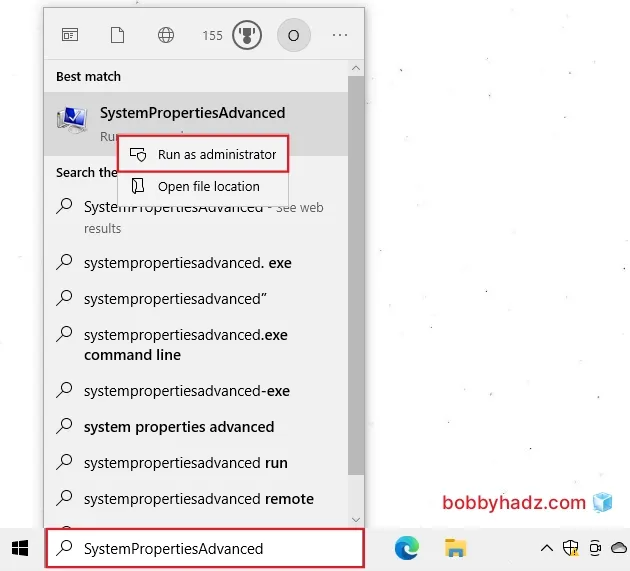
Right-click on "SystemPropertiesAdvanced" and select "Run as administrator".
In the Advanced tab, under Performance, click on Settings....
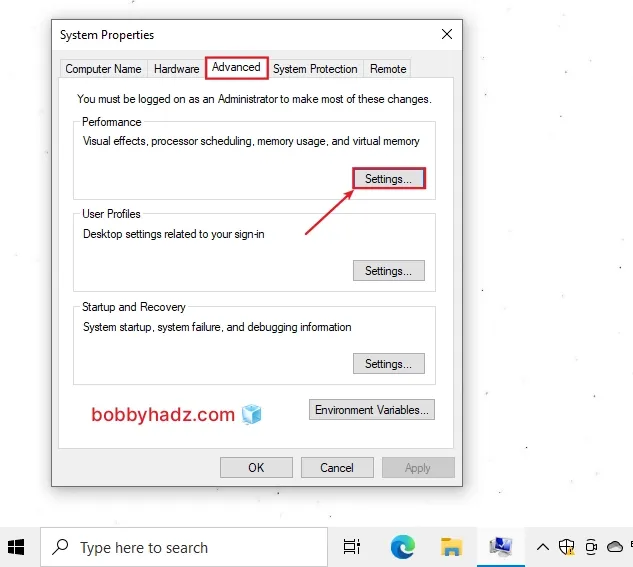
- Click on the Advanced tab and then click Change....
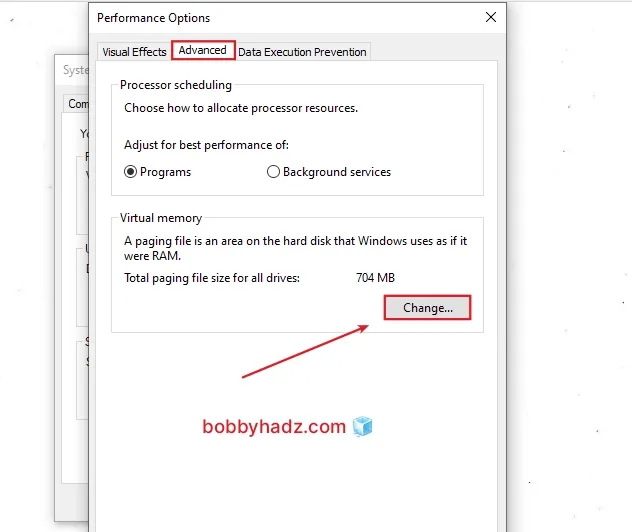
Uncheck the "Automatically manage paging file size for all drives" checkbox.
Click on "Custom size" and type in your preferred Initial and Maximum sizes in MB.
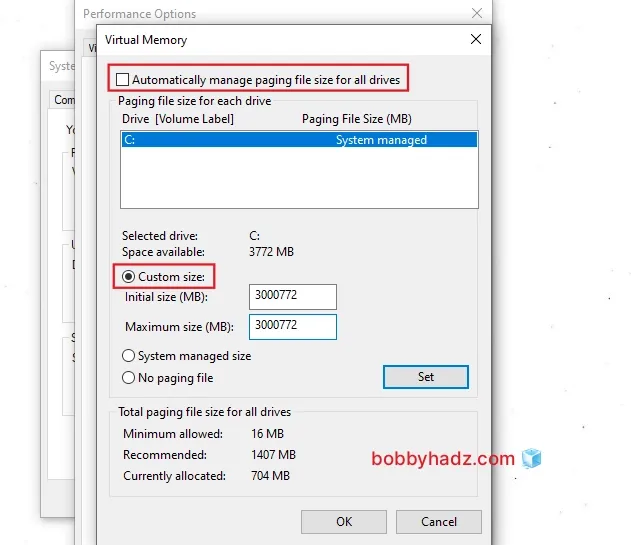
Click on Set, press OK to confirm and exit.
Restart your computer.
If your PC has enough memory to process your NumPy array, the error will be resolved.
The formula for calculating the initial size is:
initial size = 1.5 * total system memory.
The formula for the maximum size is: maximum size = 3 * initial size.
For example, if you have 16 GB of memory (1024 MB * 16 = 16384 MB).
The initial size would be 16384 * 1.5 = 24576.
The maximum size would be 3 * 24576 = 73728.
# Make sure your Python installation is 64-bit
Another thing you should check is that your Python installation is 64-bit.
I've written a detailed guide on how to Check if Python is running as 32-bit or 64-bit.
In short, you can use the following command.
python -c "import sys; print(sys.maxsize > 2**32)"
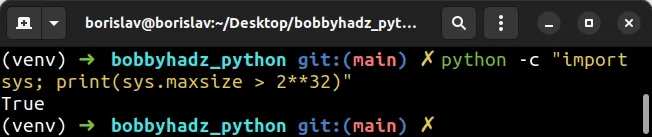
It will return True if your Python interpreter is running in 64-bit.
If you get a False value back, then your Python installation is 32-bit.
Even if your PC has more than 4 GB of RAM, they will remain unallocated if your Python interpreter is 32-bit.
You have to visit the official Python downloads page and download the 64-bit Python version (x86-64 label).
You might also run into this issue if you install the 32-bit version of the PyCharm IDE by mistake.
Make sure to install the 64-bit version instead.
# Try setting the dtype argument to uint8
If the error persists, try to set the dtype argument to "uint8" when
creating the array.
import numpy as np arr = np.zeros((26816, 36, 55406), dtype='uint8') print(arr)
The uint8 data type represents unsigned integers of 8 bits.
It contains all whole numbers from 0 to 255.
Note that the numbers are unsigned, so they cannot be negative.
The uint8 data type takes less space than float64 or int64, so it often
helps resolve memory issues.
If you got the error when working with a Pandas DataFrame, use the
astype()
method to set the type of the values to uint8.
import numpy as np import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'x': np.array([1, 2, 3]) }) df['x'] = df['x'].astype(np.uint8) print(df)

The code sample sets the types of the values in the X column to uint8.
# Splitting the data structure or reading it in chunks
If the error persists, you might be able to split the dataset you're working with in multiple chunks.
If the object is already initialized and stores all of the data, you might be able to only read a certain amount of the dataset at a time.
Each chunk should be processed separately, so you don't run out of memory.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to flatten only some Dimensions of a NumPy array
- Remove the Duplicate elements from a NumPy Array
- NumPy: Apply a Mask from one Array to another Array
- How to iterate over the Columns of a NumPy Array
- Pandas: Find an element's Index in Series [7 Ways]
- numpy.linalg.LinAlgError: Singular matrix [Solved]
- Removing the Top and Right axis (spines) in Matplotlib
- Sklearn ValueError: Unknown label type: 'continuous' [Fixed]
- TypeError: type numpy.ndarray doesn't define __round__ method

