AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'shape'
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'shape'
- AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'reshape'
- AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'astype'
# AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'shape'
The Python "AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'shape'" occurs
when we try to access the shape attribute on a list.
To solve the error, pass the list to the numpy.array() method to create a
numpy array before accessing the shape attribute.
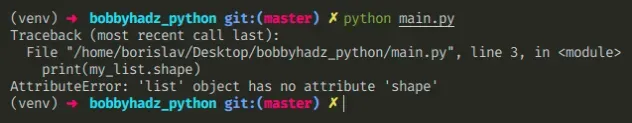
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
my_list = [1, 2, 3] # # ⛔️ AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'shape' print(my_list.shape)
Native Python lists don't have a shape attribute, instead, you have to convert
the list to a NumPy array.
# Convert the list to a NumPy array
To solve the error, pass the list to the np.array() method to create a numpy
array.
import numpy as np np_array = np.array([1, 2, 3]) print(np_array.shape) # 👉️ (3,)
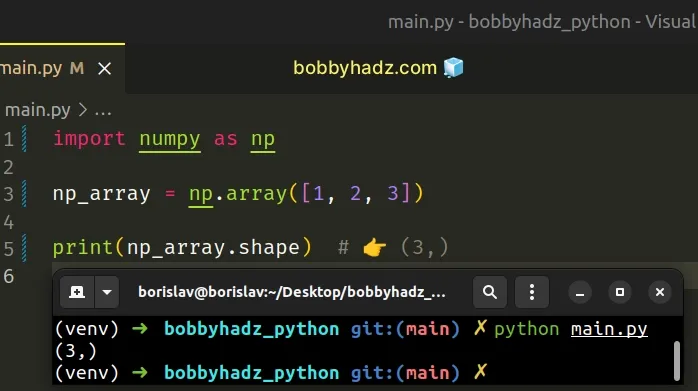
The numpy.array() method takes an array-like object as an argument and creates an array.
You might also use the
numpy.asarray()
method to convert a list to a NumPy array before accessing the shape
attribute.
import numpy as np np_array = np.asarray([1, 2, 3]) print(np_array.shape) # 👉️ (3,)
# Passing the list directly to the shape() method
Alternatively, you can pass the list directly to the numpy.shape() method.
import numpy as np array_shape = np.shape([1, 2, 3]) print(array_shape) # 👉️ (3,) print(np.shape([[1, 2]])) # 👉️ (1, 2) print(np.shape([0])) # 👉️ (1,)
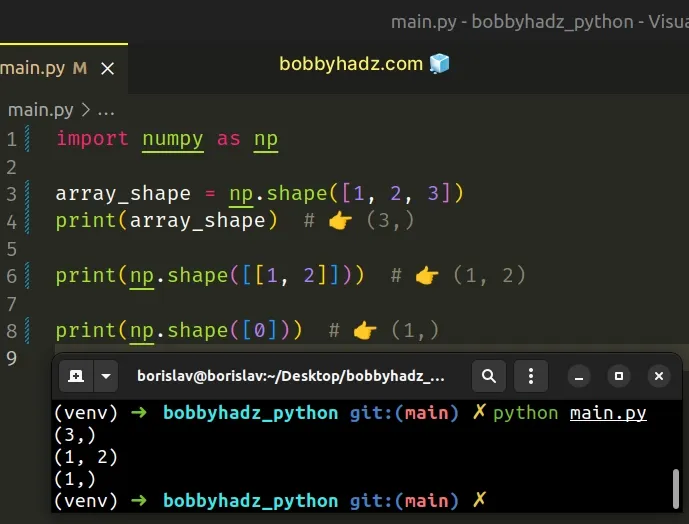
The numpy.shape() method takes an array-like object as an argument and returns
the shape of the array.
The elements of the shape tuple give the lengths of the corresponding array
dimensions.
# Getting the length of a list
If you need to get the length of a list, use the len() function.
my_list = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]] # 👇️ Get the length of the entire list print(len(my_list)) # 👉️ 2 # 👇️ Get the length of the list item at index 0 print(len(my_list[0])) # 👉️ 3
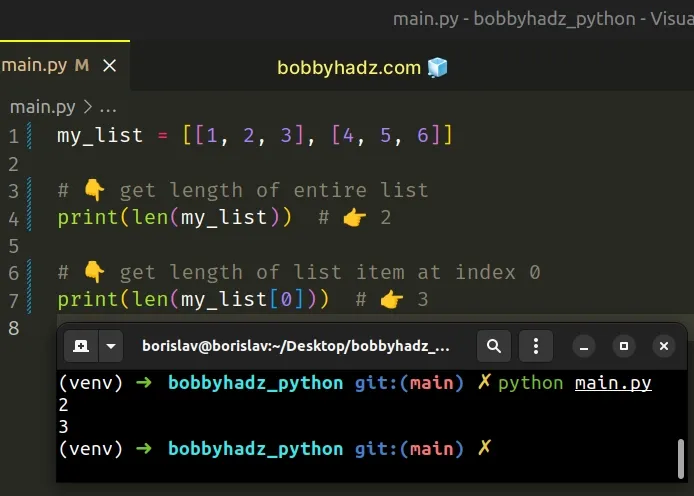
The len() function returns the length (the number of items) of an object.
# Checking all of the attributes of an object
You can view all the attributes an object has by using the dir() function.
my_list = ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com'] # 👉️ [... 'append', 'clear', 'copy', 'count', 'extend', 'index', # 'insert', 'pop', 'remove', 'reverse', 'sort' ...] print(dir(my_list))
If you pass a class to the dir() function, it returns a list of names of the class's attributes, and recursively of the attributes of its bases.
If you try to access any attribute that is not in this list, you will get the "AttributeError: list object has no attribute" error.
# Table of Contents
- AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'reshape'
- AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'astype'
# AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'reshape'
The Python "AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'reshape'" occurs
when we try to call the reshape() method on a list.
To solve the error, pass the list to the numpy.array() method to create a
numpy array before calling the reshape method.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
my_list = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5] # ⛔️ AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'reshape' reshaped = my_list.reshape((3, 2))
Python lists don't have a reshape() attribute. To solve the error, convert the
list to a NumPy array.
# Convert the list to an array before calling reshape()
To solve the error, pass the list to the np.array() method to create a numpy
array.
import numpy as np my_list = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5] np_array = np.array(my_list) # [[0 1] # [2 3] # [4 5]] print(np_array.reshape((3, 2)))
The numpy.array() method takes an array-like object as an argument and creates an array.
You might also use the
numpy.asarray()
method to convert a list into a numpy array before calling the reshape
method.
import numpy as np my_list = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5] np_array = np.asarray(my_list) # [[0 1] # [2 3] # [4 5]] print(np_array.reshape((3, 2)))
# Passing the list directly to the numpy.reshape() method
Alternatively, you can pass the list directly to the numpy.reshape method.
import numpy as np my_list = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5] reshaped = np.reshape(my_list, (3, 2)) # [[0 1] # [2 3] # [4 5]] print(reshaped)
The numpy.reshape method gives a new shape to an array without changing its
data.
import numpy as np my_list = [[0, 1, 2], [3, 4, 5]] reshaped = np.reshape(my_list, 6) print(reshaped) # [0 1 2 3 4 5]
The np.reshape() method takes an array-like object as an argument and an int
or tuple of integers that represent the new shape.
The new shape should be compatible with the original shape.
If an integer is passed for the new shape argument, the result will be a 1-D array of that length.
If you need to get the length of a list, use the len() function.
my_list = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]] # 👇️ Get the length of the entire list print(len(my_list)) # 👉️ 2 # 👇️ Get the length of the list item at index 0 print(len(my_list[0])) # 👉️ 3
The len() function returns the length (the number of items) of an object.
You can view all the attributes an object has by using the dir() function.
my_list = ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com'] # 👉️ [... 'append', 'clear', 'copy', 'count', 'extend', 'index', # 'insert', 'pop', 'remove', 'reverse', 'sort' ...] print(dir(my_list))
If you pass a class to the dir() function, it returns a list of names of the class's attributes, and recursively of the attributes of its bases.
If you try to access any attribute that is not in this list, you will get the "AttributeError: list object has no attribute" error.
# AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'astype'
The Python "AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'astype'" occurs
when we try to call the astype() method on a list.
To solve the error, pass the list to the numpy.array() method to create a
numpy array before calling the astype method.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
my_list = [1, 2, 2.5, 3.6] # ⛔️ AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'astype' result = my_list.astype(int)
Native Python lists don't have an astype attribute.
To solve the error, we have to convert the list to a NumPy array.
# Convert the list to an array before using astype()
To solve the error, pass the list to the np.array() method to create a NumPy
array.
import numpy as np my_list = [1, 2, 2.5, 3.6] np_array = np.array(my_list, dtype=np.int32) print(np_array) # 👉️ [1 2 2 3]
The dtype keyword argument can be used to set the data type of the array's elements.
You can use the astype method on a NumPy array to copy the array and cast it to a specified type.
import numpy as np my_list = [1, 2, 2.5, 3.6] np_array = np.array(my_list, dtype=np.int32) print(np_array) # 👉️ [1 2 2 3] result = np_array.astype(np.float32) print(result) # 👉️ [1. 2. 2. 3.]
The only parameter we passed to the astype method is the data type to which
the array is cast.
import numpy as np my_list = [1, 2, 2.5, 3.6] np_array = np.array(my_list) result = np_array.astype(int) print(result) # 👉️ [1 2 2 3]
You can view all the attributes an object has by using the dir() function.
my_list = ['a', 'b', 'c'] # 👉️ [... 'append', 'clear', 'copy', 'count', 'extend', 'index', # 'insert', 'pop', 'remove', 'reverse', 'sort' ...] print(dir(my_list))
If you pass a class to the dir() function, it returns a list of names of the class's attributes, and recursively of the attributes of its bases.
If you try to access any attribute that is not in this list, you will get the "AttributeError: list object has no attribute" error.

