How to filter a JSON array in Python
Last updated: Apr 10, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- How to filter a JSON array in Python
- How to filter a JSON array using a
forloop - Filter a JSON array that is stored in a file in Python
- Filter a JSON array using the
filter()function
# How to filter a JSON array in Python
To filter a JSON array in Python:
- Use the
json.loads()method to convert the JSON array to a Python list. - Use a list comprehension to iterate over the list.
- Check if each item in the list meets a certain condition and return the result.
import json json_array = json.dumps( [ {'name': 'Alice', 'salary': 100}, {'name': 'Bobby', 'salary': 50}, {'name': 'Carl', 'salary': 75} ] ) a_list = json.loads(json_array) filtered_list = [ dictionary for dictionary in a_list if dictionary['salary'] > 50 ] # 👇️ [{'name': 'Alice', 'salary': 100}, {'name': 'Carl', 'salary': 75}] print(filtered_list)
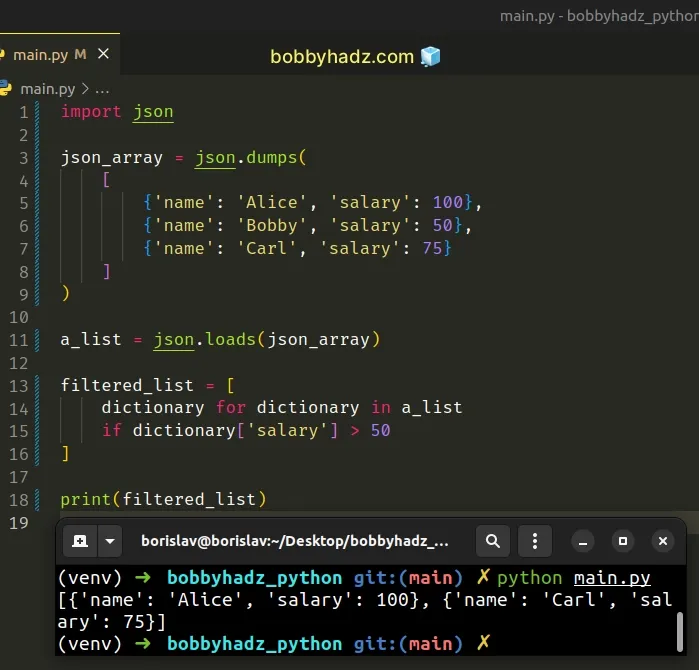
The json.dumps() method converts a Python object to a JSON formatted string.
Conversely, the json.loads() method parses a JSON string into a native Python object.
json.loads() method to convert the JSON array to a native Python list.We then used a list comprehension to iterate over the list.
On each iteration, we check if a certain condition is met and return the result.
The code sample checks if each dictionary has a salary key with a value
greater than 50.
import json json_array = json.dumps( [ {'name': 'Alice', 'salary': 100}, {'name': 'Bobby', 'salary': 50}, {'name': 'Carl', 'salary': 75} ] ) a_list = json.loads(json_array) filtered_list = [ dictionary for dictionary in a_list if dictionary['salary'] > 50 ] # 👇️ [{'name': 'Alice', 'salary': 100}, {'name': 'Carl', 'salary': 75}] print(filtered_list)
The new list only contains the dictionaries that meet the condition.
You can use this approach to check for any condition.
Alternatively, you can use a for loop.
# How to filter a JSON array using a for loop
This is a four-step process:
- Use the
json.loads()method to convert the JSON array to a Python list. - Use a
forloop to iterate over the list. - Check if each list item meets a certain condition.
- Append the matching items to a new list.
import json json_array = json.dumps( [ {'name': 'Alice', 'salary': 100}, {'name': 'Bobby', 'salary': 50}, {'name': 'Carl', 'salary': 75} ] ) a_list = json.loads(json_array) filtered_list = [] for dictionary in a_list: if dictionary['salary'] > 50: filtered_list.append(dictionary) # 👇️ [{'name': 'Alice', 'salary': 100}, {'name': 'Carl', 'salary': 75}] print(filtered_list)
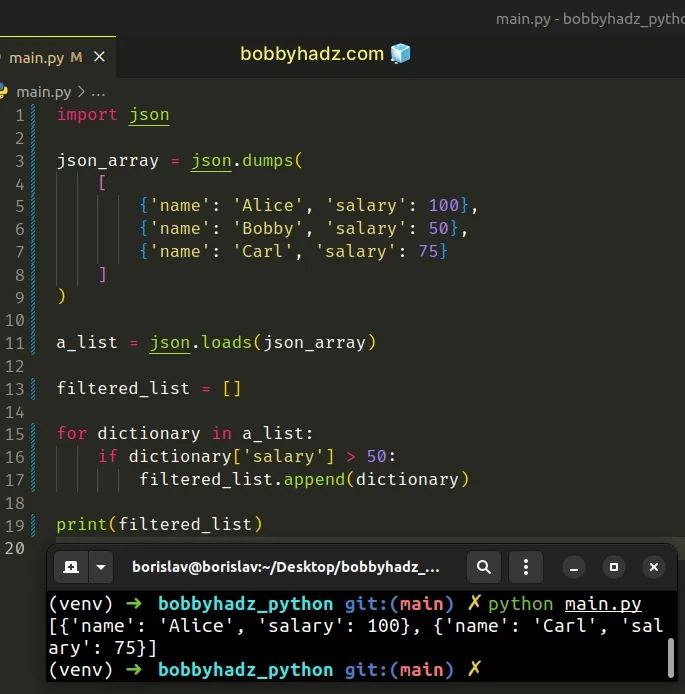
We used a for loop to iterate over the list.
On each iteration, we check if the current dictionary has a salary key with a
value greater than 50.
If the condition is met, we use the list.append() method to
append the dictionary to a new list.
The list.append() method adds an item to the end of the list.
The new list only contains the items of the original list that meet the condition.
You can use the same approach to filter a JSON array stored in a file.
# Filter a JSON array that is stored in a file in Python
To filter a JSON array that is stored in a file:
- Open the JSON file in reading mode.
- Use the
JSON.load()method to deserialize the file to a Python list. - Use a list comprehension to filter the list.
import json file_name = 'example.json' with open(file_name, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f: a_list = json.load(f) # 👇️ [{'name': 'Alice', 'salary': 100}, {'name': 'Bobby', 'salary': 50}, {'name': 'Carl', 'salary': 75}] print(a_list) filtered_list = [ dictionary for dictionary in a_list if dictionary['salary'] > 50 ] # 👇️ [{'name': 'Alice', 'salary': 100}, {'name': 'Carl', 'salary': 75}] print(filtered_list)
The code sample assumes that you have an example.json file stored in the same
directory as your main.py script.
[ {"name": "Alice", "salary": 100}, {"name": "Bobby", "salary": 50}, {"name": "Carl", "salary": 75} ]
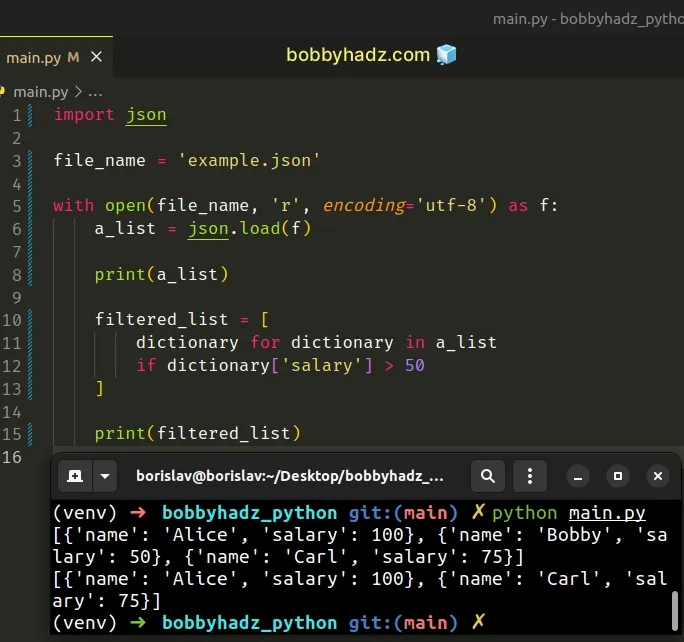
The json.load() method is used to deserialize a file to a Python object.
On the other hand, the json.loads() method is used to deserialize a JSON string to a Python object.
json.load() method expects a text file or a binary file containing a JSON document that implements a .read() method.Once we have the data from the JSON file parsed to a native Python list, we can
use a list comprehension or a for loop to filter the list.
You can also use the filter() function to filter a JSON array.
# Filter a JSON array using the filter() function
This is a three-step process:
- Use the
json.loads()function to parse the JSON array into a Python list. - Pass a
lambdafunction and the list to thefilter()function. - The
lambdafunction should check if each list item meets a condition.
import json json_array = json.dumps( [ {'name': 'Alice', 'salary': 100}, {'name': 'Bobby', 'salary': 50}, {'name': 'Carl', 'salary': 75} ] ) a_list = json.loads(json_array) filtered_list = list( filter( lambda dictionary: dictionary['salary'] > 50, a_list ) ) # 👇️ [{'name': 'Alice', 'salary': 100}, {'name': 'Carl', 'salary': 75}] print(filtered_list)
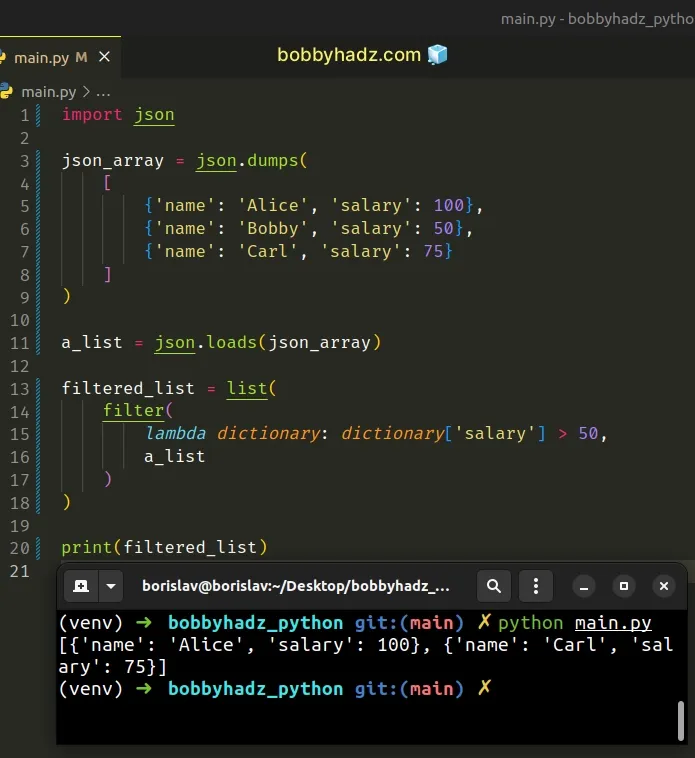
The filter() function takes a function and an iterable as arguments and constructs an iterator from the elements of the iterable for which the function returns a truthy value.
lambda function we passed to filter() gets called with each dictionary from the list.The function checks if the dictionary meets a certain condition and returns the result.
The last step is to use the list() class to
convert the filter object to a list.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to Convert JSON NULL values to None using Python
- How to convert a Tuple to JSON in Python
- How to Delete a JSON object from a List in Python
- ValueError: malformed node or string in Python [Solved]
- Check the syntax of a Python script without executing it
- Mock multiple return values in a Python unit Test
- Python: Assert that Mock was called with specific Arguments
- Python: Sending multipart/form-data request with requests
- Python: Don't run a module's code when it is imported
- How to keep a Python script output Window open
- How to merge multiple JSON files in Python [3 Ways]
- ValueError: Circular reference detected in Python [Solved]
- How to convert an HSV color to RGB in Python
- Python argparse: unrecognized arguments error [Solved]
- Python argparse: Pass a List as command-line argument
- Python: How to calculate the MD5 Hash of a File
- python.exe: can't find
__main__module in Path - -215:Assertion failed !_src.empty() in function 'cvtColor'
- _tkinter.TclError: no display name and no $DISPLAY environment variable
- Matplotlib is currently using agg, which is non-GUI backend
- Python: Not all parameters were used in the SQL statement
- How to convert Dataclass to JSON in Python

