NumPy RuntimeWarning: divide by zero encountered in log10
Last updated: Apr 10, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# NumPy RuntimeWarning: divide by zero encountered in log10
The NumPy "RuntimeWarning: divide by zero encountered in log10" is shown when
you pass an array that contains zeros to the numpy.log10() method.
To resolve the issue, use the numpy.seterr() method to disable the warnings
or use a context manager.
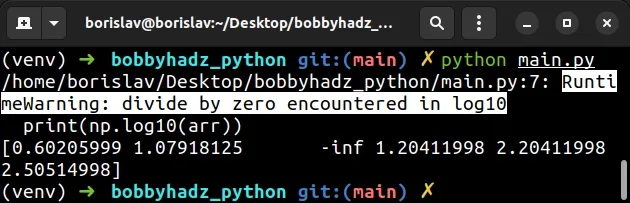
Here is an example of how the warning is shown.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([4, 12, 0, 16, 160, 320]) # /home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/main.py:14: # RuntimeWarning: divide by zero encountered in log10 print(np.log10(arr))
The array contains a zero value which is the cause of the warning.
The numpy.log10() method returns the base 10 logarithm of the supplied array, element-wise.
One way to resolve the issue is to use a context manager to set the error state
for the division to ignore.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([4, 12, 0, 16, 160, 320]) with np.errstate(divide='ignore'): print(np.log10(arr))
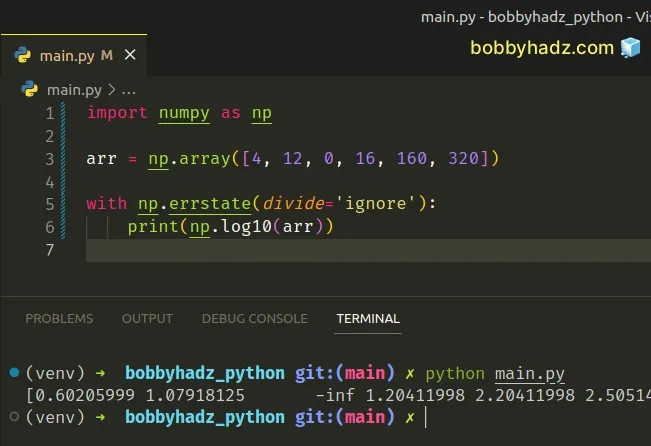
The numpy.errstate context manager is used for floating-point error handling.
The context manager uses the numpy.seterr() method under the hood.
We set the divide keyword argument to ignore, so NumPy is instructed to ignore
division errors in the indented code block.
The divide keyword argument is used to determine how division by zero is
treated.
Once we exit the context manager, the error-handling behavior is reverted to the default.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([4, 12, 0, 16, 160, 320]) with np.errstate(divide='ignore'): # 👇️ No error here print(np.log10(arr)) # 👇️ This causes the error print(np.log10(arr))
As shown in the code sample, once we exit the context, the error-handling behavior is reset.
# Using the seterr method to disable the warning
You can also use the numpy.seterr() method to manually disable the warning.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([4, 12, 0, 16, 160, 320]) np.seterr(divide='ignore') print(np.log10(arr)) np.seterr(divide='warn')
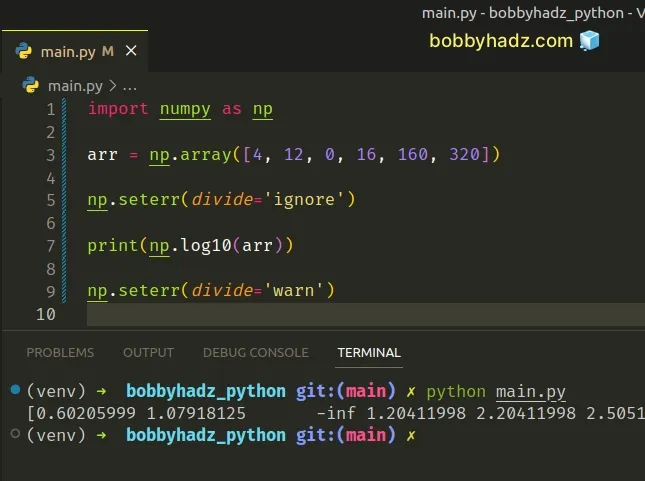
The numpy.seterr() method determines how floating-point errors are handled.
The divide argument is used to set the behavior when dividing by zero.
ignore, no action is taken when a division by zero exception occurs.We set the divide keyword argument to warn in the second call to the
np.seterr() method.
np.seterr(divide='warn')
This resets the error-handling behavior.
When the keyword argument is set to warn, a RuntimeWarning is printed when a
division by zero exception occurs.
If you use the np.log10() method with an array containing zeros after the
error handling behavior is reset, you'd get the warning.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([4, 12, 0, 16, 160, 320]) np.seterr(divide='ignore') # 👇️ This doesn't raise the warning print(np.log10(arr)) np.seterr(divide='warn') # 👇️ This causes the warning print(np.log10(arr))
The second call to numpy.log10() shows the warning.
# Using the where keyword argument to resolve the issue
You can also set the where keyword argument in the call to the numpy.log10()
method to resolve the issue.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([4, 12, 0, 16, 160, 320]) result = np.log10(arr, where=arr > 0) print(result)
The where keyword argument checks each array element for the specified
condition.
The numpy.log10() method is only applied to the non-zero values in the array.
I've also written an article on how to convert a NumPy array to 0 or 1 based on a threshold.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

