ValueError: Shape of passed values is X, indices imply Y
Last updated: Apr 11, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- ValueError: Shape of passed values is X, indices imply Y
- Solve the error by passing the transposed array to pandas.DataFrame()
- Solving the error when you have duplicate index values
- If you got the error when using concat(), try using join() instead
# ValueError: Shape of passed values is X, indices imply Y
The Pandas "ValueError: Shape of passed values is X, indices imply Y" most
commonly occurs when the shape of the passed values to pandas.DataFrame
doesn't match the shape of the indices (or columns).
To solve the error, make sure the shape of the data matches the columns array.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import pandas as pd import numpy as np arr = np.array([ [1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12] ]) print(arr.shape) # 👉️ (3, 4) df = pd.DataFrame(arr, columns=['A', 'B', 'C']) # ValueError: Shape of passed values is (3, 4), indices imply (3, 3) print(df)
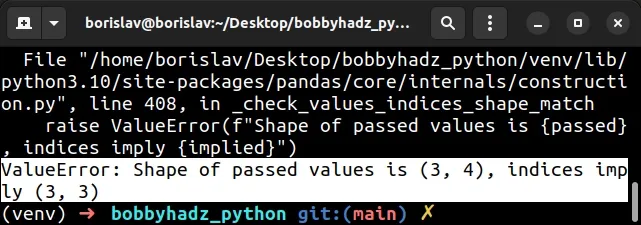
The NumPy array has a shape of (3, 4). In other words, 3 rows and 4 columns.
However, when instantiating the pandas.DataFrame class, we only specified 3 column names.
As shown in the code sample, you can use the ndarray.shape() method to get a tuple of the array's dimensions.
One way to solve the error is to specify exactly as many columns as the array
has when constructing the DataFrame.
import pandas as pd import numpy as np arr = np.array([ [1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12] ]) print(arr.shape) # 👉️ (3, 4) df = pd.DataFrame(arr, columns=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D']) # A B C D # 0 1 2 3 4 # 1 5 6 7 8 # 2 9 10 11 12 print(df)
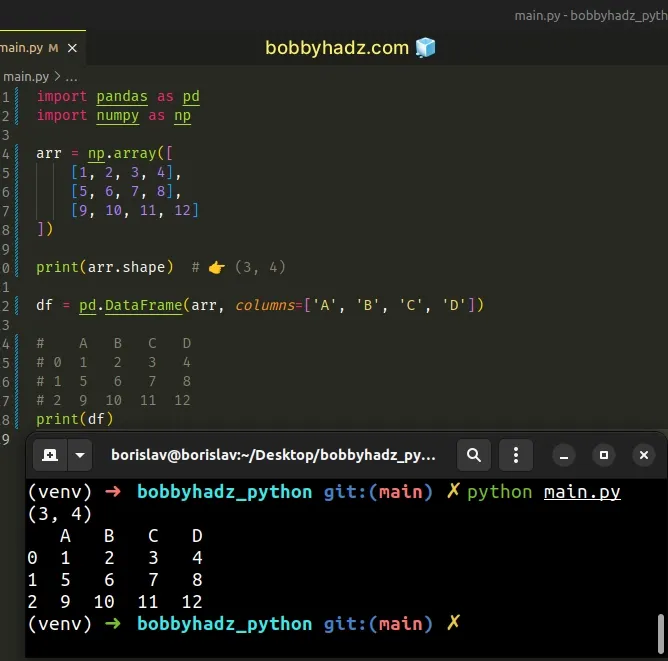
The array has 4 columns, so we passed 4 column names when instantiating the
pandas.DataFrame class.
columns argument is used to specify the column labels that are used for the resulting frame when the supplied data doesn't have them.The argument defaults to RangeIndex(0, 1, 2, ..., n).
# Solve the error by passing the transposed array to pandas.DataFrame()
In some cases, you might want to pass the transposed version of the array to
pandas.DataFrame() class to solve the error.
import pandas as pd import numpy as np arr = np.array([ [1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12] ]) print(arr.shape) # 👉️ (3, 4) print('-' * 50) # [[ 1 5 9] # [ 2 6 10] # [ 3 7 11] # [ 4 8 12]] print(arr.T) print('-' * 50) print(arr.T.shape) # 👉️ (4, 3) df = pd.DataFrame(arr.T, columns=['A', 'B', 'C']) print('-' * 50) # A B C # 0 1 5 9 # 1 2 6 10 # 2 3 7 11 # 3 4 8 12 print(df)
The NumPy array in the example has 3 rows and 4 columns.
However, notice that we only specified 3 columns when calling
pandas.DataFrame().
We did this by getting a view of the transposed array with ndarray.T.
Using the attribute is the same as calling the numpy.transpose() method.
The method returns an array with the axes transposed.
# Solving the error when you have duplicate index values
The error is also raised when you have
duplicate index values
in your DataFrame or Series.
YOu can use the index.is_unique attribute to check if the index has unique values only.
import pandas as pd import numpy as np df = pd.DataFrame( np.array([ [1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12] ]), columns=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'], index=[0, 1, 2] ) # 👇️ Check if index is unique print(df.index.is_unique) # 👉️ True series = pd.Series( [13, 14, 15], name='ser', index=[0, 1, 2] ) # 👇️ Check if index is unique print(series.index.is_unique) # 👉️ True # A B C D ser # 0 1 2 3 4 13 # 1 5 6 7 8 14 # 2 9 10 11 12 15 print(pd.concat([df, series], axis=1))
The index.is_unique attribute will return False if your index has duplicate
values.
import pandas as pd import numpy as np idx = pd.Index([1, 3, 3, 5]) print(idx.is_unique) # 👉️ False
If you have duplicate values, use the DataFrame.drop_duplicates method to remove them.
import pandas as pd import numpy as np df = pd.DataFrame( np.array([ [1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12] ]), columns=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'], index=[0, 1, 2] ) # remove duplicates in place df.drop_duplicates(inplace=True) series = pd.Series( [13, 14, 15], name='ser', index=[0, 1, 2] ) # remove duplicates in place series.drop_duplicates(inplace=True) # A B C D ser # 0 1 2 3 4 13 # 1 5 6 7 8 14 # 2 9 10 11 12 15 print(pd.concat([df, series], axis=1))
The DataFrame.drop_duplicates() method removes the duplicate rows from the
DataFrame.
The method mutated the original DataFrame because we set the inplace
argument to True.
If the error persists, try to use the DataFrame.reset_index method.
import pandas as pd import numpy as np df = pd.DataFrame( np.array([ [1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12] ]), columns=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'], index=[0, 1, 2] ) # df.drop_duplicates(inplace=True) df.reset_index(drop=True, inplace=True) series = pd.Series( [13, 14, 15], name='ser', index=[0, 1, 2] ) series.reset_index(drop=True, inplace=True) # A B C D ser # 0 1 2 3 4 13 # 1 5 6 7 8 14 # 2 9 10 11 12 15 print(pd.concat([df, series], axis=1))
The DataFrame.reset_index() method resets the index of the DataFrame and
uses the default one instead.
You can also remove the duplicate indices by using the
DataFrame.index.duplicated() method.
import pandas as pd import numpy as np df = pd.DataFrame( np.array([ [1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12] ]), columns=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'], index=[0, 1, 2] ) df = df.loc[~df.index.duplicated()] series = pd.Series( [13, 14, 15], name='ser', index=[0, 1, 2] ) series = series.loc[~series.index.duplicated()] # A B C D ser # 0 1 2 3 4 13 # 1 5 6 7 8 14 # 2 9 10 11 12 15 print(pd.concat([df, series], axis=1))
The index.duplicated() method returns a boolean array that indicates the duplicate index values.
import pandas as pd import numpy as np idx = pd.Index([1, 3, 3, 5]) # 👇️ [False False True False] print(idx.duplicated())
The array stores True for each duplicate value.
The tilde ~ character is then used to get the non-duplicate records.
# If you got the error when using concat(), try using join() instead
If you got the error when using the DataFrame.concat method, try to use the DataFrame.join method instead.
import pandas as pd import numpy as np df = pd.DataFrame( np.array([ [1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12] ]), columns=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'], index=[0, 1, 2] ) series = pd.Series( [13, 14, 15], name='ser', index=[0, 1, 2] ) # A B C D ser # 0 1 2 3 4 13 # 1 5 6 7 8 14 # 2 9 10 11 12 15 print(df.join(series))
The DataFrame.join() method joins the columns of a DataFrame with another
DataFrame, either on an index or on a key column.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- FutureWarning: pandas.Int64Index is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version
- You are trying to merge on int64 and object columns [Fixed]
- Copy a column from one DataFrame to another in Pandas
- ValueError: cannot reindex on an axis with duplicate labels
- IndexError: single positional indexer is out-of-bounds [Fix]
- Python OSError: [Errno 98] Address already in use [Solved]
- Count number of non-NaN values in each column of DataFrame
- Index(...) must be called with a collection of some kind
- Reindexing only valid with uniquely valued Index objects
- Pandas: Select distinct across multiple DataFrame columns
- Pandas: Sum the values in a Column that match a Condition
- Pandas: How to get the Max and Min Dates in a DataFrame

