Converting a Nested Dictionary to a Pandas DataFrame
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Converting a Nested Dictionary to a Pandas DataFrame
- Converting a nested dictionary to a DataFrame with keys as columns
- Setting the column name of the index column
- Converting a nested dictionary to a DataFrame by using pd.DataFrame
- Converting a nested dictionary with list values to DataFrame
- Converting a nested dictionary to a DataFrame and explicitly setting the columns
# Converting a Nested Dictionary to a Pandas DataFrame
To convert a nested dictionary to a Pandas DataFrame:
- Use the
DataFrame.from_dict()method. - Set the
orientkeyword argument toindex. - When the
orientargument is set toindex, the keys of thedictwill be rows.
import pandas as pd nested_dict = { '1': {'name': 'Alice', 'salary': 1500}, '2': {'name': 'Bobby', 'salary': 1200}, } df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(nested_dict, orient='index') # name salary # 1 Alice 1500 # 2 Bobby 1200 print(df)
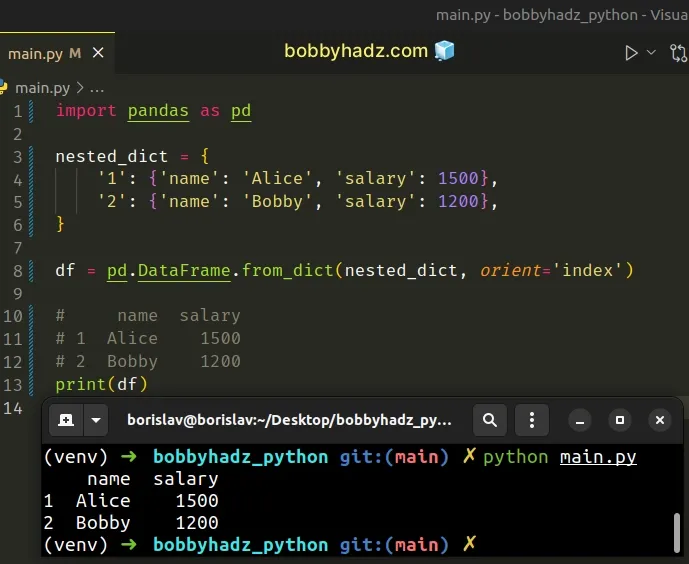
The
DataFrame.from_dict()
method constructs a DataFrame from a dictionary.
The orient argument determines the orientation of the data.
# Converting a nested dictionary to a DataFrame with keys as columns
If the keys of the supplied dictionary should be columns of the DataFrame,
then set the argument to "columns" (which is the default).
Here is an example of converting a nested dictionary to a DataFrame by setting
orient to "columns".
import pandas as pd nested_dict = { '1': {'name': 'Alice', 'salary': 1500}, '2': {'name': 'Bobby', 'salary': 1200}, } df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(nested_dict, orient='columns') # 1 2 # name Alice Bobby # salary 1500 1200 print(df)
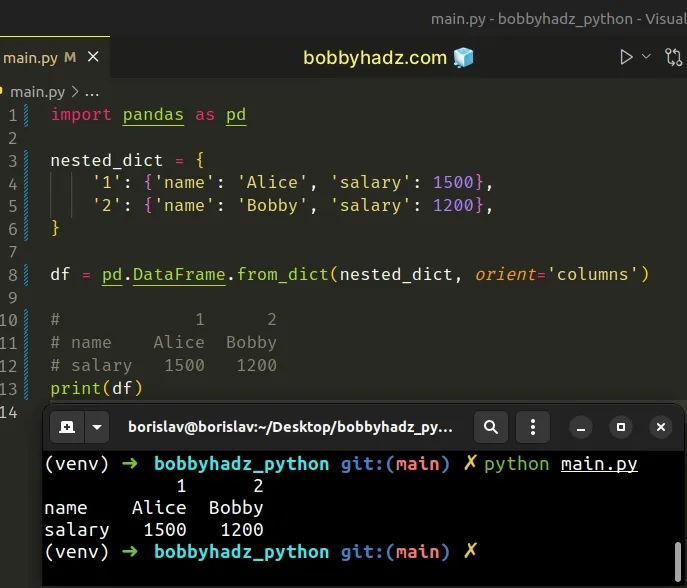
"index".# Setting the column name of the index column
If you want to set the column name for the index column, use the index.name
attribute.
import pandas as pd nested_dict = { '1': {'name': 'Alice', 'salary': 1500}, '2': {'name': 'Bobby', 'salary': 1200}, } df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(nested_dict, orient='index') df.index.name = 'Emp' # name salary # Emp # 1 Alice 1500 # 2 Bobby 1200 print(df)
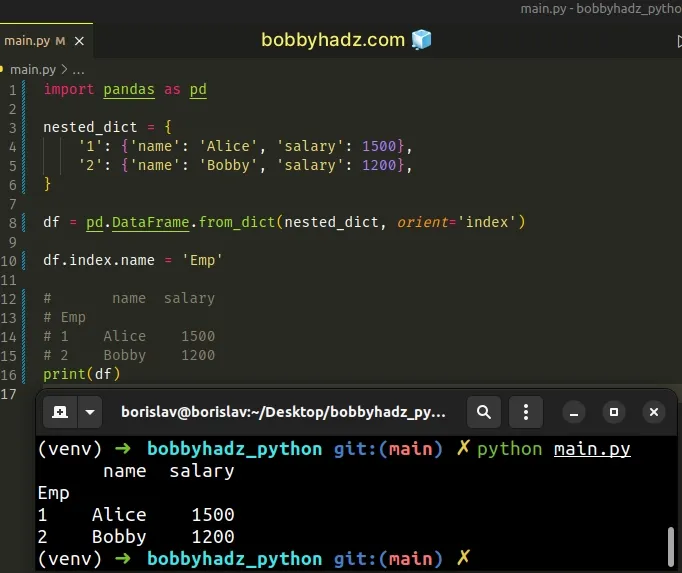
# Converting a nested dictionary to a DataFrame by using pd.DataFrame
You can also directly use the pandas.DataFrame() constructor to convert a
nested dictionary to a DataFrame.
import pandas as pd nested_dict = { '1': {'name': 'Alice', 'salary': 1500}, '2': {'name': 'Bobby', 'salary': 1200}, } df = pd.DataFrame(nested_dict) # 1 2 # name Alice Bobby # salary 1500 1200 print(df)
As shown in the code sample, the dictionary's keys become columns in the
constructed DataFrame.
If the keys of the dictionary should be rows, access the T (transpose)
attribute of the constructed DataFrame.
import pandas as pd nested_dict = { '1': {'name': 'Alice', 'salary': 1500}, '2': {'name': 'Bobby', 'salary': 1200}, } df = pd.DataFrame(nested_dict).T # name salary # 1 Alice 1500 # 2 Bobby 1200 print(df)
Accessing the DataFrame.T is equivalent to calling
DataFrame.transpose().
The method tranposes index and columns.
In other words, it writes rows as columns and vice-versa.
# Converting a nested dictionary with list values to DataFrame
You can also use the DataFrame.from_dict() method if you need to convert a
nested dictionary with list values to a DataFrame.
import pandas as pd nested_dict = { 'Dog': {'Age': [3, 5], 'Speed': [35, 45]}, 'Cat': {'Age': [1, 3], 'Speed': [25, 30]}, } df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(nested_dict, orient='index') # Age Speed # Dog [3, 5] [35, 45] # Cat [1, 3] [25, 30] print(df) print('-' * 50) # Dog Age 3 # Age 5 # Speed 35 # Speed 45 # Cat Age 1 # Age 3 # Speed 25 # Speed 30 # dtype: object print(df.stack().explode())
You can optionally
create a new row for each element in the lists
by using DataFrame.explode().
# Converting a nested dictionary to a DataFrame and explicitly setting the columns
In some cases, the column names might not be contained in the nested dictionary.
You can use the columns argument to set the columns explicitly.
import pandas as pd nested_dict = { 'dev': {'frontend': 29, 'backend': 30, 'fullstack': 31}, 'designer': {'react': 15, 'vue': 9}, } df = pd.DataFrame([[k1, k2, value] for k1, d in nested_dict.items() for k2, value in d.items()], columns=['title', 'technology', 'count']) # title technology count # 0 dev frontend 29 # 1 dev backend 30 # 2 dev fullstack 31 # 3 designer react 15 # 4 designer vue 9 print(df)
We used a nested list comprehension to iterate over the dictionary's items (and
each nested dict).
List comprehensions are used to perform some operation for every element or select a subset of elements that meet a condition.
nested_dict = { 'dev': {'frontend': 29, 'backend': 30, 'fullstack': 31}, 'designer': {'react': 15, 'vue': 9}, } # [['dev', 'frontend', 29], # ['dev', 'backend', 30], # ['dev', 'fullstack', 31], # ['designer', 'react', 15], # ['designer', 'vue', 9]] print([[k1, k2, value] for k1, d in nested_dict.items() for k2, value in d.items()])
On each iteration, we return a list containing the outer dict key, the nested
dict key and its value.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Usecols do not match columns, columns expected but not found
- Pandas: Create new row for each element in List in DataFrame
- ValueError: Cannot merge a Series without a name [Solved]
- Index(...) must be called with a collection of some kind
- ValueError: Shape of passed values is X, indices imply Y
- Reindexing only valid with uniquely valued Index objects
- How to add a Level to Pandas MultiIndex in Python
- Pandas: Strip whitespace from Column Headers in DataFrame
- Replace negative Numbers in a Pandas DataFrame with Zero

