Pandas: Get the Business Days between two Dates
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Pandas: Get the Business Days between two Dates
- Pandas: Get the Business Days between two Dates excluding National Holidays
- Pandas: Get the Business Days between two Dates using pandas.date_range
# Pandas: Get the Business Days between two Dates
Use the pandas.bdate_range() method to get the business days between two
dates in Pandas.
The method returns a fixed frequency DateTimeIndex with business day as the
default.
import pandas as pd date1 = '2023-08-16' date2 = '2023-08-21' business_days = pd.bdate_range(start=date1, end=date2) # DatetimeIndex(['2023-08-16', '2023-08-17', '2023-08-18', '2023-08-21'], dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='B') print(business_days) print(len(business_days)) # 👉️ 4
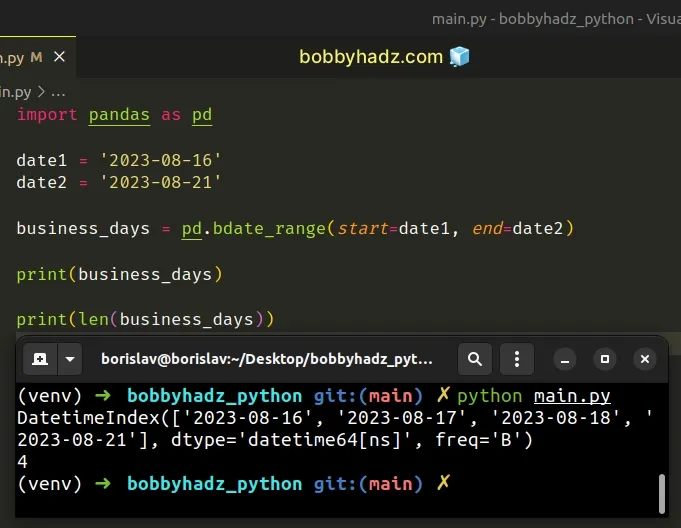
If you need to get the number of business days between 2 dates, use the len()
function as shown in the code sample.
The
pandas.bdate_range()
method returns a fixed DatetimeIndex containing the business days between the
two dates.
By default, the start and end dates are inclusive.
This can be changed by using the inclusive keyword argument when calling
pandas.bdate_range().
The values for the inclusive argument are:
"both"- includes thestartandenddates. This is the default value."neither"- excludes thestartandenddates."left"- includes thestartdate but excludes theenddate."right"- excludes thestartdate but includes theenddate.
Here is an example of setting the argument to "neither".
import pandas as pd date1 = '2023-08-16' date2 = '2023-08-21' business_days = pd.bdate_range( start=date1, end=date2, inclusive='neither' ) # DatetimeIndex(['2023-08-17', '2023-08-18'], dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='B') print(business_days) print(len(business_days)) # 👉️ 2
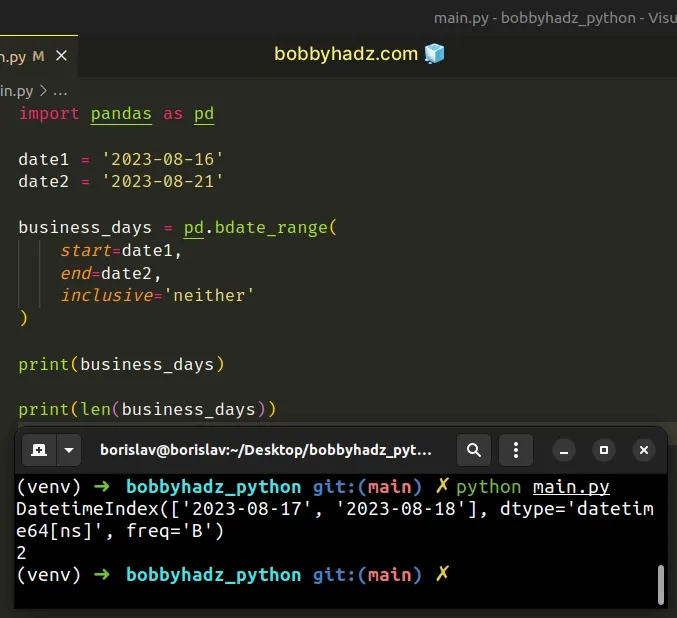
Notice that the start and end dates are excluded from the range.
When using this approach, we consider business days to be Monday through Friday (we exclude weekends).
However, this approach doesn't exclude national holidays.
# Pandas: Get the Business Days between two Dates excluding National Holidays
If you want to get the business days between two dates excluding the national holidays, use the Custom business days classes.
import pandas as pd from pandas.tseries.holiday import USFederalHolidayCalendar from pandas.tseries.offsets import CustomBusinessDay date1 = '2023-11-20' date2 = '2023-11-24' us_business_days = CustomBusinessDay(calendar=USFederalHolidayCalendar()) business_days = pd.bdate_range( start=date1, end=date2, freq=us_business_days ) # DatetimeIndex(['2023-11-20', '2023-11-21', '2023-11-22', '2023-11-24'], dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='C') print(business_days) print(len(business_days)) # 👉️ 4
The USFederalHolidayCalendar class initializes a holiday object with a given
set of rules.
The CustomBusinessDay class provides a parametric BusinessDay class that can
be used to create customized business day calendars that take local holidays and
local weekend conventions into consideration.
Notice that the output doesn't include November the 23rd (Thanksgiving)
# DatetimeIndex(['2023-11-20', '2023-11-21', '2023-11-22', '2023-11-24'], dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='C') print(business_days)
If you want to get the number of business days in the range, use the len()
function.
print(len(business_days)) # 👉️ 4
You can read more about using the CustomBusinessDay class in
this section of the docs.
# Pandas: Get the Business Days between two Dates using pandas.date_range
You can also use the pandas.date_range method to get the business days between
two dates.
- Use the
pandas.date_range()method, passing it the two dates as parameters. - Set the
freqargument to"B"to select only the business days.
import pandas as pd date1 = '2023-09-26' date2 = '2023-09-30' business_days = pd.date_range(date1, date2, freq='B') # DatetimeIndex( # ['2023-09-26', '2023-09-27', '2023-09-28', '2023-09-29'], dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='B') print(business_days) print(len(business_days)) # 👉️ 4
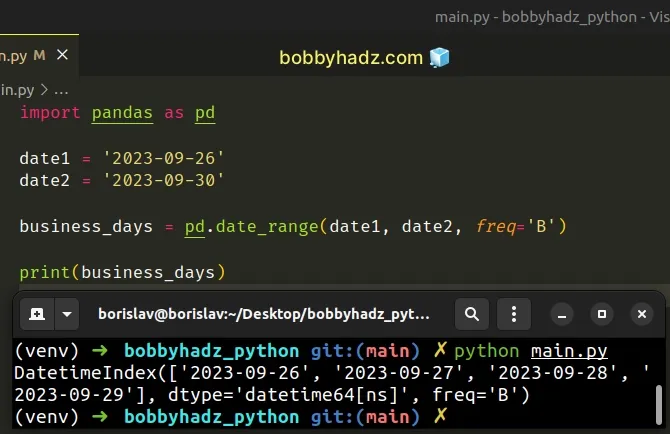
The
pandas.date_range()
method returns a fixed frequency DatetimeIndex.
The first argument we passed to the method is the start date and the second is
the end date.
The freq argument is the frequency of the generated dates.
business_days = pd.date_range(date1, date2, freq='B') # DatetimeIndex( # ['2023-09-26', '2023-09-27', '2023-09-28', '2023-09-29'], dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='B') print(business_days)
If you need to get the number of business days between two dates, use the len() function.
print(len(business_days)) # 👉️ 4
The len() function returns the length (the number of items) of an object.
The freq argument must be set to an
offset alias.
By default, the argument is set to "D" (calendar day frequency).
"B" (business day frequency).You can view all of the available offset aliases in this section of the docs.
The 30th of September is a Saturday (not a business day), so it wasn't included in the list.
When using this approach, we consider business days to be Monday through Friday (we exclude weekends).
However, this approach doesn't exclude national holidays.
import pandas as pd date1 = '2023-11-20' date2 = '2023-11-24' business_days = pd.date_range(date1, date2, freq='B') # DatetimeIndex( # ['2023-11-20', '2023-11-21', '2023-11-22', '2023-11-23', # '2023-11-24'], # dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='B') print(business_days)
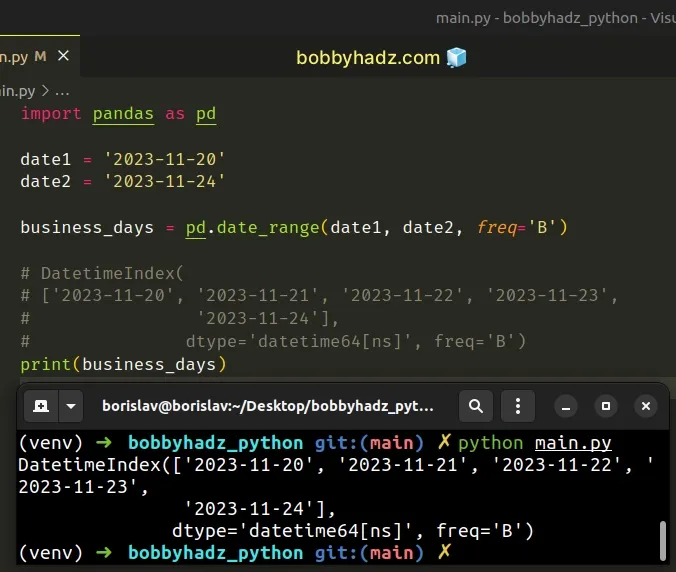
Notice that the list contains The 23rd of November (Thanksgiving).
I've also written an article on how to check if a date is during the weekend in Pandas.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Cannot set a DataFrame with multiple columns to single column
- Pandas ValueError: cannot insert X, already exists [Solved]
- How to Multiply two or more Columns in Pandas
- How to swap two DataFrame columns in Pandas
- NumPy: Get the indices of the N largest values in an Array
- Pandas: How to Query a Column name with Spaces
- Pandas: Create a Tuple from two DataFrame Columns
- Cannot mask with non-boolean array containing NA / NaN values
- Disable the TOKENIZERS_PARALLELISM=(true | false) warning
- RuntimeError: Expected scalar type Float but found Double
- Pandas: Convert timezone-aware DateTimeIndex to naive timestamp
- RuntimeError: Input type (torch.FloatTensor) and weight type (torch.cuda.FloatTensor) should be the same
- ValueError: Failed to convert a NumPy array to a Tensor (Unsupported object type float)
- ValueError: Failed to convert a NumPy array to a Tensor (Unsupported object type float)
- Cannot convert non-finite values (NA or inf) to integer
- Pandas: How to efficiently Read a Large CSV File
- RuntimeError: CUDA out of memory. Tried to allocate X MiB
- OSError: [E050] Can't find model 'en_core_web_sm'

