Comparing Previous/Next row values in a Pandas DataFrame
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- Comparing Previous row values in a Pandas DataFrame
- Comparing Previous row values in a Pandas DataFrame using equality operator
- Comparing Previous row values in a Pandas DataFrame using numpy
- Comparing Next row values in a Pandas DataFrame
# Comparing Previous row values in a Pandas DataFrame
To compare the previous row's values to the current row in a DataFrame:
- Select the specific column.
- Use the
DataFrame.eq()method to compare the column and the result of callingshift()on the column. - The expression will return
Truefor the cases where the previous row is equal to the current row.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan', 'Ethan'], 'experience': [1, 1, 5, 7, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4, 210.5], }) df['prev_equal'] = df['experience'].eq(df['experience'].shift()) # name experience salary prev_equal # 0 Alice 1 175.1 False # 1 Bobby 1 180.2 True # 2 Carl 5 190.3 False # 3 Dan 7 205.4 False # 4 Ethan 7 210.5 True print(df)
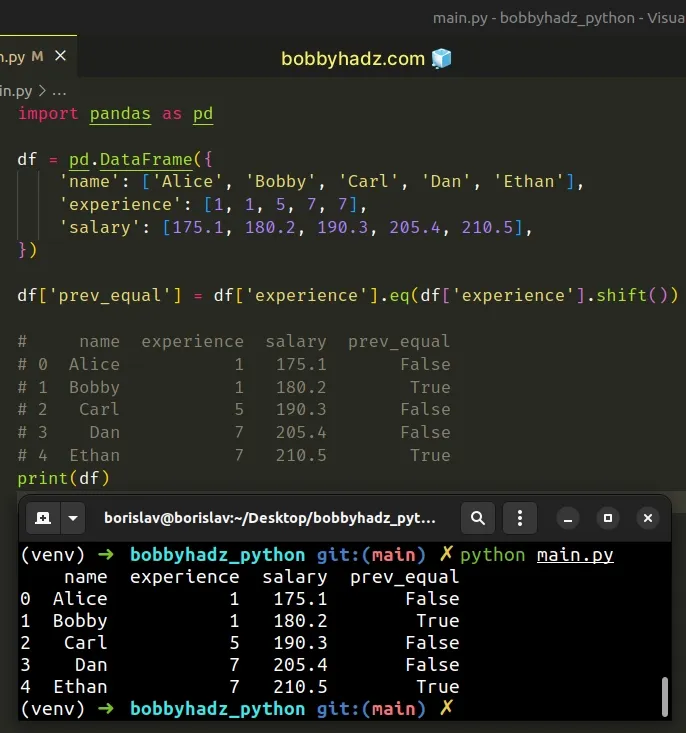
The DataFrame.shift() method shifts the index without realigning the data.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan', 'Ethan'], 'experience': [1, 1, 5, 7, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4, 210.5], }) # 0 NaN # 1 1.0 # 2 1.0 # 3 5.0 # 4 7.0 # Name: experience, dtype: float64 print(df['experience'].shift())
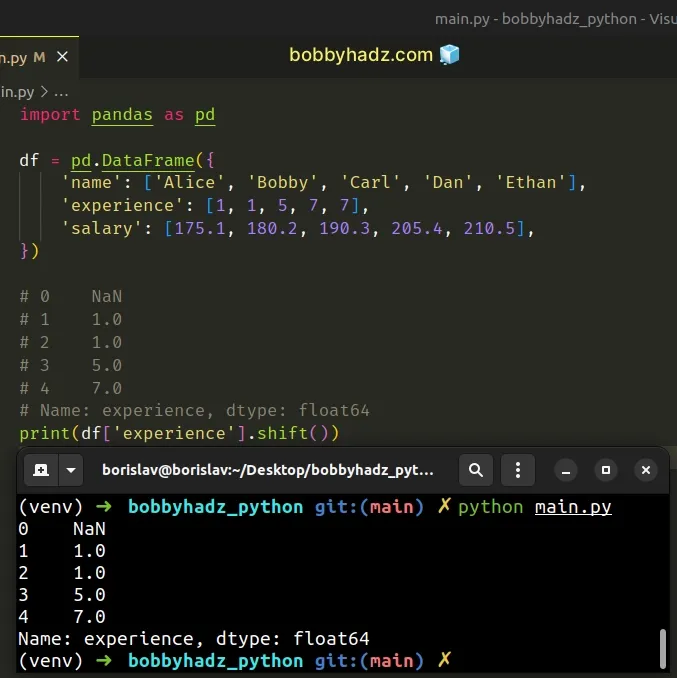
We used the
DataFrame.eq()
method to compare the "experience" column to the result of calling shift()
on the column.
df['prev_equal'] = df['experience'].eq(df['experience'].shift()) # name experience salary prev_equal # 0 Alice 1 175.1 False # 1 Bobby 1 180.2 True # 2 Carl 5 190.3 False # 3 Dan 7 205.4 False # 4 Ethan 7 210.5 True print(df)
The prev_equal column contains True values in the cases where the value in
the previous row is equal to the value in the current row.
# Comparing Previous row values in a Pandas DataFrame using equality operator
You can also manually use the equality operator to achieve the same result.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan', 'Ethan'], 'experience': [1, 1, 5, 7, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4, 210.5], }) df['prev_equal'] = df['experience'] == df['experience'].shift() # name experience salary prev_equal # 0 Alice 1 175.1 False # 1 Bobby 1 180.2 True # 2 Carl 5 190.3 False # 3 Dan 7 205.4 False # 4 Ethan 7 210.5 True print(df)
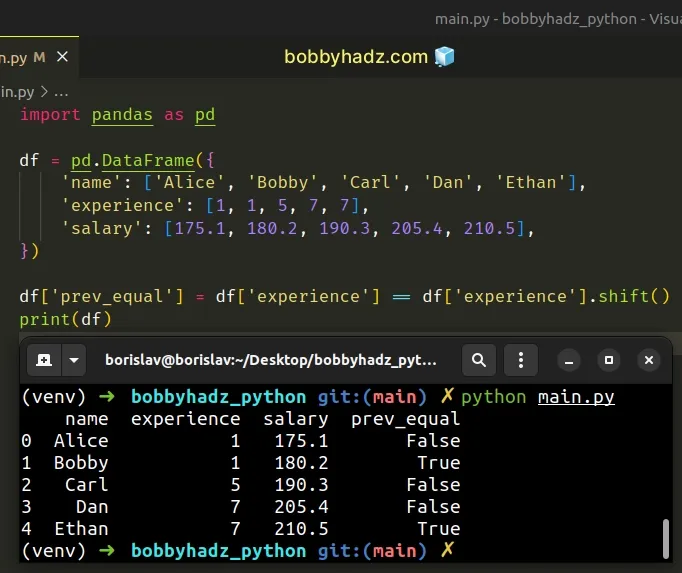
The code sample is equivalent to the one from the previous subheading but uses
the equality == operator instead of the DataFrame.eq() method.
Which approach you pick is a matter of personal preference, but if you need to
optimize for performance, use the eq() method.
# Comparing Previous row values in a Pandas DataFrame using numpy
You can also use the
numpy.concatenate()
method to compare previous row values to the current row in a DataFrame.
First, make sure you have the numpy module installed.
pip install numpy # or with pip3 pip3 install numpy
Now, import and use the module as follows.
import pandas as pd import numpy as np df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan', 'Ethan'], 'experience': [1, 1, 5, 7, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4, 210.5], }) experience_values = df['experience'].values df['prev_equal'] = np.concatenate( ([False], experience_values[1:] == experience_values[:-1]) ) # name experience salary prev_equal # 0 Alice 1 175.1 False # 1 Bobby 1 180.2 True # 2 Carl 5 190.3 False # 3 Dan 7 205.4 False # 4 Ethan 7 210.5 True print(df)
The numpy.concatenate() method joins a sequence of arrays along an existing axis.
# Comparing Next row values in a Pandas DataFrame
You can also use the DataFrame.shift() method to compare the next row values
to the current row values in a DataFrame.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan', 'Ethan'], 'experience': [1, 1, 5, 7, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4, 210.5], }) df['next_equal'] = df['experience'] == df['experience'].shift(-1) # name experience salary next_equal # 0 Alice 1 175.1 True # 1 Bobby 1 180.2 False # 2 Carl 5 190.3 False # 3 Dan 7 205.4 True # 4 Ethan 7 210.5 False print(df)
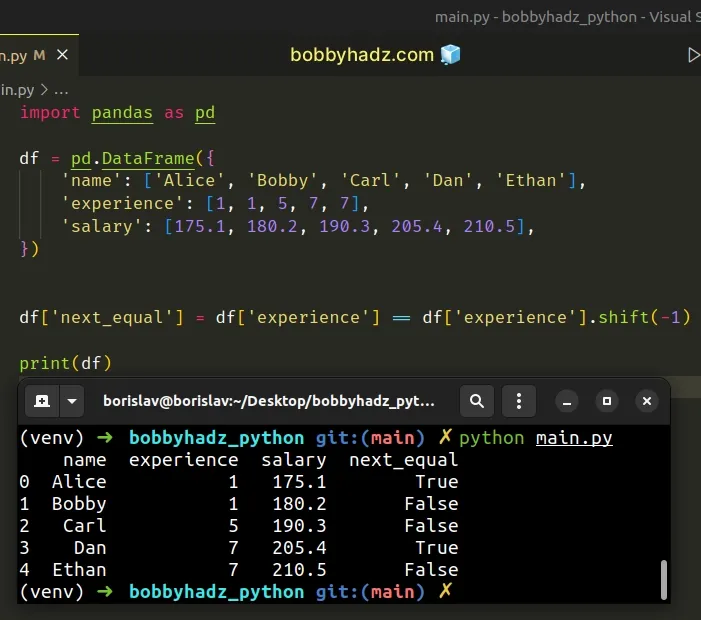
We used the DataFrame.shift() method to shift the experience column -1
period.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan', 'Ethan'], 'experience': [1, 1, 5, 7, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4, 210.5], }) df['next_experience'] = df['experience'].shift(-1) # name experience salary next_experience # 0 Alice 1 175.1 1.0 # 1 Bobby 1 180.2 5.0 # 2 Carl 5 190.3 7.0 # 3 Dan 7 205.4 7.0 # 4 Ethan 7 210.5 NaN print(df)
The previous code sample uses the equality == operator to check if the next
row value is equal to the current row value, however, you can also use the
DataFrame.eq() method.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan', 'Ethan'], 'experience': [1, 1, 5, 7, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4, 210.5], }) df['next_equal'] = df['experience'].eq(df['experience'].shift(-1)) # name experience salary next_equal # 0 Alice 1 175.1 True # 1 Bobby 1 180.2 False # 2 Carl 5 190.3 False # 3 Dan 7 205.4 True # 4 Ethan 7 210.5 False print(df)
This code sample is equivalent to the previous one, however, it uses the
DataFrame.eq() method which is a bit more performant.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Cannot perform 'rand_' with a dtyped [int64] array and scalar of type [bool]
- Pandas ValueError: Cannot index with multidimensional key
- ValueError: Grouper for 'X' not 1-dimensional [Solved]
- Cannot subset columns with tuple with more than one element
- Pandas: Get Nth row or every Nth row in a DataFrame
- Pandas: Describe not showing all columns in DataFrame [Fix]
- Pandas: Convert entire DataFrame to numeric (int or float)
- Pandas: Select Rows between two values in DataFrame
- Pandas: How to Filter a DataFrame by value counts
- Pandas: Convert a DataFrame to a List of Dictionaries
- Pandas: GroupBy columns with NaN (missing) values
- Pandas: Split a Column of Lists into Multiple Columns
- Matplotlib: No artists with labels found to put in legend
- All the input arrays must have same number of dimensions
- ValueError: Index contains duplicate entries, cannot reshape
- Export a Pandas DataFrame to Excel without the Index
- How to Split a Pandas DataFrame into Chunks

