Pandas: Convert a DataFrame to a List of Dictionaries
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- Pandas: Convert a DataFrame to a List of Dictionaries
- Including the index value in each dictionary in the list
- Pandas: Convert a DataFrame to a List of Dictionaries using values()
- Only converting a specific column of the DataFrame to a list of dictionaries
# Pandas: Convert a DataFrame to a List of Dictionaries
To convert a Pandas DataFrame to a list of dictionaries:
- Call the
DataFrame.to_dict()method on theDataFrame. - Set the
orientargument to"records"when callingto_dict(). - The
to_dict()method will convert theDataFrameto a list of dictionaries.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'experience': [1, 3, 5, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) list_of_dicts = df.to_dict('records') # [{'name': 'Alice', 'experience': 1, 'salary': 175.1}, {'name': 'Bobby', 'experience': 3, 'salary': 180.2}, {'name': 'Carl', 'experience': 5, 'salary': 190.3}, {'name': 'Dan', 'experience': 7, 'salary': 205.4}] print(list_of_dicts)
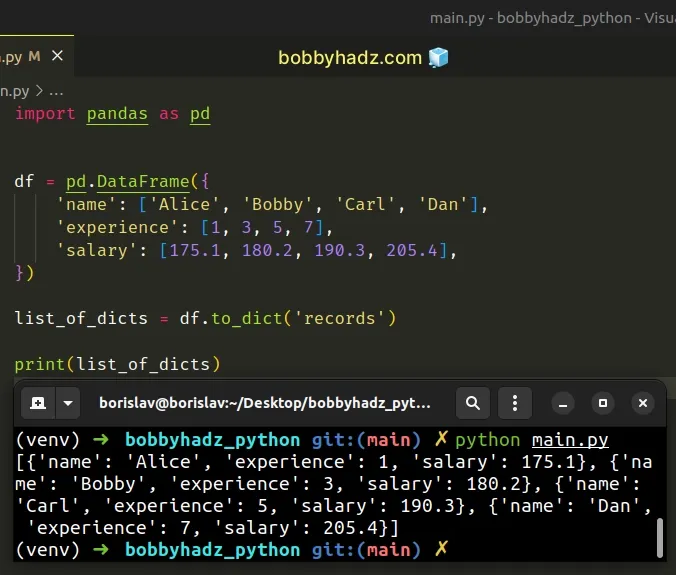
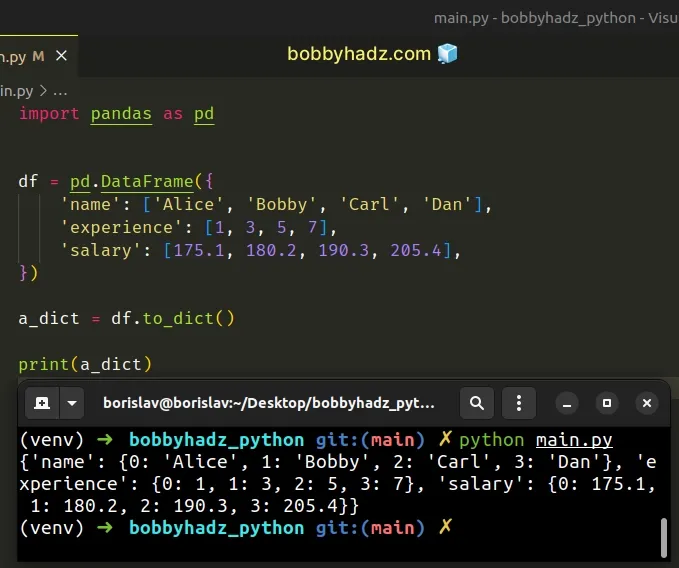
By default, the
DataFrame.to_dict()
method converts the DataFrame to a dictionary.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'experience': [1, 3, 5, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) a_dict = df.to_dict() # {'name': {0: 'Alice', 1: 'Bobby', 2: 'Carl', 3: 'Dan'}, 'experience': {0: 1, 1: 3, 2: 5, 3: 7}, 'salary': {0: 175.1, 1: 180.2, 2: 190.3, 3: 205.4}} print(a_dict)
However, when the orient argument is set to "records", the to_dict method
converts the DataFrame to a list of dictionaries.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'experience': [1, 3, 5, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) list_of_dicts = df.to_dict('records') print(list_of_dicts) print(type(list_of_dicts)) print(type(list_of_dicts[0]))
Running the code sample produces the following output.
[{'name': 'Alice', 'experience': 1, 'salary': 175.1}, {'name': 'Bobby', 'experience': 3, 'salary': 180.2}, {'name': 'Carl', 'experience': 5, 'salary': 190.3}, {'name': 'Dan', 'experience': 7, 'salary': 205.4}] <class 'list'> <class 'dict'>
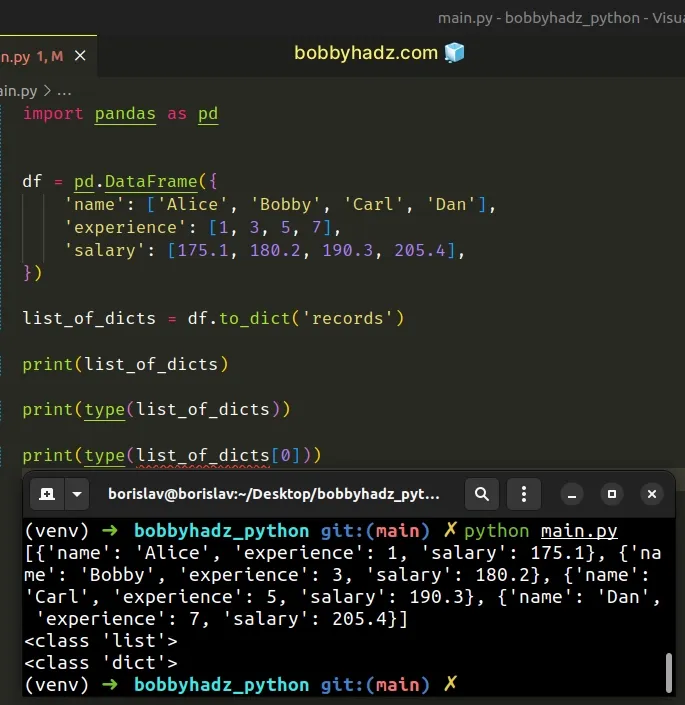
The type class returns the type of an object.
# Including the index value in each dictionary in the list
If you need to include the index value of each row in the dictionaries, call
the DataFrame.reset_index()
method before calling to_dict().
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'experience': [1, 3, 5, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) list_of_dicts = df.reset_index().to_dict('records') # [{'index': 0, 'name': 'Alice', 'experience': 1, 'salary': 175.1}, {'index': 1, 'name': 'Bobby', 'experience': 3, 'salary': 180.2}, {'index': 2, 'name': 'Carl', 'experience': 5, 'salary': 190.3}, {'index': 3, 'name': 'Dan', 'experience': 7, 'salary': 205.4}] print(list_of_dicts)
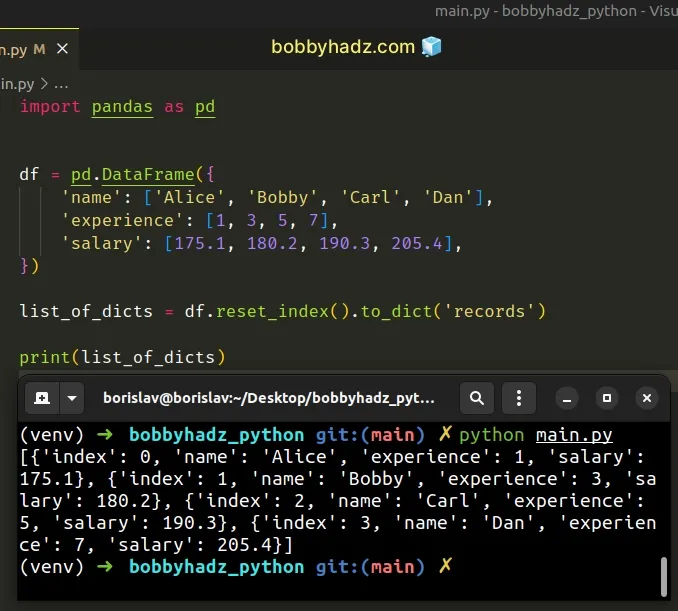
If you want to have the indices as dictionary keys, set the orient argument to
"index" when calling to_dict().
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'experience': [1, 3, 5, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) list_of_dicts = df.to_dict('index') # {0: {'name': 'Alice', 'experience': 1, 'salary': 175.1}, 1: {'name': 'Bobby', 'experience': 3, 'salary': 180.2}, 2: {'name': 'Carl', 'experience': 5, 'salary': 190.3}, 3: {'name': 'Dan', 'experience': 7, 'salary': 205.4}} print(list_of_dicts)
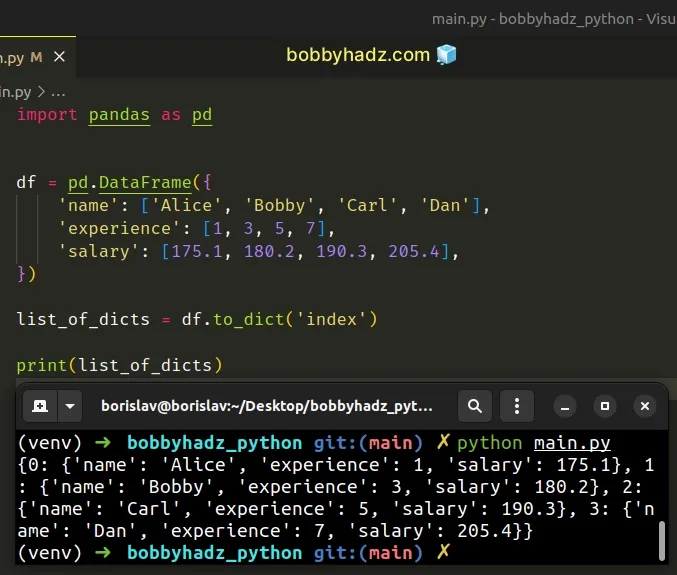
When the orient argument is set to "index", the to_dict() method returns a
nested dictionary where the indices are the dictionary's keys.
# Pandas: Convert a DataFrame to a List of Dictionaries using values()
You can also use the
dict.values() method after
transposing the DataFrame to
convert it to a list of dictionaries.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'experience': [1, 3, 5, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) list_of_dicts = list(df.T.to_dict().values()) # [{'name': 'Alice', 'experience': 1, 'salary': 175.1}, {'name': 'Bobby', 'experience': 3, 'salary': 180.2}, {'name': 'Carl', 'experience': 5, 'salary': 190.3}, {'name': 'Dan', 'experience': 7, 'salary': 205.4}] print(list_of_dicts)
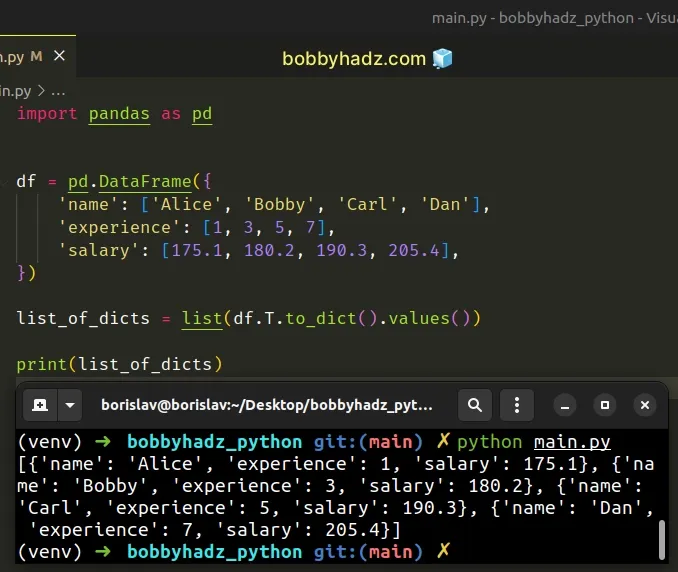
The DataFrame.T property is an accessor for the
DataFrame.transpose method.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'experience': [1, 3, 5, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) # 0 1 2 3 # name Alice Bobby Carl Dan # experience 1 3 5 7 # salary 175.1 180.2 190.3 205.4 print(df.T)
The transpose() method writes the DataFrame rows as columns and vice versa.
Once you convert the transposed DataFrame to a dictionary with to_dict(),
call the values() method on the result.
list_of_dicts = list(df.T.to_dict().values())
The dict.values() method returns a view of the dictionary's values.
The method returns a view object, so we had to use the list class to convert the result to a list.
# Only converting a specific column of the DataFrame to a list of dictionaries
If you only need to convert a specific column of the DataFrame to a list of
dictionaries, use two sets of square brackets to select the column and call the
to_dict() method on the result.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'experience': [1, 3, 5, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) list_of_dicts = df[['experience']].to_dict('records') # [{'experience': 1}, {'experience': 3}, {'experience': 5}, {'experience': 7}] print(list_of_dicts)

Notice that we used two sets of square brackets [[]] when selecting the
"experience" column.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bobby', 'Carl', 'Dan'], 'experience': [1, 3, 5, 7], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4], }) # experience # 0 1 # 1 3 # 2 5 # 3 7 print(df[['experience']])
The last step is to call the to_dict() method on the result, setting the
orient argument to "records".
list_of_dicts = df[['experience']].to_dict('records')
When the orient argument is set to "records", the to_dict method returns a
list of dictionaries containing the results.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Convert Epoch to Datetime in a Pandas DataFrame
- Calculate the Average for each Row in a Pandas DataFrame
- How to drop all Rows in a Pandas DataFrame in Python
- Pandas: Drop columns if Name contains a given String
- Pandas: How to get the Max and Min Dates in a DataFrame
- Pandas SpecificationError: nested renamer is not supported
- Pandas: Convert a DataFrame to a List of Dictionaries
- Pandas: GroupBy columns with NaN (missing) values
- Panda: Using fillna() with specific columns in a DataFrame
- NumPy: Get the indices of the N largest values in an Array
- First argument must be an iterable of pandas objects [Fix]
- ValueError: Index contains duplicate entries, cannot reshape

