How to Split a Pandas DataFrame into Chunks
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- How to Split a Pandas DataFrame into Chunks
- Split a Pandas DataFrame into chunks every N rows
- Split a Pandas DataFrame into chunks using DataFrame.iloc
- Split a Pandas DataFrame every N rows using a list comprehension
# How to Split a Pandas DataFrame into Chunks
Use the numpy.array_split() method to split a DataFrame into chunks.
The method takes the DataFrame and the number of chunks as parameters and
splits the DataFrame.
First, make sure that
you've installed the numpy module.
pip install numpy pandas # or with pip3 pip3 install numpy pandas
Now, import and use the module as follows.
import pandas as pd import numpy as np df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F'], 'experience': [1, 1, 5, 7, 7, 10], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4, 210.5, 225.3], }) list_of_dataframes = np.array_split(df, 2) print(list_of_dataframes)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
[ name experience salary 0 A 1 175.1 1 B 1 180.2 2 C 5 190.3, name experience salary 3 D 7 205.4 4 E 7 210.5 5 F 10 225.3]
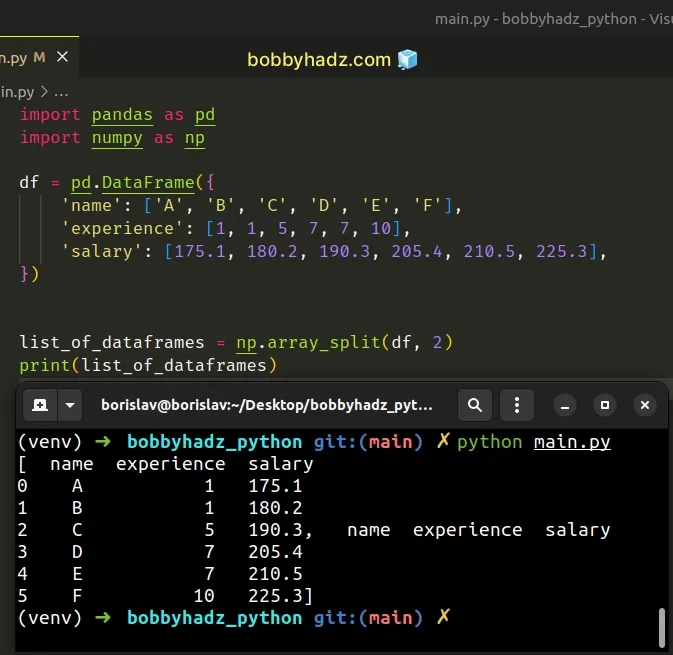
The
numpy.array_split()
method splits an array (or a DataFrame) into multiple sub-arrays.
import numpy as np list_of_dataframes = np.array_split(df, 2)
The first argument we passed to the method is the DataFrame and the second is
the number of chunks we want to get in the resulting list.
The method returns a list of DataFrames, so you can access a specific
DataFrame at an index.
import pandas as pd import numpy as np df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F'], 'experience': [1, 1, 5, 7, 7, 10], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4, 210.5, 225.3], }) list_of_dataframes = np.array_split(df, 2) # name experience salary # 0 A 1 175.1 # 1 B 1 180.2 # 2 C 5 190.3 print(list_of_dataframes[0])
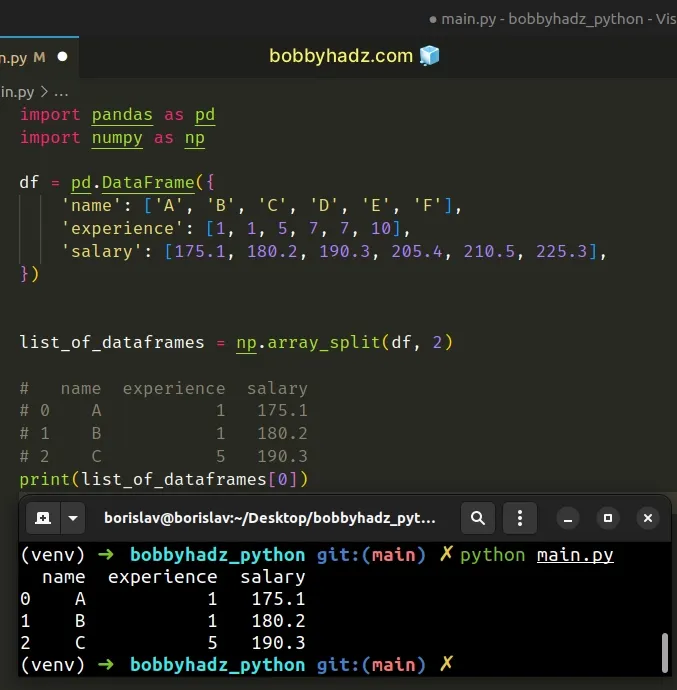
The code sample accesses the first DataFrame (index 0).
You can also use a for loop to iterate over
the list of DataFrame chunks.
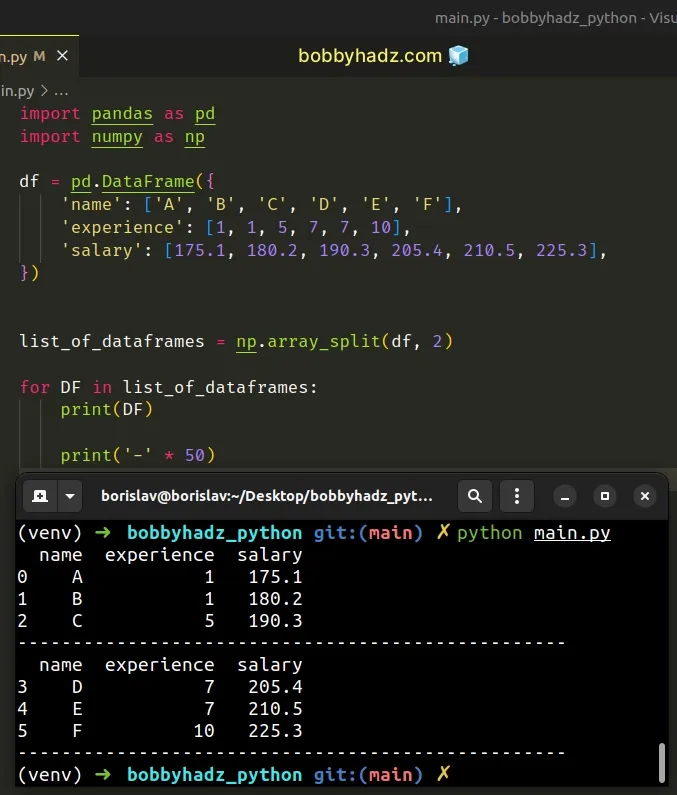
import pandas as pd import numpy as np df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F'], 'experience': [1, 1, 5, 7, 7, 10], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4, 210.5, 225.3], }) list_of_dataframes = np.array_split(df, 2) for DF in list_of_dataframes: print(DF) print('-' * 50)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
name experience salary 0 A 1 175.1 1 B 1 180.2 2 C 5 190.3 -------------------------------------------------- name experience salary 3 D 7 205.4 4 E 7 210.5 5 F 10 225.3 --------------------------------------------------
If you need to split the DataFrame into N chunks, make sure to pass N as the
second argument to numpy.array_split().
import pandas as pd import numpy as np df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F'], 'experience': [1, 1, 5, 7, 7, 10], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4, 210.5, 225.3], }) list_of_dataframes = np.array_split(df, 3) print(list_of_dataframes)
The code sample splits the DataFrame into 3 chunks.
Running the code sample produces the following output.
[ name experience salary 0 A 1 175.1 1 B 1 180.2, name experience salary 2 C 5 190.3 3 D 7 205.4, name experience salary 4 E 7 210.5 5 F 10 225.3]
# Split a Pandas DataFrame into chunks every N rows
If you need to split a DataFrame every N rows, use the following reusable
function.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F'], 'experience': [1, 1, 5, 7, 7, 10], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4, 210.5, 225.3], }) def split_every_n_rows(dataframe, chunk_size=2): chunks = [] num_chunks = len(dataframe) // chunk_size + 1 for index in range(num_chunks): chunks.append(dataframe[index * chunk_size:(index+1) * chunk_size]) return chunks list_of_dataframes = split_every_n_rows(df, 2) print(list_of_dataframes)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
[ name experience salary 0 A 1 175.1 1 B 1 180.2, name experience salary 2 C 5 190.3 3 D 7 205.4, name experience salary 4 E 7 210.5 5 F 10 225.3]
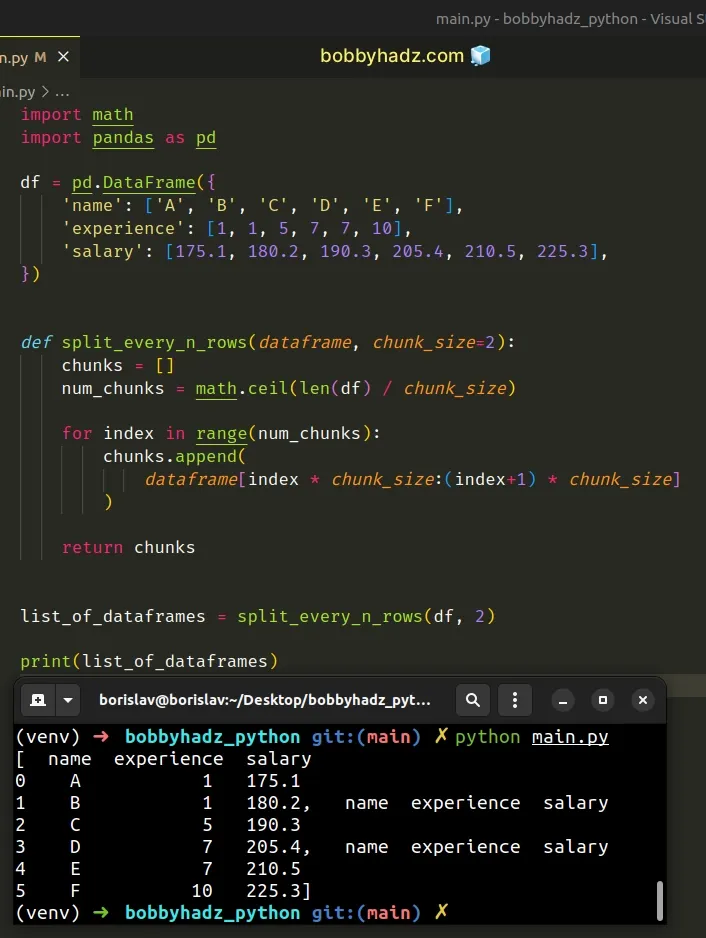
The function splits the DataFrame every chunk_size rows (by default 2 rows).
The function returns a list of DataFrames.
You can access the list at a specific index to get a specific DataFrame chunk
or you can iterate over the list to access each chunk.
# Split a Pandas DataFrame into chunks using DataFrame.iloc
You can also use the DataFrame.iloc
integer-based indexer to split a Pandas DataFrame into chunks.
import math import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F'], 'experience': [1, 1, 5, 7, 7, 10], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4, 210.5, 225.3], }) def split_every_n_rows(dataframe, chunk_size=2): chunks = [] num_chunks = math.ceil(int(dataframe.shape[0] / chunk_size)) for index in range(0, dataframe.shape[0], num_chunks): chunks.append( dataframe.iloc[index:index + chunk_size] ) return chunks list_of_dataframes = split_every_n_rows(df, 2) print(list_of_dataframes)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
[ name experience salary 0 A 1 175.1 1 B 1 180.2, name experience salary 3 D 7 205.4 4 E 7 210.5]
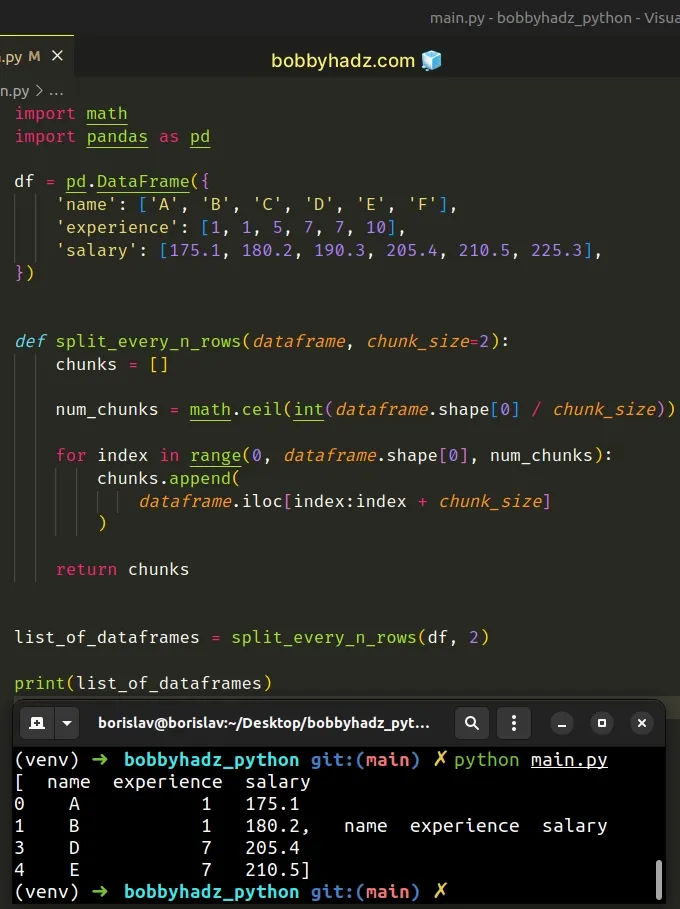
The function takes a DataFrame and the number of chunks as parameters and
returns a list containing the DataFrame chunks.
By default, the function splits the DataFrame into 2 chunks, however, you can
set the chunk_size argument to any other value.
# Split a Pandas DataFrame every N rows using a list comprehension
Here is a reusable function that splits a Pandas DataFrame every N rows using
a list comprehension.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F'], 'experience': [1, 1, 5, 7, 7, 10], 'salary': [175.1, 180.2, 190.3, 205.4, 210.5, 225.3], }) def split_every_n_rows(dataframe, chunk_size=2): return [ dataframe[index:index + chunk_size] for index in range(0, df.shape[0], chunk_size) ] list_of_dataframes = split_every_n_rows(df, 2) print(list_of_dataframes)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
[ name experience salary 0 A 1 175.1 1 B 1 180.2, name experience salary 2 C 5 190.3 3 D 7 205.4, name experience salary 4 E 7 210.5 5 F 10 225.3]
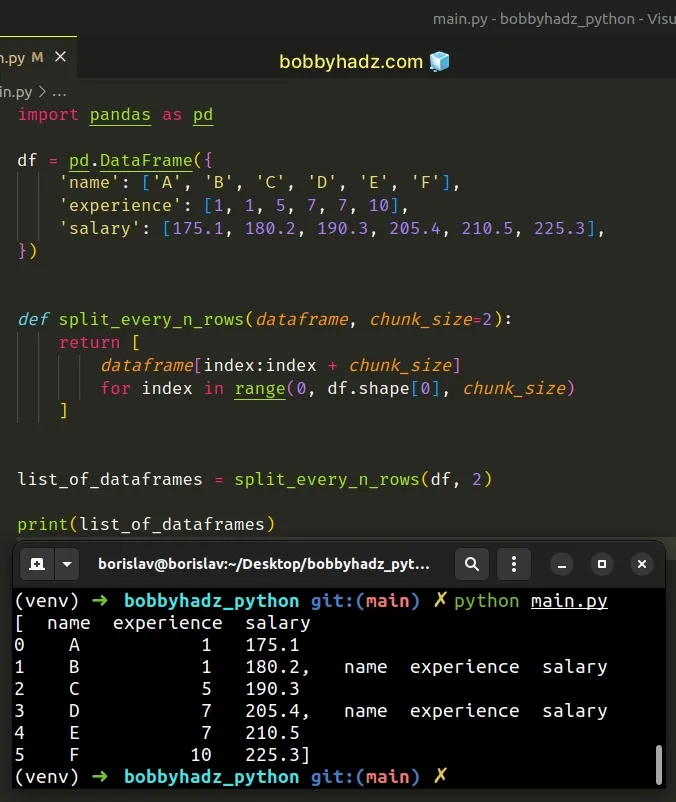
The function splits the DataFrame every N rows using a list comprehension.
It iterates over a range() object with a step
of chunk_size and returns a list containing the DataFrame chunks.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

