How to Delete a JSON object from a List in Python
Last updated: Apr 9, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Delete a JSON object from a list in Python
- Deleting a JSON object from an array outside a file
- JSON.load() vs JSON.loads()
- Use the break statement if you only want to remove 1 dictionary
- Delete a JSON object from a list using a list comprehension
- Delete a JSON object from a list using filter()
# Delete a JSON object from a list in Python
To delete a JSON object from a list:
- Parse the JSON object into a Python list of dictionaries.
- Use the
enumerate()function to iterate over the list. - Check if each dictionary is the one you want to remove and use the
pop()method to remove the matching dict.
import json file_name = 'example.json' with open(file_name, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f: my_list = json.load(f) # [{'id': 1, 'name': 'Alice'}, # {'id': 2, 'name': 'Bob'}, # {'id': 3, 'name': 'Carl'}] print(my_list) for idx, obj in enumerate(my_list): if obj['id'] == 2: my_list.pop(idx) new_file_name = 'new-file.json' with open(new_file_name, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f: f.write(json.dumps(my_list, indent=2))
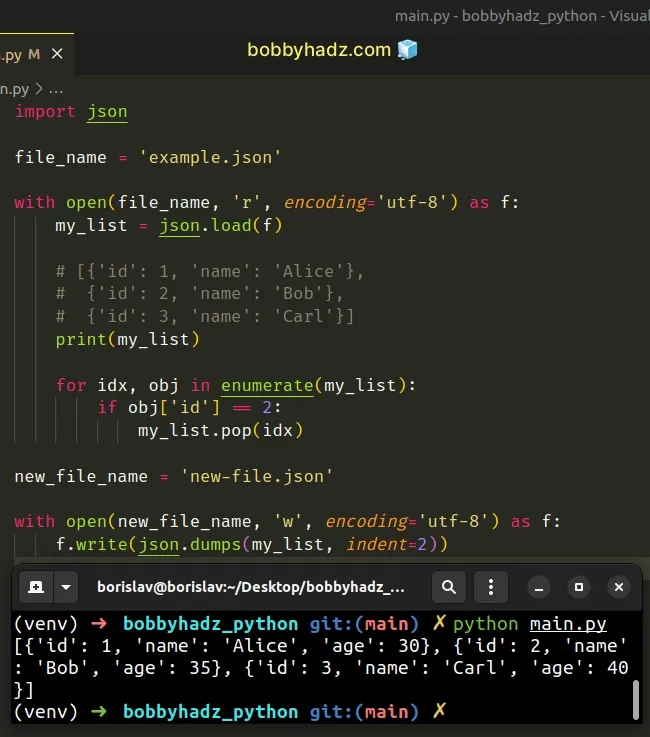
The code sample shows how to delete a JSON object from an array of objects in a file.
The code assumes that you have an example.json file with the following
contents.
[ {"id": 1, "name": "Alice", "age": 30}, {"id": 2, "name": "Bob", "age": 35}, {"id": 3, "name": "Carl", "age": 40} ]
We used an if statement to check if each object has an id property with a
value of 2.
If the condition is met, we remove the object from the list and write the result to another file.
The file with the name new-file.json has the following contents after the
operation.
[ { "id": 1, "name": "Alice", "age": 30 }, { "id": 3, "name": "Carl", "age": 40 } ]
Notice that the JSON object with an id of 2 got removed.
# Deleting a JSON object from an array outside a file
You can use the same approach to delete a JSON object from an array of objects outside of a file.
import json my_json = '[{"id": 1, "name": "Alice"}, {"id": 2, "name": "Bob"}]' my_list = json.loads(my_json) for idx, dictionary in enumerate(my_list): if dictionary['id'] == 2: my_list.pop(idx) # 👇️ [{'id': 1, 'name': 'Alice'}] print(my_list) json_again = json.dumps(my_list) print(json_again) # 👉️ '[{"id": 1, "name": "Alice"}]'
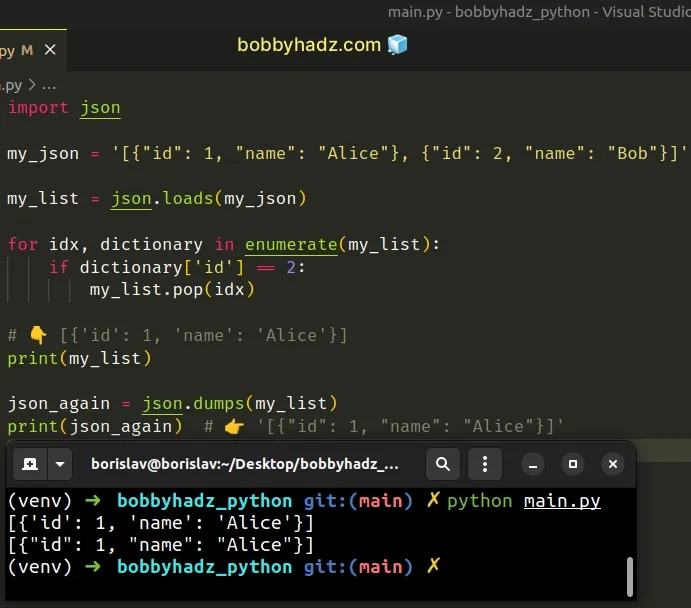
If your JSON is located in a file, use the json.load() method to parse the
json.
# JSON.load() vs JSON.loads()
The json.load() method is used to deserialize a file to a Python object, whereas the json.loads() method is used to deserialize a JSON string to a Python object.
The next step is to iterate over the list and check if a key in each dictionary has a specific value.
import json file_name = 'example.json' with open(file_name, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f: my_list = json.load(f) # 👇️ [{'id': 1, 'name': 'Alice'}, {'id': 2, 'name': 'Bob'}, {'id': 3, 'name': 'Carl'}] print(my_list) for idx, obj in enumerate(my_list): if obj['id'] == 2: my_list.pop(idx) new_file_name = 'new-file.json' with open(new_file_name, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f: f.write(json.dumps(my_list, indent=2))
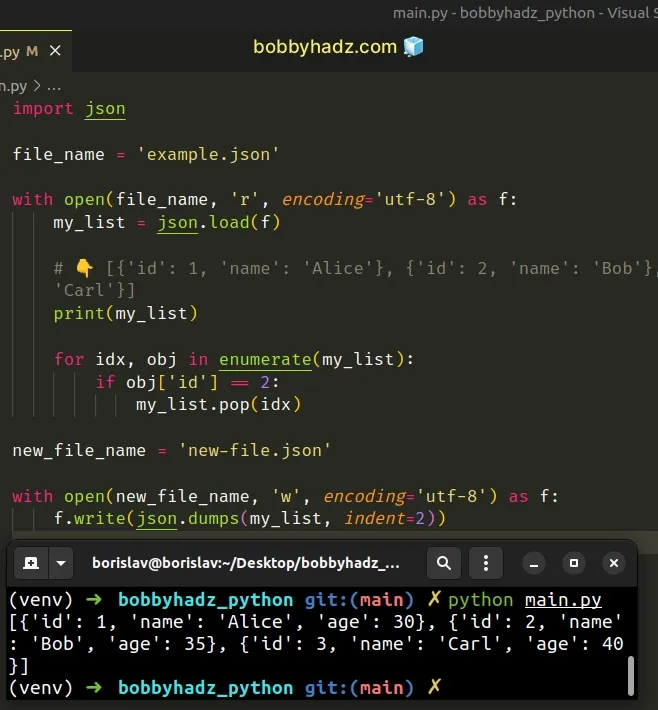
Once we find the matching dictionary, we have to use the list.pop() method to
remove it from the list.
The list.pop method removes the item at the given position in the list and
returns it.
# Use the break statement if you only want to remove 1 dictionary
You can also add a break statement if you only want to remove 1 dictionary
from the list.
for idx, obj in enumerate(my_list): if obj['id'] == 2: my_list.pop(idx) break
This saves you some time in needless iterations if the dictionary is towards the beginning of the list.
# Writing the result to a new file
The last step is to open a new file, serialize the list to json and write it
to the file.
new_file_name = 'new-file.json' with open(new_file_name, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f: f.write(json.dumps(my_list, indent=2))
The file called new-file.json reflects the changes and the original file
remains unchanged.
[ { "id": 1, "name": "Alice", "age": 30 }, { "id": 3, "name": "Carl", "age": 40 } ]
# Delete a JSON object from a list using a list comprehension
You can also use a list comprehension to delete a JSON object from a list.
import json my_json = '[{"id": 1, "name": "Alice"}, {"id": 2, "name": "Bob"}]' my_list = json.loads(my_json) # [{'id': 1, 'name': 'Alice'}, {'id': 2, 'name': 'Bob'}] print(my_list) new_list = [dictionary for dictionary in my_list if dictionary['name'] != 'Bob'] # [{'id': 1, 'name': 'Alice'}] print(new_list)
We used the JSON.loads() method to convert the JSON array to a Python list of
dictionaries and use a list comprehension to iterate over the list.
On each iteration, we check if the current dictionary doesn't have a name key
with a specific value and return the result.
The new list only contains the dictionaries that meet the condition.
# Delete a JSON object from a list using filter()
You can also use the filter() function to delete a JSON object from a list.
import json my_json = '[{"id": 1, "name": "Alice"}, {"id": 2, "name": "Bob"}]' my_list = json.loads(my_json) # [{'id': 1, 'name': 'Alice'}, {'id': 2, 'name': 'Bob'}] print(my_list) new_list = list( filter(lambda x: x['name'] != 'Bob', my_list) ) # [{'id': 1, 'name': 'Alice'}] print(new_list)
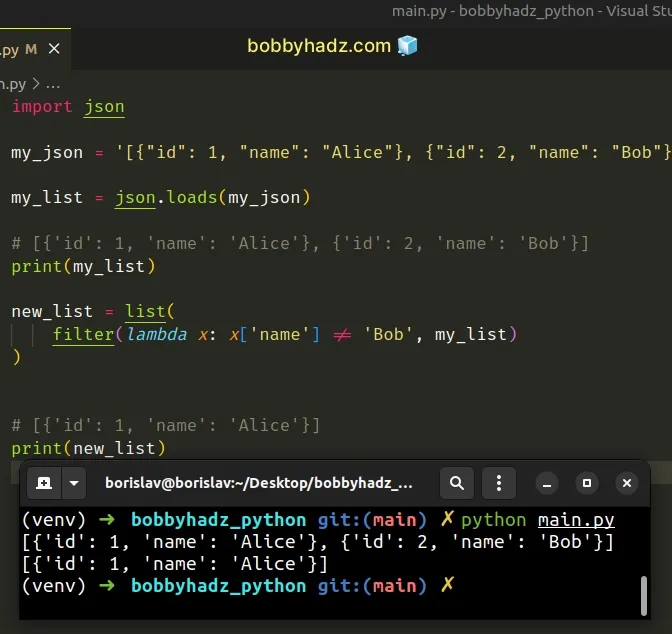
The filter() function takes a function and an iterable as arguments and constructs an iterator from the elements of the iterable for which the function returns a truthy value.
The lambda function we passed to filter() gets called with each dictionary of
the list.
The lambda checks if the name key in each dictionary doesn't have a specific
value.
The filter object only contains the dictionaries for which the condition is
met.
The last step is to use the list() class to
convert the filter object to a list.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

