-215:Assertion failed !_src.empty() in function 'cvtColor'
Last updated: Apr 13, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# -215:Assertion failed !_src.empty() in function 'cvtColor'
The Python OpenCV error "(-215:Assertion failed) !_src.empty() in function
'cvtColor'" occurs when the image you passed to cv2.cvtColor() didn't load
correctly and was empty.
Make sure the image path you passed to cv2.imread() exists and the image at
the path is not empty.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
import cv2 img = cv2.imread('thumbnail123.webp') print(img) # 👉️ None img_hsv = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV) # ⛔️ cv2.error: OpenCV(4.8.0) /io/opencv/modules/imgproc/src/color.cpp:182: error: (-215:Assertion failed) !_src.empty() in function 'cvtColor' print(img_hsv)
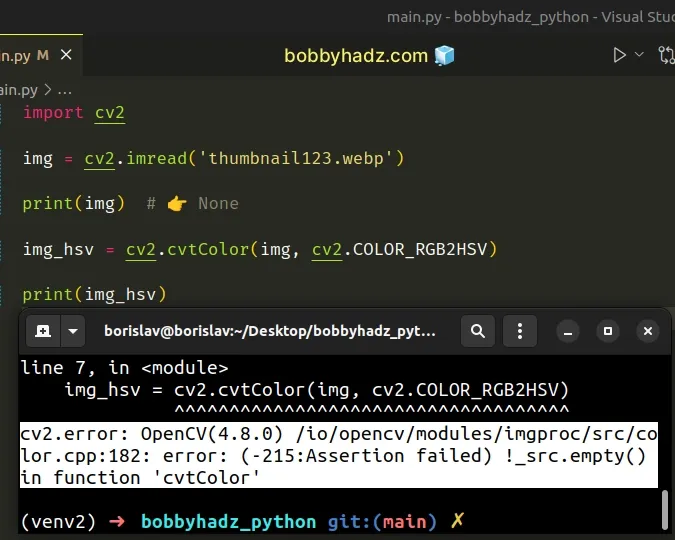
The error in the example is caused because the path we passed to cv2.imread()
doesn't point to an image that exists and is not empty.
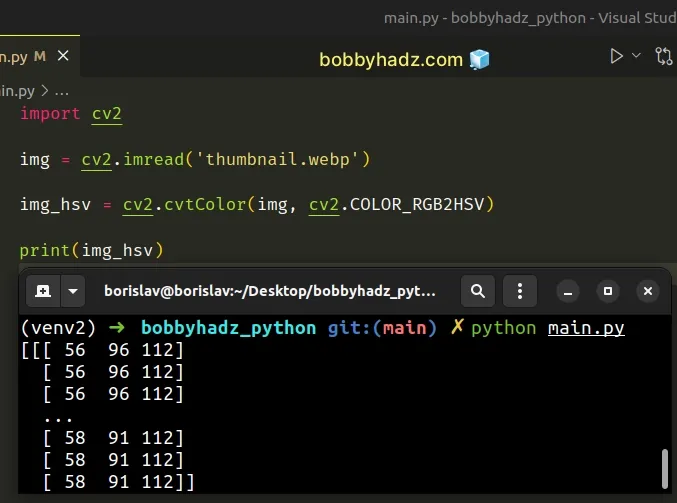
If I replace the path with this of a valid image that exists, everything works as expected.
import cv2 img = cv2.imread('thumbnail.webp') img_hsv = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV) print(img_hsv)
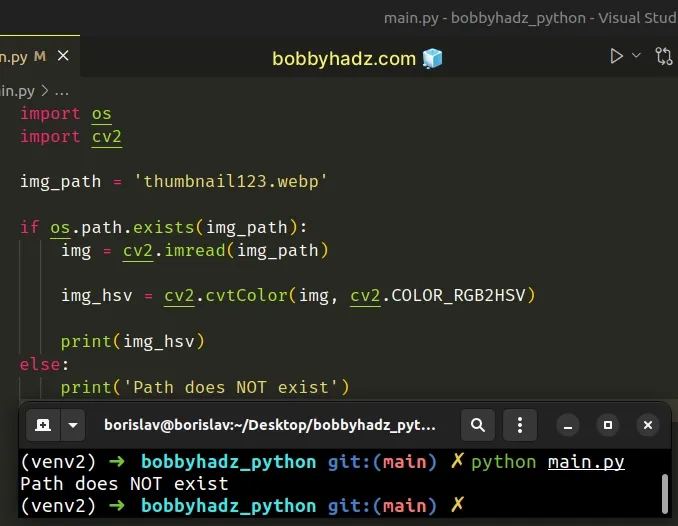
If you need to check if the specified path exists, use the os.path.exists() method.
import os import cv2 img_path = 'thumbnail123.webp' if os.path.exists(img_path): img = cv2.imread(img_path) img_hsv = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV) print(img_hsv) else: print('Path does NOT exist', img_path)
If you're running into issues when specifying the path in the call to
csv.imread(), check out the following article:
# The !_src.empty() error message means that the image frame is empty
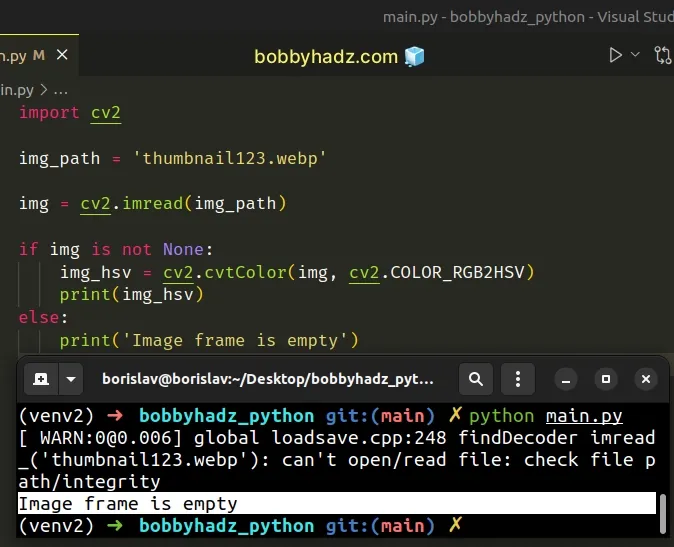
The !_src.empty() error message means that the image frame is empty.
Therefore, you can't pass an empty frame to the cv2.cvtColor() method.
You can use an if statement to
check if the image frame is not None.
import cv2 img_path = 'thumbnail123.webp' img = cv2.imread(img_path) if img is not None: img_hsv = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV) print(img_hsv) else: print('Image frame is empty')
# Running into issues when reading a frame from a Webcam
If you're getting the error when reading a frame from a webcam, make sure the webcam is not being used by another program.
If your webcam is used by another program, the frame will likely be empty, resulting in the error.
If that didn't help and the error is caused when reading a frame from a webcam, make sure your webcam drivers are up-to-date.
If you're grabbing the image data from a camera, make sure the camera connection hasn't failed and the camera is configured correctly.
# Try to use a raw string for the path
If that didn't help, try to specify the path using a raw string.
For example, on Windows, it might look something like this.
import cv2 img_path_windows = r'C:\Users\YourUser\Desktop\your-image.png' print(img_path_windows)
Strings that are prefixed with r are called
raw strings
and treat backslashes as literal characters.
r didn't help, make sure the image's extension is specified in the file path and is correct.The path to the image should also not contain special characters or umlauts.
Also, if you're only specifying an image name when calling cv2.imread() make
sure your terminal is located in the same directory as the image and the Python
script.
If you're calling the cv2.VideoCapture() method, pass it 0 on Windows or
-1 on Linux as a parameter.
For example, on Windows, use this:
import cv2 # ... # ✅ Correct for Windows cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
If you are on Linux, use this:
import cv2 # ... # ✅ Correct for Linux cap = cv2.VideoCapture(-1)
# Try using skimage.io.imread() instead of cv2.imread()
Another thing you can try is to use the skimage.io.imread() method instead of
cv2.imread().
First, install the scikit-image module
by running the following command.
pip install scikit-image pip3 install scikit-image
Now, import and use the module as follows.
import cv2 from skimage import io img_path = 'thumbnail.webp' img = io.imread(img_path) img_hsv = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV) print(img_hsv)
You can pass the img object that is returned from skimage.io.imread() to the
cv2.cvtColor() method.
# Make sure you aren't running into permission issues
Make sure you aren't running into permission issues and the image file is accessible from your current user.
For example, you might've blocked your camera from accessing applications.
If you get the message: Warning: can't open/read file: check file path/integrity, click on the link and follow the instructions.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Using f-string for conditional formatting in Python
- Check if all/any elements in List meet condition in Python
- ValueError: Circular reference detected in Python [Solved]
- Process finished with exit code 139 (interrupted by signal 11: SIGSEGV)
- Python argparse: unrecognized arguments error [Solved]
- How to exit an if statement in Python [5 Ways]
- TypeError: Can not infer schema for type: <class 'float'>
- OpenCV TypeError: Expected cv::UMat for argument [Solved]
- OMP: Error #15 Initializing libiomp5md.dll, but found mk2iomp5md.dll already initialized

