How to convert a Tuple to JSON in Python
Last updated: Apr 9, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Convert a Tuple to JSON in Python
Use the json.dumps() method to convert a tuple to JSON.
The json.dumps() method will convert the Python tuple to a JSON array and
will return the result.
import json my_tuple = ('bobby', 'hadz', 'com') json_str = json.dumps(my_tuple) print(json_str) # 👉️ '["bobby", "hadz", "com"]' print(type(json_str)) # 👉️ <class 'str'>
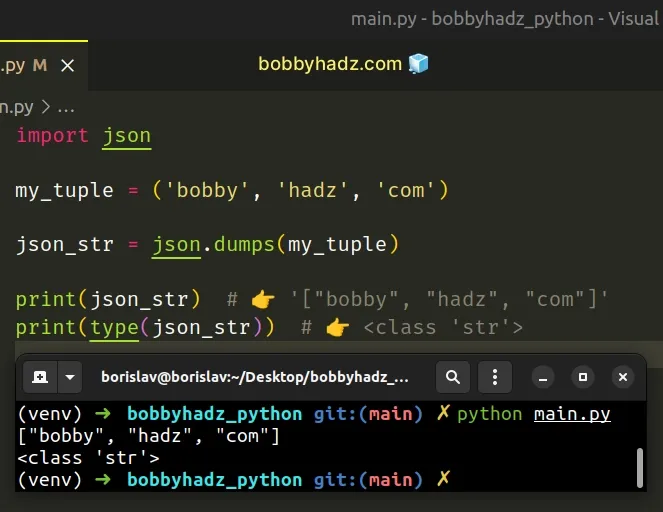
We used the json.dumps() method to convert a tuple to a JSON string.
The json.dumps() method converts a Python object to a JSON formatted string.
# Python tuples are JSON serializable
Python tuples are JSON serializable, just like lists or dictionaries.
The JSONEncoder class supports the following objects and types by default.
| Python | JSON |
|---|---|
| dict | object |
| list, tuple | array |
| str | string |
| int, float, int and float derived Enums | number |
| True | true |
| False | false |
| None | null |
The process of converting a tuple (or any other native Python object) to a JSON string is called serialization.
Whereas, the process of converting a JSON string to a native Python object is called deserialization.
# Parsing the JSON string returns a Python list
When you parse the JSON string into a native Python object, you get a list
back.
import json my_tuple = ('bobby', 'hadz', 'com') # ✅ convert tuple to JSON json_str = json.dumps(my_tuple) print(json_str) # 👉️ '["bobby", "hadz", "com"]' print(type(json_str)) # 👉️ <class 'str'> # -------------------------------- # ✅ parse JSON string to native Python object parsed = json.loads(json_str) print(parsed) # 👉️ ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com'] print(type(parsed)) # 👉️ <class 'list'> print(parsed[0]) # 👉️ bobby print(parsed[1]) # 👉️ hadz
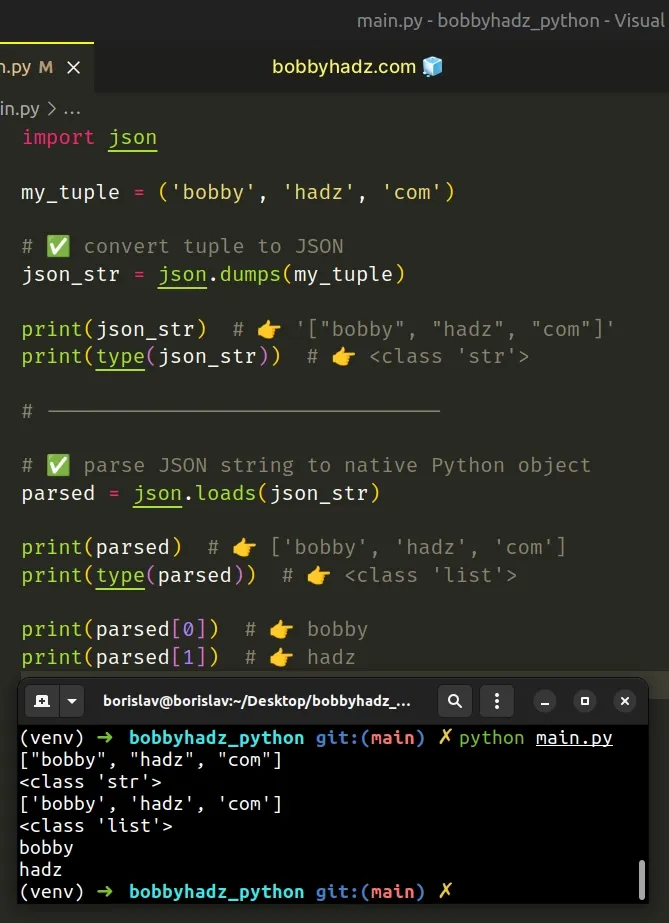
The json.loads() method parses a JSON string into a native Python object.
Notice that we got a list object after parsing the JSON string.
This is because both list and tuple objects get converted to a JSON array when serialized.
You can use the tuple() class to convert the list to a tuple after parsing the JSON string.
import json my_tuple = ('bobby', 'hadz', 'com') json_str = json.dumps(my_tuple) print(json_str) # 👉️ '["bobby", "hadz", "com"]' print(type(json_str)) # 👉️ <class 'str'> # -------------------------------- # 👇️ convert to tuple parsed = tuple(json.loads(json_str)) print(parsed) # 👉️ ('bobby', 'hadz', 'com') print(type(parsed)) # 👉️ <class 'tuple'> print(parsed[0]) # 👉️ bobby print(parsed[1]) # 👉️ hadz
The example uses the tuple() class to convert the list we got after parsing
the JSON string.
You can use bracket notation to access the tuple at a specific index after parsing the JSON.
Tuples are very similar to lists, but implement fewer built-in methods and are immutable (cannot be changed).
# Converting a mixed tuple to JSON
You can also use the json.dumps method to convert a tuple containing elements
of multiple types to JSON.
import json my_tuple = ('bobby', 1, 'hadz', 2, 'com') json_str = json.dumps(my_tuple) print(json_str) # 👉️ '["bobby", 1, "hadz", 2, "com"]' print(type(json_str)) # 👉️ <class 'str'>
However, you have to make sure that your tuple contains one of the supported types.
The JSONEncoder class supports the following objects and types by default.
| Python | JSON |
|---|---|
| dict | object |
| list, tuple | array |
| str | string |
| int, float, int and float derived Enums | number |
| True | true |
| False | false |
| None | null |
If your tuple stores values of a type that is not contained in the column on the left, the default JSONEncoder won't be able to convert the tuple to JSON.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

