How to convert Dataclass to JSON in Python [5 Ways]
Last updated: Apr 13, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- How to convert Dataclass to JSON in Python
- Converting a Dataclass to JSON with a custom JSONEncoder
- Convert a Dataclass to JSON with the dataclasses_json package
- Converting a dataclass object to a JSON string with the default argument
# How to convert Dataclass to JSON in Python
To convert a dataclass to JSON in Python:
- Use the
dataclasses.asdict()method to convert thedataclassto a dictionary. - Pass the dictionary to the
json.dumps()method.
import json from dataclasses import dataclass, asdict @dataclass class InventoryItem: name: str unit_price: float quantity_available: int = 0 item1 = InventoryItem('A', 100, 1) print(item1) print('-' * 50) to_json = json.dumps(asdict(item1)) print(to_json) print('-' * 50) print(type(to_json))
Running the code sample produces the following output.
InventoryItem(name='A', unit_price=100, quantity_available=1) -------------------------------------------------- {"name": "A", "unit_price": 100, "quantity_available": 1} -------------------------------------------------- <class 'str'>
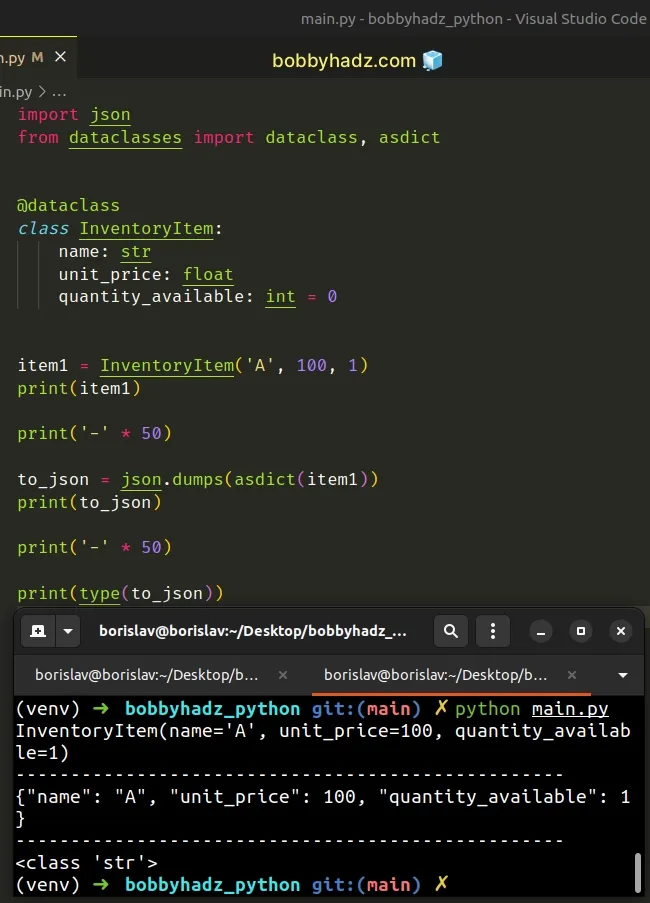
The
dataclasses.asdict()
method converts the supplied dataclass instance to a dictionary.
from dataclasses import dataclass, asdict @dataclass class InventoryItem: name: str unit_price: float quantity_available: int = 0 item1 = InventoryItem('A', 100, 1) print(item1) print('-' * 50) print(asdict(item1))
Running the code sample produces the following output.
InventoryItem(name='A', unit_price=100, quantity_available=1) -------------------------------------------------- {'name': 'A', 'unit_price': 100, 'quantity_available': 1}
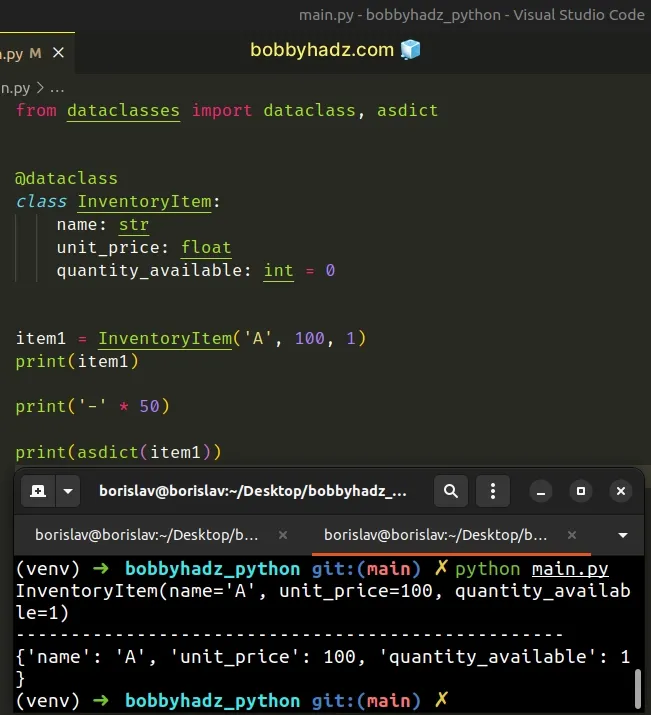
The dictionary contains the name: value pairs of the dataclass object.
The last step is to pass the dictionary to the json.dumps() method.
import json from dataclasses import dataclass, asdict @dataclass class InventoryItem: name: str unit_price: float quantity_available: int = 0 item1 = InventoryItem('A', 100, 1) print(item1) print('-' * 50) print(json.dumps(asdict(item1)))
Running the code sample produces the following output.
InventoryItem(name='A', unit_price=100, quantity_available=1) -------------------------------------------------- {"name": "A", "unit_price": 100, "quantity_available": 1}
The json.dumps() method converts a Python object to a JSON formatted string.
The json.dumps() method handles the conversion of a dictionary to a JSON
string without any issues.
# Converting a Dataclass to JSON with a custom JSONEncoder
You can also extend the built-in JSONEncoder class to convert a dataclass
object to a JSON string.
import json from dataclasses import dataclass, asdict, is_dataclass @dataclass class InventoryItem: name: str unit_price: float quantity_available: int = 0 item1 = InventoryItem('A', 100, 1) print(item1) print('-' * 50) class DCJSONEncoder(json.JSONEncoder): def default(self, o): if is_dataclass(o): return asdict(o) return super().default(o) json_str = json.dumps(item1, cls=DCJSONEncoder) print(json_str)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
InventoryItem(name='A', unit_price=100, quantity_available=1) -------------------------------------------------- {"name": "A", "unit_price": 100, "quantity_available": 1}
We extended the default
JSONEncoder
class to be able to handle the conversion of dataclass objects to JSON.
The JSONEncoder class supports the following objects and types by default.
| Python | JSON |
|---|---|
| dict | object |
| list, tuple | array |
| str | string |
| int, float, int and float derived Enums | number |
| True | true |
| False | false |
| None | null |
By default, the JSONEncoder class doesn't support conversion of dataclass
objects to JSON.
You can change the default behavior by implementing a default method.
import json from dataclasses import dataclass, asdict, is_dataclass class DCJSONEncoder(json.JSONEncoder): def default(self, o): if is_dataclass(o): return asdict(o) return super().default(o) json_str = json.dumps(item1, cls=DCJSONEncoder) print(json_str)
If the supplied object is a dataclass object, we return the result of calling
asdict() with the object.
If the object is any other type, we use the default behavior.
Notice that we have to set the cls argument to the custom JSONEncoder class
when calling json.dumps().
json_str = json.dumps(item1, cls=DCJSONEncoder)
If you forget to pass the cls argument, the default JSONEncoder is used and
you'd get an error.
# Convert a Dataclass to JSON with the dataclasses_json package
You can also use the
dataclasses-json module to convert
a dataclass object to JSON.
First, open your terminal in your project's root directory and install the package.
pip install dataclasses-json # or with pip3 pip3 install dataclasses-json
Now import the module and use the dataclass_json method as a decorator.
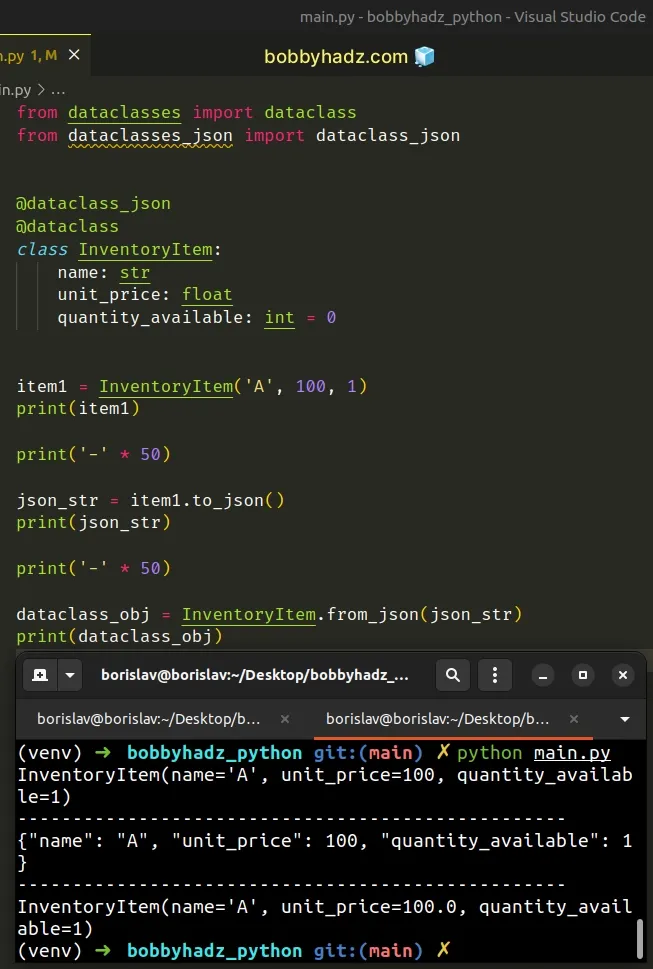
from dataclasses import dataclass from dataclasses_json import dataclass_json @dataclass_json @dataclass class InventoryItem: name: str unit_price: float quantity_available: int = 0 item1 = InventoryItem('A', 100, 1) print(item1) print('-' * 50) json_str = item1.to_json() print(json_str)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
InventoryItem(name='A', unit_price=100, quantity_available=1) -------------------------------------------------- {"name": "A", "unit_price": 100, "quantity_available": 1}
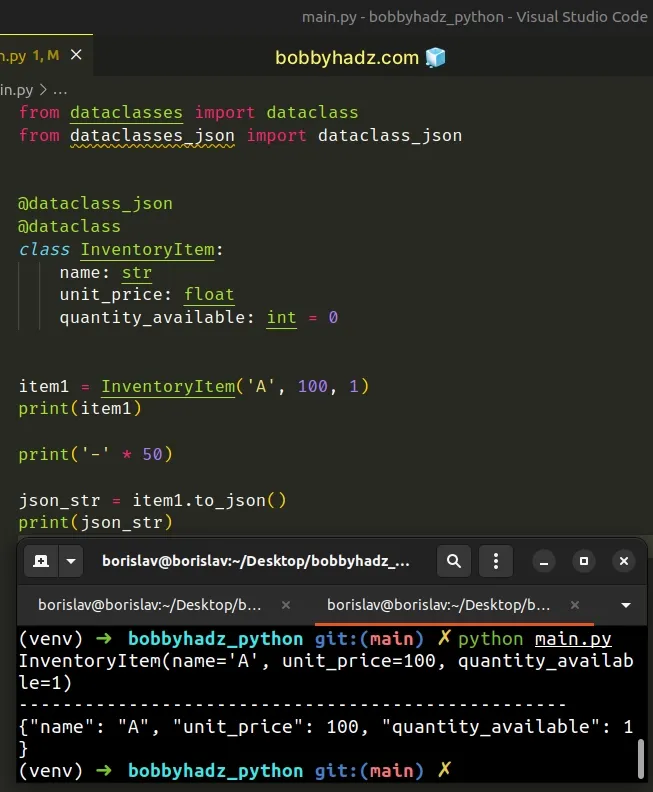
Notice that we used the dataclass_json method to decorate the class.
from dataclasses import dataclass from dataclasses_json import dataclass_json @dataclass_json @dataclass class InventoryItem: name: str unit_price: float quantity_available: int = 0
The next step is to call the to_json() method on the dataclass object.
json_str = item1.to_json() print(json_str)
If you need to convert the JSON string back to a dataclass object, use the
InventoryItem.from_json() method.
from dataclasses import dataclass from dataclasses_json import dataclass_json @dataclass_json @dataclass class InventoryItem: name: str unit_price: float quantity_available: int = 0 item1 = InventoryItem('A', 100, 1) print(item1) print('-' * 50) json_str = item1.to_json() print(json_str) print('-' * 50) dataclass_obj = InventoryItem.from_json(json_str) print(dataclass_obj)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
InventoryItem(name='A', unit_price=100, quantity_available=1) -------------------------------------------------- {"name": "A", "unit_price": 100, "quantity_available": 1} -------------------------------------------------- InventoryItem(name='A', unit_price=100.0, quantity_available=1)
Notice that I called the from_json() method on the decorated class.
dataclass_obj = InventoryItem.from_json(json_str) print(dataclass_obj)
# Converting a dataclass object to a JSON string with the default argument
You can also specify the default argument when calling json.dumps() to
convert a dataclass object to a JSON string.
import json from dataclasses import dataclass @dataclass class InventoryItem: name: str unit_price: float quantity_available: int = 0 item1 = InventoryItem('A', 100, 1) print(item1) print('-' * 50) json_str = json.dumps(item1, default=lambda dc: dc.__dict__) print(json_str)
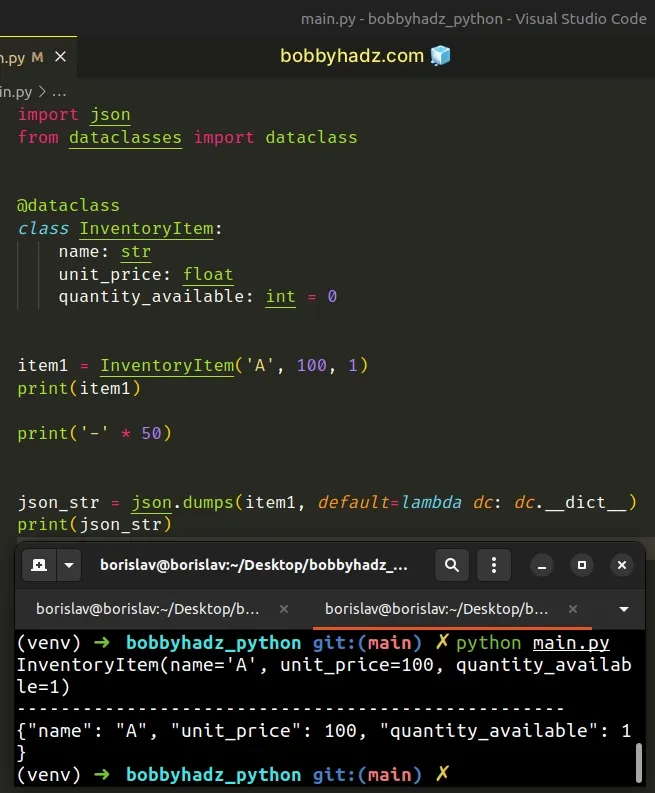
Running the code sample produces the following output.
InventoryItem(name='A', unit_price=100, quantity_available=1) -------------------------------------------------- {"name": "A", "unit_price": 100, "quantity_available": 1}
The default argument should be set to a function that gets invoked for objects
that cannot be otherwise deserialized.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

