How to merge multiple JSON files in Python [3 Ways]
Last updated: Jun 20, 2023
Reading time·6 min

# Table of Contents
- How to merge multiple JSON files in Python
- Merging JSON files in Python by iterating line by line
- How to merge multiple JSON files in Python using pandas
# How to merge multiple JSON files in Python
To merge multiple JSON files into one using Python:
- Iterate over a list containing the paths to the files
- Open and parse each
.jsonfile and store its contents in a list. - Open the output
.jsonfile and write the merged file contents to the file.
The example assumes that you have the following folder structure.
my-project/ └── main.py └── employees_1.json └── employees_2.json
Here is the code for the employees_1.json file.
[ {"id": 1, "name": "Alice", "salary": "100"}, {"id": 2, "name": "Bobby", "salary": "200"} ]
And here is the code for the employees_2.json file.
[ {"id": 3, "name": "Carl", "salary": "300"}, {"id": 4, "name": "Dan", "salary": "400"} ]
This is the main.py file that merges the two .json files into one.
import json def merge_json_files(file_paths): merged_contents = [] for file_path in file_paths: with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file_in: merged_contents.extend(json.load(file_in)) with open('employees_final.json', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file_out: json.dump(merged_contents, file_out) paths = [ 'employees_1.json', 'employees_2.json' ] merge_json_files(paths)
After running the python main.py command, the following employees_final.json
file is produced.
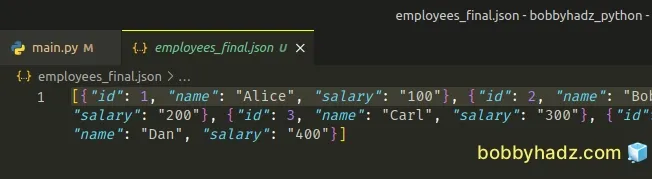
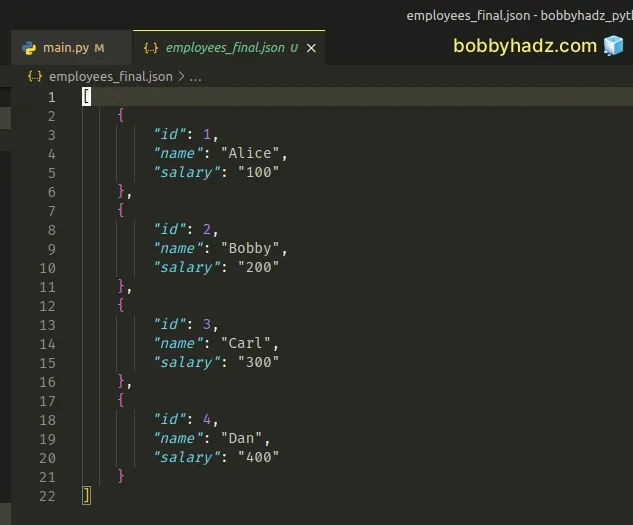
If you want to prettify the resulting .json file, pass the indent keyword
argument to the json.dump() method.
import json def merge_json_files(file_paths): merged_contents = [] for file_path in file_paths: with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file_in: merged_contents.extend(json.load(file_in)) with open('employees_final.json', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file_out: # ✅ Pass indent keyword argument to json.dump() json.dump(merged_contents, file_out, indent=4) paths = [ 'employees_1.json', 'employees_2.json' ] merge_json_files(paths)
The merge_json_files() function takes a list of file paths and merges the JSON
files.
We used a for loop to iterate over the list of files.
for file_path in file_paths: with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file_in: merged_contents.extend(json.load(file_in))
On each iteration, we use the with open() statement to open the current file path.
The with open() statement takes care of closing the file automatically, even
if an error is raised.
The json.load method is used to deserialize a file to a Python object.
The list.extend method takes an iterable (such as a list or a tuple) and extends the list by appending all of the items from the iterable.
list_1 = [ {"id": 1, "name": "Alice", "salary": "100"}, {"id": 2, "name": "Bobby", "salary": "200"} ] list_2 = [ {"id": 3, "name": "Carl", "salary": "300"}, {"id": 4, "name": "Dan", "salary": "400"} ] list_3 = [] list_3.extend(list_1) list_3.extend(list_2) # [{'id': 1, 'name': 'Alice', 'salary': '100'}, # {'id': 2, 'name': 'Bobby', 'salary': '200'}, # {'id': 3, 'name': 'Carl', 'salary': '300'}, # {'id': 4, 'name': 'Dan', 'salary': '400'}] print(list_3)
At this point, we've added the contents of the files to the merged_contents
list.
The next step is to open the output file and write the merged contents to it.
with open('employees_final.json', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file_out: json.dump(merged_contents, file_out, indent=4)
The json.dump() method serializes the supplied object as a JSON formatted stream and writes it to a file.
# Merging JSON files in Python by iterating line by line
In some cases, you might have to iterate over the .json files line by line and
parse each line.
The example project has the following folder structure.
my-project/ └── main.py └── json-files/ └── employees_1.json └── employees_2.json
Here are the contents of the json-files/employees_1.json file.
{"id": 1, "name": "Alice", "salary": "100"} {"id": 2, "name": "Bobby", "salary": "200"}
And here are the contents of the json-files/employees_1.json file.
{"id": 3, "name": "Carl", "salary": "300"} {"id": 4, "name": "Dan", "salary": "400"}
This is the code for the main.py file that merges the two .json files.
import json import glob merged_contents = [] for f in glob.glob('json-files/*.json'): with open(f, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file_in: for line in file_in: a_dict = json.loads(line) merged_contents.append(a_dict) # [{'id': 3, 'name': 'Carl', 'salary': '300'}, # {'id': 4, 'name': 'Dan', 'salary': '400'}, # {'id': 1, 'name': 'Alice', 'salary': '100'}, # {'id': 2, 'name': 'Bobby', 'salary': '200'}] print(merged_contents) with open('employees_final.json', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file_out: json.dump(merged_contents, file_out, indent=4)
We used the glob.glob()
method to get a list of the paths of all .json files in the json-files/
directory.
We then used a for loop to iterate over the list of file paths.
On each iteration, we use the with open() statement to open the file in
reading mode.
for f in glob.glob('json-files/*.json'): with open(f, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file_in: for line in file_in: a_dict = json.loads(line) merged_contents.append(a_dict)
The nested for loop iterates over the lines of each file.
The loop uses the json.loads method to parse each JSON line into a native Python dictionary.
We then append the dictionary to a list.
The last part of the code opens the output .json file in writing mode and uses
the json.dump method to
serialize the supplied object as a JSON formatted stream and write it to the
file.
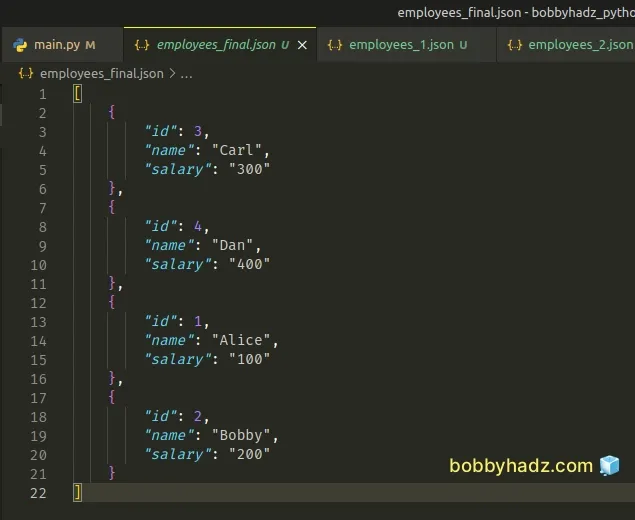
The produced employees_final.json file has the following contents.
[ { "id": 3, "name": "Carl", "salary": "300" }, { "id": 4, "name": "Dan", "salary": "400" }, { "id": 1, "name": "Alice", "salary": "100" }, { "id": 2, "name": "Bobby", "salary": "200" } ]
# How to merge multiple JSON files in Python using pandas
You can also use the pandas library to merge multiple JSON files in Python.
Make sure you have the pandas module installed to be able to run the code sample.
pip install pandas pip3 install pandas
The example assumes that you have the following folder structure.
my-project/ └── main.py └── employees_1.json └── employees_2.json
Here is the code for the employees_1.json file.
[ {"id": 1, "name": "Alice", "salary": "100"}, {"id": 2, "name": "Bobby", "salary": "200"} ]
And here is the code for the employees_2.json file.
[ {"id": 3, "name": "Carl", "salary": "300"}, {"id": 4, "name": "Dan", "salary": "400"} ]
This is the main.py file that merges the two .json files.
import json import pandas as pd file_path_1 = 'employees_1.json' with open(file_path_1, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file_1: data_1 = json.load(file_1) file_path_2 = 'employees_2.json' with open(file_path_2, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file_2: data_2 = json.load(file_2) df1 = pd.DataFrame([data_1]) df2 = pd.DataFrame([data_2]) merged_contents = pd.concat([df1, df2], axis=1) merged_contents.to_json('employees_final.json', orient='split')
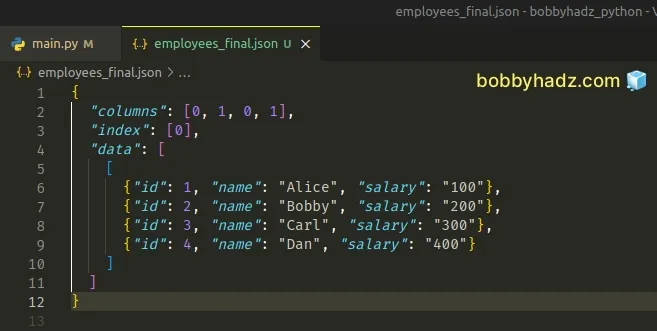
Running the python main.py command produces an employees_final.json file
with the following output.
{ "columns": [0, 1, 0, 1], "index": [0], "data": [ [ {"id": 1, "name": "Alice", "salary": "100"}, {"id": 2, "name": "Bobby", "salary": "200"}, {"id": 3, "name": "Carl", "salary": "300"}, {"id": 4, "name": "Dan", "salary": "400"} ] ] }
We used the with open() statement and the json.load() method to parse the
.json files into native Python objects.
import json import pandas as pd file_path_1 = 'employees_1.json' with open(file_path_1, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file_1: data_1 = json.load(file_1) file_path_2 = 'employees_2.json' with open(file_path_2, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file_2: data_2 = json.load(file_2)
The next step is to use the pandas.DataFrame() class to create DataFrame
objects from the JSON data.
df1 = pd.DataFrame([data_1]) df2 = pd.DataFrame([data_2]) merged_contents = pd.concat([df1, df2], axis=1) merged_contents.to_json('employees_final.json', orient='split')
Once we have the DataFrame objects, we can use the
pandas.concat
method to merge them.
The pandas.concat method concatenates pandas objects along a particular
axis.
- When the axis is set to
0, then thepandasobjects are concatenated along the indexes axis. - When the axis is set to
1, then thepandasobjects are concatenated along the columns axis.
The
DataFrame.to_json
method converts the DataFrame object to a JSON string.
The orient parameter is used to specify the expected JSON string format.
merged_contents.to_json('employees_final.json', orient='split')
The default value for DataFrame objects is
columns.
The allowed values for the orient parameter are: split, records, index,
columns, values, table.
You can try to specify a different value for the orient parameter to adjust
the output of the JSON string.
For example, if I set the parameter to values:
merged_contents.to_json('employees_final.json', orient='values')
The following employees_final.json file is produced.
[ [ {"id": 1, "name": "Alice", "salary": "100"}, {"id": 2, "name": "Bobby", "salary": "200"}, {"id": 3, "name": "Carl", "salary": "300"}, {"id": 4, "name": "Dan", "salary": "400"} ] ]
You can also try using the columns value depending on your data.
merged_contents.to_json('employees_final.json', orient='values')
However, the DataFrame columns must be unique when the orient is set to
columns.
I've also written a detailed guide on how to merge two JSON objects in Python.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Count number of unique Words in a String or File in Python
- Create a file name using Variables in Python
- How to get the File path of a Class in Python
- Taking a file path from user input in Python
- How to check if a File is Empty in Python
- NameError: name '__file__ is not defined in Python [Fixed]
- Write a String to a File on a New Line every time in Python
- How to unzip a .gz file using Python [5 simple Ways]
- How to merge text files in Python [5 simple Ways]
- csv.Error: line contains NULL byte Python error [Solved]
- OSError [Errno 22] invalid argument in Python [Solved]
- How to update a JSON file in Python [3 Ways]
- How to recursively delete a Directory in Python
- pygame.error: video system not initialized [Solved]
- How to open an HTML file in the Browser using Python
- Pandas: Get a List of Categories or Categorical Columns
- Python: Get the Type, File and Line Number of Exception
- Python: Check if a File path is symlink (symbolic link)
- How to convert Dataclass to JSON in Python
- Python: How to ignore #comment lines in a File

